Voir Conjugation in All 8 Tenses
Voir in French is one of the most frequently used verbs. The meaning of voir is “to see”.
This article gives you voir conjugation in the most common indicative tenses of the French language, as well as some hints on how you would use them in everyday speech. This article will also help you to learn correct grammar so your speech and communication skills in French become top notch!
Why only the 8 indicative tenses? Because those are the tenses you’ll hear when practicing your French! There are 13 other tenses but they have more to do with mood and intent. On top of that they’re rarely used, so even if you’re an intermediate or advanced French learner then the indicative 8 are ALL you need!
Before you continue: Corrector provides a free tool to help you correct grammar and spelling in any language (including conjugations)! Just click here to access it!
French Tenses for Voir Conjugation
- Présent. Something that is happening now. This can either be ongoing or instant. Eg: I see. / I’m seeing.
- Imparfait (imperfect). Used to describe ongoing, continual or habitual past events. Eg: I was seeing.
- Passé simple is not common and normally found in formal or literary contexts. If you’re a beginner or even intermediate French learner then you can safely ignore it for now (but it’s still included below for convenience). Eg: I saw
- Passé composé. Widely used to talk about completed past actions. Eg: I saw.
- Futur simple (simple future) is used when you intend to describe a general future state of being. Eg: I will see. Once again, beginners can generally ignore this conjugation as there’s a much simpler version (next in list) that will suffice for now.
- Futur proche (near future) describes an upcoming action. In English this would be “I am going to see …“. This should be your go to future tense when learning conjugations.
- Plus-que-parfait (pluperfect). This tense indicates that an action had taken place and was completed before another past action took place. Eg: I saw it before eating my meal.
- Passé antérieur is not common at all (just like passé simple), and again is found in formal or literary contexts. Eg: I had seen.
- Futur antérieur (future perfect) is used to describe a future action that will be completed in the future before another action is started. For example: I will have seen it before eating breakfast.
Mastering voir conjugation in at least 3 tenses (present, passé composé and futur proche is essential for becoming proficient in French. In fact I would concentrate on these 3 and only study the others when they come up in literature or other contexts.
The following tables also give usage examples of voir used in its respective tense.
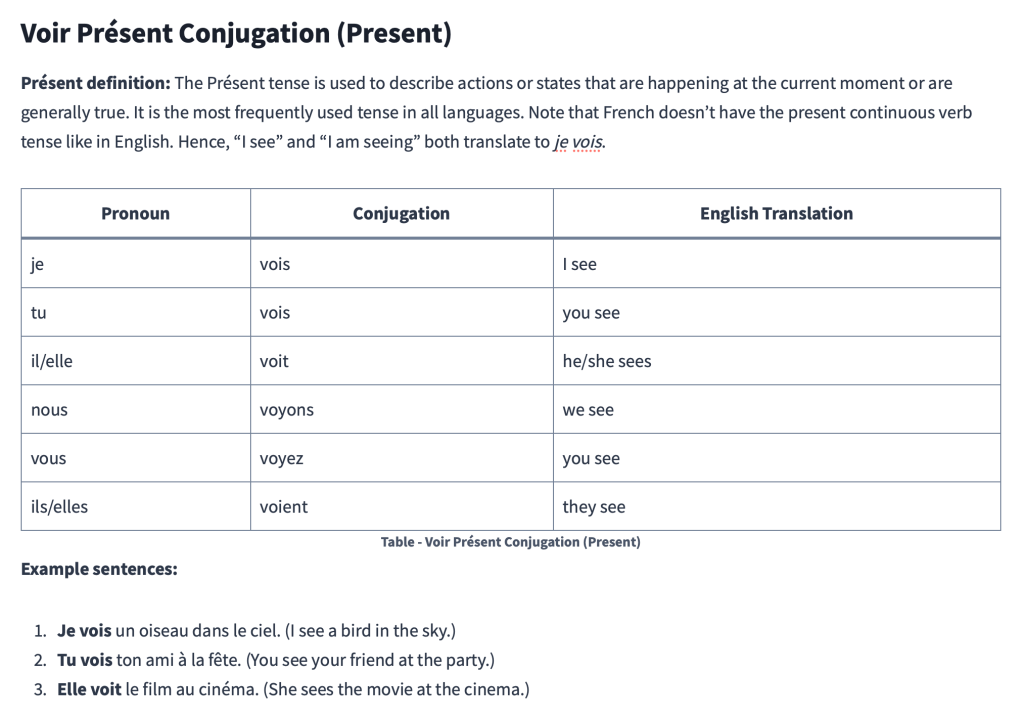
Voir Présent Conjugation (Present)
Présent definition: The Présent tense is used to describe actions or states that are happening at the current moment or are generally true. It is the most frequently used tense in all languages. Note that French doesn’t have the present continuous verb tense like in English. Hence, “I see” and “I am seeing” both translate to je vois.
