Conditionnel Passé (Conditional Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb gaffer
Introduction to the verb gaffer
The English translation of the French verb gaffer is “to make a mistake” or “to screw up.” It is pronounced as “gah-fay” in its infinitive form.
The word “gaffer” comes from the Old French word “gafer” which means “to seize” or “to hold onto tightly.” Over time, its meaning evolved to also include the idea of clumsiness or mishandling, resulting in its modern meaning of making a mistake.
In everyday French, gaffer is often used in the Conditionnel Passé tense to express a regret about a past action or to indicate something that could have been done differently. Here are three simple examples of its usage in this tense, along with their English translations:
-
J’aurais dû écouter mon père, j’ai gaffé en ne suivant pas ses conseils.
Translation: I should have listened to my father, I made a mistake by not following his advice. -
Si j’avais suivi mon intuition, je n’aurais pas gaffé dans ce projet.
Translation: If I had followed my intuition, I wouldn’t have made a mistake in this project. -
Nous aurions pu gagner le match si notre gardien n’avait pas gaffé au dernier moment.
Translation: We could have won the game if our goalkeeper hadn’t made a mistake at the last moment.
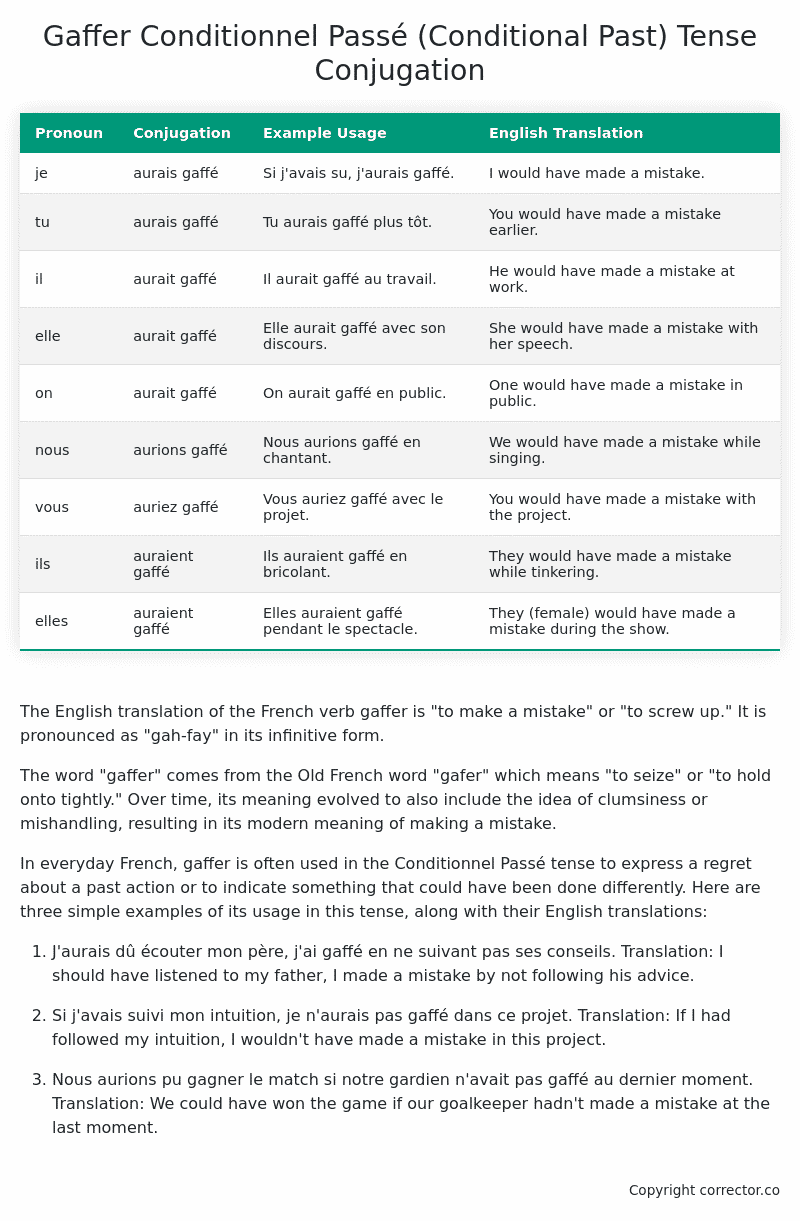
Table of the Conditionnel Passé (Conditional Past) Tense Conjugation of gaffer
| Pronoun | Conjugation | Example Usage | English Translation |
|---|---|---|---|
| je | aurais gaffé | Si j’avais su, j’aurais gaffé. | I would have made a mistake. |
| tu | aurais gaffé | Tu aurais gaffé plus tôt. | You would have made a mistake earlier. |
| il | aurait gaffé | Il aurait gaffé au travail. | He would have made a mistake at work. |
| elle | aurait gaffé | Elle aurait gaffé avec son discours. | She would have made a mistake with her speech. |
| on | aurait gaffé | On aurait gaffé en public. | One would have made a mistake in public. |
| nous | aurions gaffé | Nous aurions gaffé en chantant. | We would have made a mistake while singing. |
| vous | auriez gaffé | Vous auriez gaffé avec le projet. | You would have made a mistake with the project. |
| ils | auraient gaffé | Ils auraient gaffé en bricolant. | They would have made a mistake while tinkering. |
| elles | auraient gaffé | Elles auraient gaffé pendant le spectacle. | They (female) would have made a mistake during the show. |
Other Conjugations for Gaffer.
Le Present (Present Tense) Conjugation of the French Verb gaffer
Imparfait (Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb gaffer
Passé Simple (Simple Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb gaffer
Passé Composé (Present Perfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb gaffer
Futur Simple (Simple Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb gaffer
Futur Proche (Near Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb gaffer
Plus-que-parfait (Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb gaffer
Passé Antérieur (Past Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb gaffer
Futur Antérieur (Future Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb gaffer
Subjonctif Présent (Subjunctive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb gaffer
Subjonctif Passé (Subjunctive Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb gaffer
Subjonctif Imparfait (Subjunctive Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb gaffer
Subjonctif Plus-que-parfait (Subjunctive Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb gaffer
Conditionnel Présent (Conditional Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb gaffer
Conditionnel Passé (Conditional Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb gaffer (this article)
L’impératif Présent (Imperative Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb gaffer
L’infinitif Présent (Infinitive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb gaffer
Struggling with French verbs or the language in general? Why not use our free French Grammar Checker – no registration required!
Get a FREE Download Study Sheet of this Conjugation 🔥
Simply right click the image below, click “save image” and get your free reference for the gaffer Conditionnel Passé tense conjugation!
Gaffer – About the French Conditionnel Passé (Conditional Past) Tense
Formation
Common Everyday Usage Patterns
Expressing Unreal Past Scenarios
Polite Requests or Suggestions
Expressing Doubt or Uncertainty
Interactions with Other Tenses
Conditional Present
Indicative Past Tenses
Conditional Future
Summary
Want More?
I hope you enjoyed this article on the verb gaffer. Still in a learning mood? Check out another TOTALLY random French verb conjugation!