| Pronoun | Conjugation | English Translation |
|---|---|---|
| je | vois | I see |
| tu | vois | you see |
| il/elle | voit | he/she sees |
| nous | voyons | we see |
| vous | voyez | you see |
| ils/elles | voient | they see |
Example sentences:
- Je vois un oiseau dans le ciel. (I see a bird in the sky.)
- Tu vois ton ami à la fête. (You see your friend at the party.)
- Elle voit le film au cinéma. (She sees the movie at the cinema.)
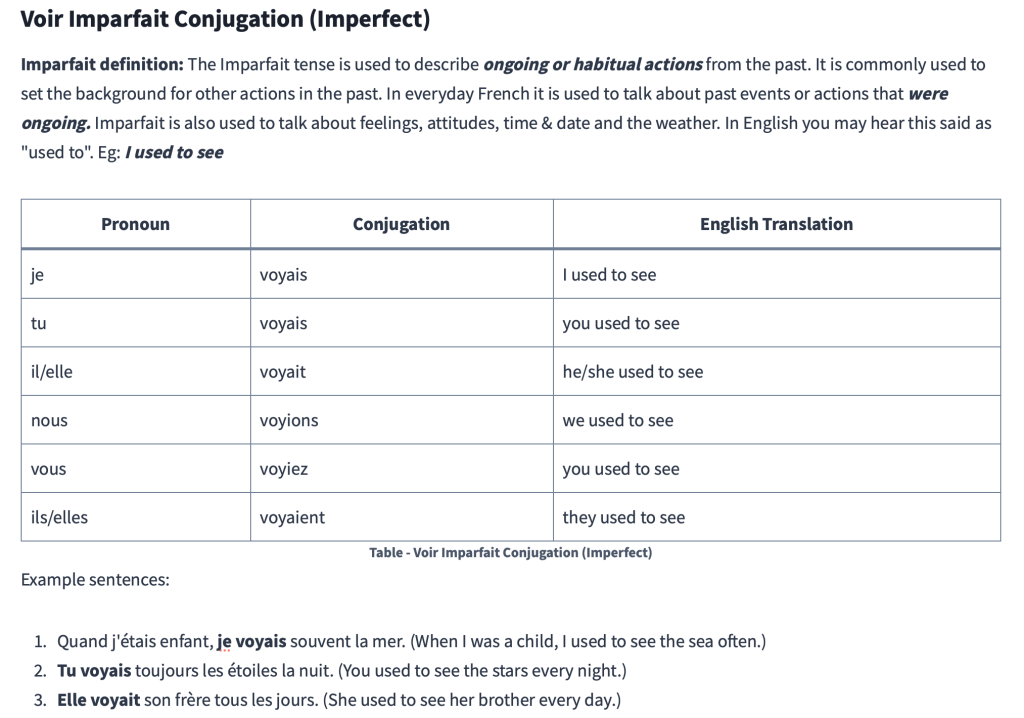
Voir Imparfait Conjugation (Imperfect)
Imparfait definition: The Imparfait tense is used to describe ongoing or habitual actions from the past. It is commonly used to set the background for other actions in the past. In everyday French it is used to talk about past events or actions that were ongoing. Imparfait is also used to talk about feelings, attitudes, time & date and the weather. In English you may hear this said as “used to”. Eg: I used to see
| Pronoun | Conjugation | English Translation |
|---|---|---|
| je | voyais | I used to see |
| tu | voyais | you used to see |
| il/elle | voyait | he/she used to see |
| nous | voyions | we used to see |
| vous | voyiez | you used to see |
| ils/elles | voyaient | they used to see |
Example sentences:
- Quand j’étais enfant, je voyais souvent la mer. (When I was a child, I used to see the sea often.)
- Tu voyais toujours les étoiles la nuit. (You used to see the stars every night.)
- Elle voyait son frère tous les jours. (She used to see her brother every day.)
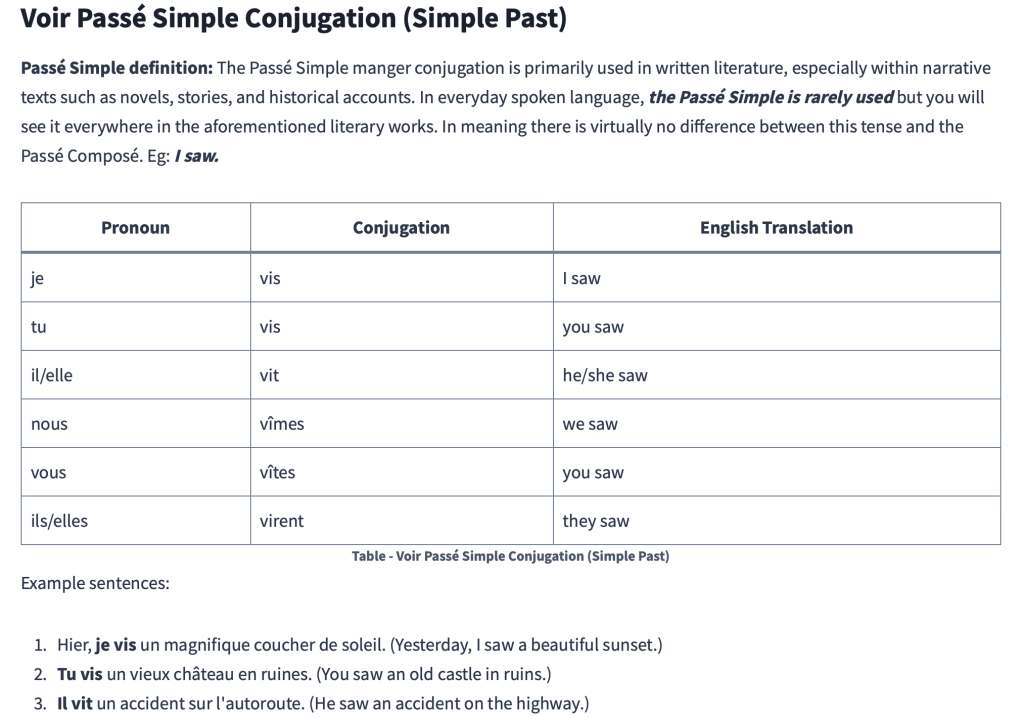
Voir Passé Simple Conjugation (Simple Past)
Passé Simple definition: The Passé Simple manger conjugation is primarily used in written literature, especially within narrative texts such as novels, stories, and historical accounts. In everyday spoken language, the Passé Simple is rarely used but you will see it everywhere in the aforementioned literary works. In meaning there is virtually no difference between this tense and the Passé Composé. Eg: I saw.
| Pronoun | Conjugation | English Translation |
|---|---|---|
| je | vis | I saw |
| tu | vis | you saw |
| il/elle | vit | he/she saw |
| nous | vîmes | we saw |
| vous | vîtes | you saw |
| ils/elles | virent | they saw |
Example sentences:
- Hier, je vis un magnifique coucher de soleil. (Yesterday, I saw a beautiful sunset.)
- Tu vis un vieux château en ruines. (You saw an old castle in ruins.)
- Il vit un accident sur l’autoroute. (He saw an accident on the highway.)
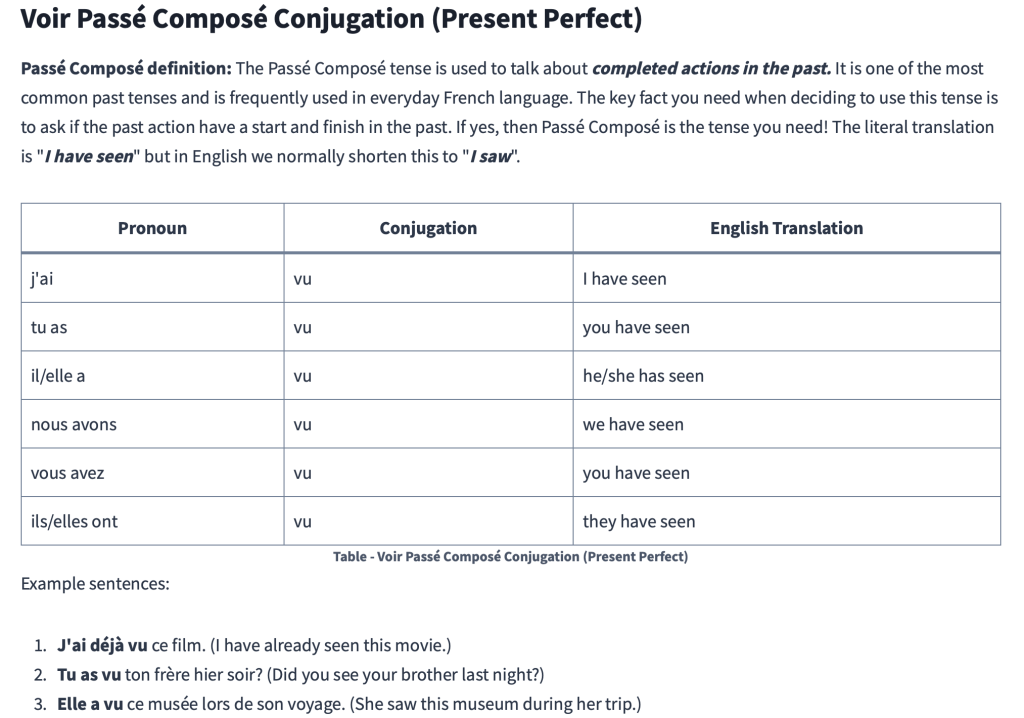
Voir Passé Composé Conjugation (Present Perfect)
Passé Composé definition: The Passé Composé tense is used to talk about completed actions in the past. It is one of the most common past tenses and is frequently used in everyday French language. The key fact you need when deciding to use this tense is to ask if the past action have a start and finish in the past. If yes, then Passé Composé is the tense you need! The literal translation is “I have seen” but in English we normally shorten this to “I saw“.
| Pronoun | Conjugation | English Translation |
|---|---|---|
| j’ai | vu | I have seen |
| tu as | vu | you have seen |
| il/elle a | vu | he/she has seen |
| nous avons | vu | we have seen |
| vous avez | vu | you have seen |
| ils/elles ont | vu | they have seen |
Example sentences:
- J’ai déjà vu ce film. (I have already seen this movie.)
- Tu as vu ton frère hier soir? (Did you see your brother last night?)
- Elle a vu ce musée lors de son voyage. (She saw this museum during her trip.)
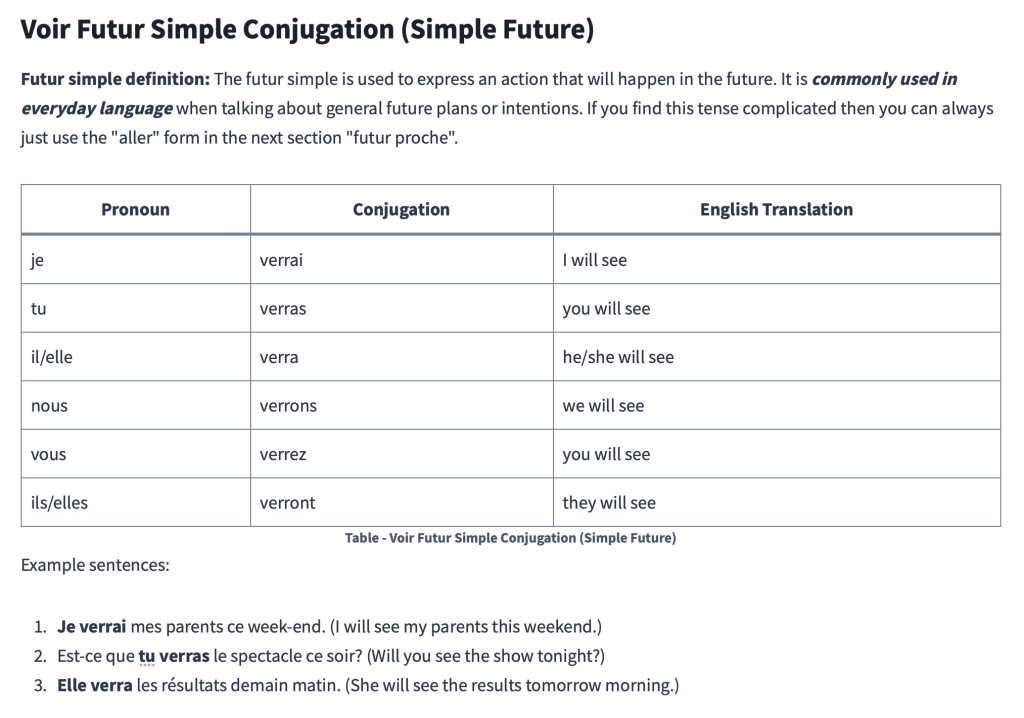
Voir Futur Simple Conjugation (Simple Future)
Futur simple definition: The futur simple is used to express an action that will happen in the future. It is commonly used in everyday language when talking about general future plans or intentions. If you find this tense complicated then you can always just use the “aller” form in the next section “futur proche”.
| Pronoun | Conjugation | English Translation |
|---|---|---|
| je | verrai | I will see |
| tu | verras | you will see |
| il/elle | verra | he/she will see |
| nous | verrons | we will see |
| vous | verrez | you will see |
| ils/elles | verront | they will see |
Example sentences:
- Je verrai mes parents ce week-end. (I will see my parents this weekend.)
- Est-ce que tu verras le spectacle ce soir? (Will you see the show tonight?)
- Elle verra les résultats demain matin. (She will see the results tomorrow morning.)
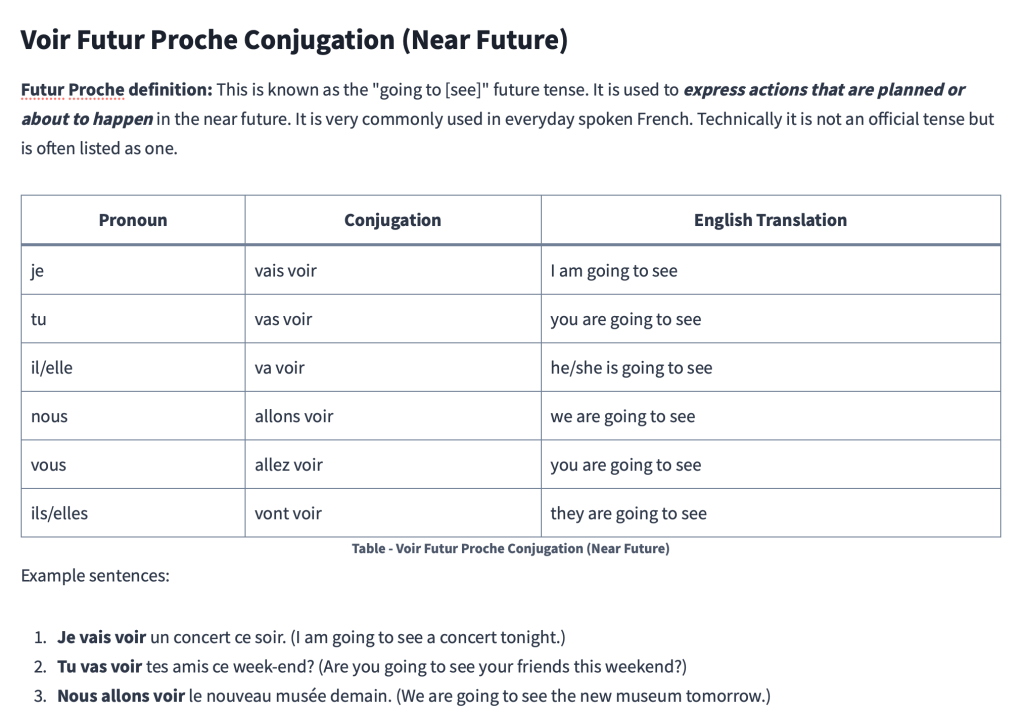
Voir Futur Proche Conjugation (Near Future)
Futur Proche definition: This is known as the “going to [see]” future tense. It is used to express actions that are planned or about to happen in the near future. It is very commonly used in everyday spoken French. Technically it is not an official tense but is often listed as one.
| Pronoun | Conjugation | English Translation |
|---|---|---|
| je | vais voir | I am going to see |
| tu | vas voir | you are going to see |
| il/elle | va voir | he/she is going to see |
| nous | allons voir | we are going to see |
| vous | allez voir | you are going to see |
| ils/elles | vont voir | they are going to see |
Example sentences:
- Je vais voir un concert ce soir. (I am going to see a concert tonight.)
- Tu vas voir tes amis ce week-end? (Are you going to see your friends this weekend?)
- Nous allons voir le nouveau musée demain. (We are going to see the new museum tomorrow.)
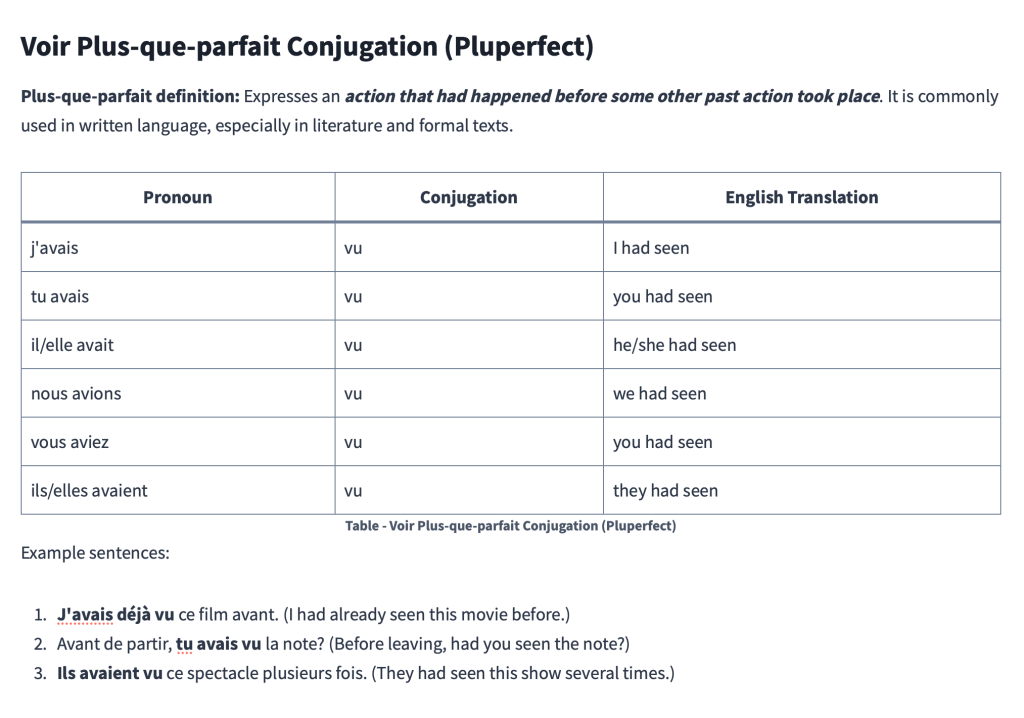
Voir Plus-que-parfait Conjugation (Pluperfect)
Plus-que-parfait definition: Expresses an action that had happened before some other past action took place. It is commonly used in written language, especially in literature and formal texts.
| Pronoun | Conjugation | English Translation |
|---|---|---|
| j’avais | vu | I had seen |
| tu avais | vu | you had seen |
| il/elle avait | vu | he/she had seen |
| nous avions | vu | we had seen |
| vous aviez | vu | you had seen |
| ils/elles avaient | vu | they had seen |
Example sentences:
- J’avais déjà vu ce film avant. (I had already seen this movie before.)
- Avant de partir, tu avais vu la note? (Before leaving, had you seen the note?)
- Ils avaient vu ce spectacle plusieurs fois. (They had seen this show several times.)
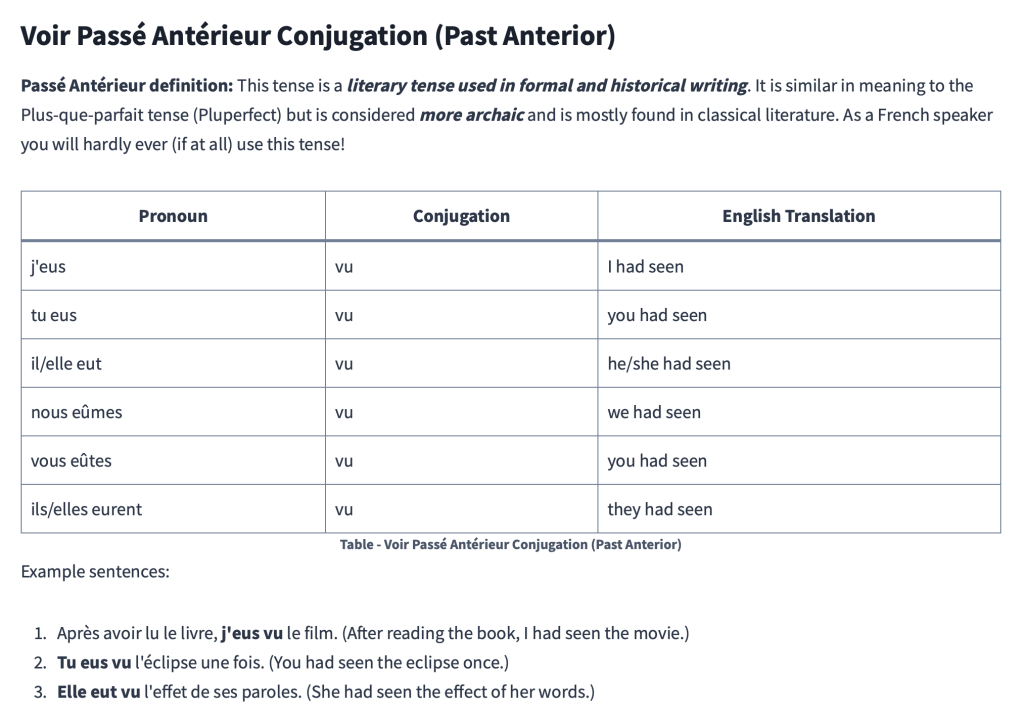
Voir Passé Antérieur Conjugation (Past Anterior)
Passé Antérieur definition: This tense is a literary tense used in formal and historical writing. It is similar in meaning to the Plus-que-parfait tense (Pluperfect) but is considered more archaic and is mostly found in classical literature. As a French speaker you will hardly ever (if at all) use this tense!
| Pronoun | Conjugation | English Translation |
|---|---|---|
| j’eus | vu | I had seen |
| tu eus | vu | you had seen |
| il/elle eut | vu | he/she had seen |
| nous eûmes | vu | we had seen |
| vous eûtes | vu | you had seen |
| ils/elles eurent | vu | they had seen |
Example sentences:
- Après avoir lu le livre, j’eus vu le film. (After reading the book, I had seen the movie.)
- Tu eus vu l’éclipse une fois. (You had seen the eclipse once.)
- Elle eut vu l’effet de ses paroles. (She had seen the effect of her words.)
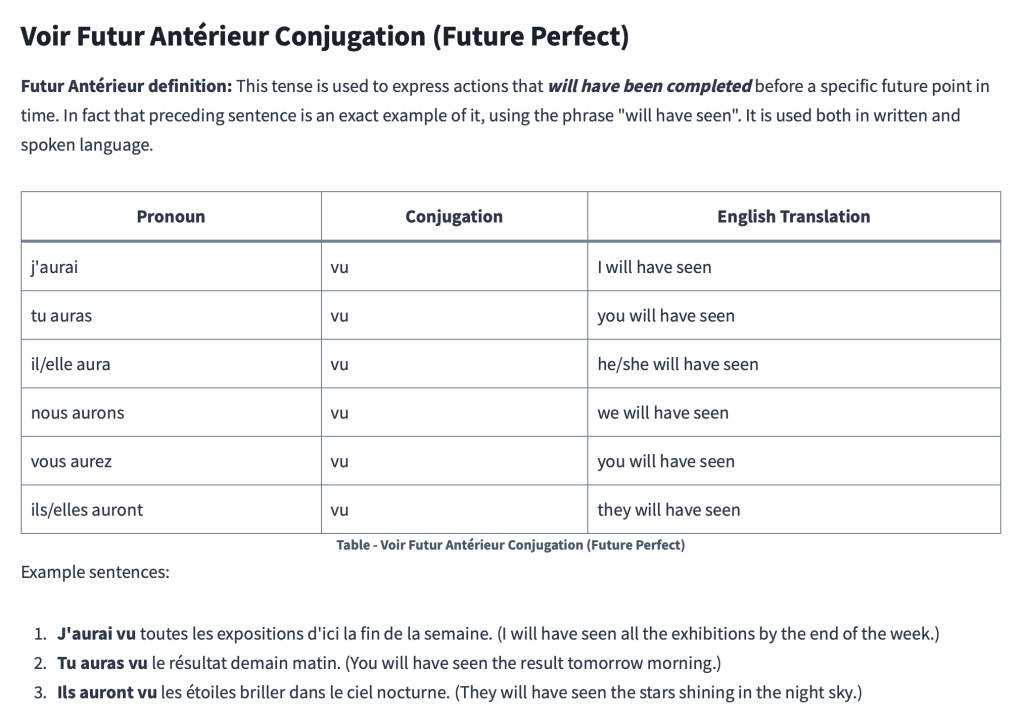
Voir Futur Antérieur Conjugation (Future Perfect)
Futur Antérieur definition: This tense is used to express actions that will have been completed before a specific future point in time. In fact that preceding sentence is an exact example of it, using the phrase “will have seen”. It is used both in written and spoken language.
| Pronoun | Conjugation | English Translation |
|---|---|---|
| j’aurai | vu | I will have seen |
| tu auras | vu | you will have seen |
| il/elle aura | vu | he/she will have seen |
| nous aurons | vu | we will have seen |
| vous aurez | vu | you will have seen |
| ils/elles auront | vu | they will have seen |
Example sentences:
- J’aurai vu toutes les expositions d’ici la fin de la semaine. (I will have seen all the exhibitions by the end of the week.)
- Tu auras vu le résultat demain matin. (You will have seen the result tomorrow morning.)
- Ils auront vu les étoiles briller dans le ciel nocturne. (They will have seen the stars shining in the night sky.)
Voir Conjugation Table Images (FREE to Download)
To download a zip file of all the Voir Conjugations simply click this link. Alternatively click the images below and save individual conjugation tables.
Wrap Up
Voir conjugation isn’t too difficult to learn as long as you stick to present, futur proche and imparfait tenses. You can safely ignore the others for now (but do come back when you’re happily proficient in French).
If you’d like to read more about French verbs, conjugation and tenses then check out this article on how to master French verb conjugations. Lot’s of great tips in there if you’re struggling!
Alternatively let us do the hard work of analysing your French texts by using our free tool! It even picks up voir conjugation mistakes!
Other French Verb Conjugations You May be Interested In
We don’t only have voir conjugations! Here are some others you may want to check out! Also, check out this link which tells you the history of the word “voir”.
