Futur Antérieur (Future Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb gager
Introduction to the verb gager
The English translation of gager is “to wager” or “to bet.” The infinitive form is pronounced as “ga-zhe.”
Gager comes from the Old French word “gagier” meaning “to pledge” or “to wager.” It is most often used in everyday French in the Futur Antérieur tense, which is the future perfect tense used to express an action that will be completed in the future.
1) Je gagerai mes économies que l’équipe va gagner le match. (I will wager my savings that the team will win the game.)
2) Nous aurons gagé nos maisons avant de prendre un prêt. (We will have wagered our houses before taking out a loan.)
3) Ils auront gagé leur honneur en acceptant le défi. (They will have wagered their honor by accepting the challenge.)
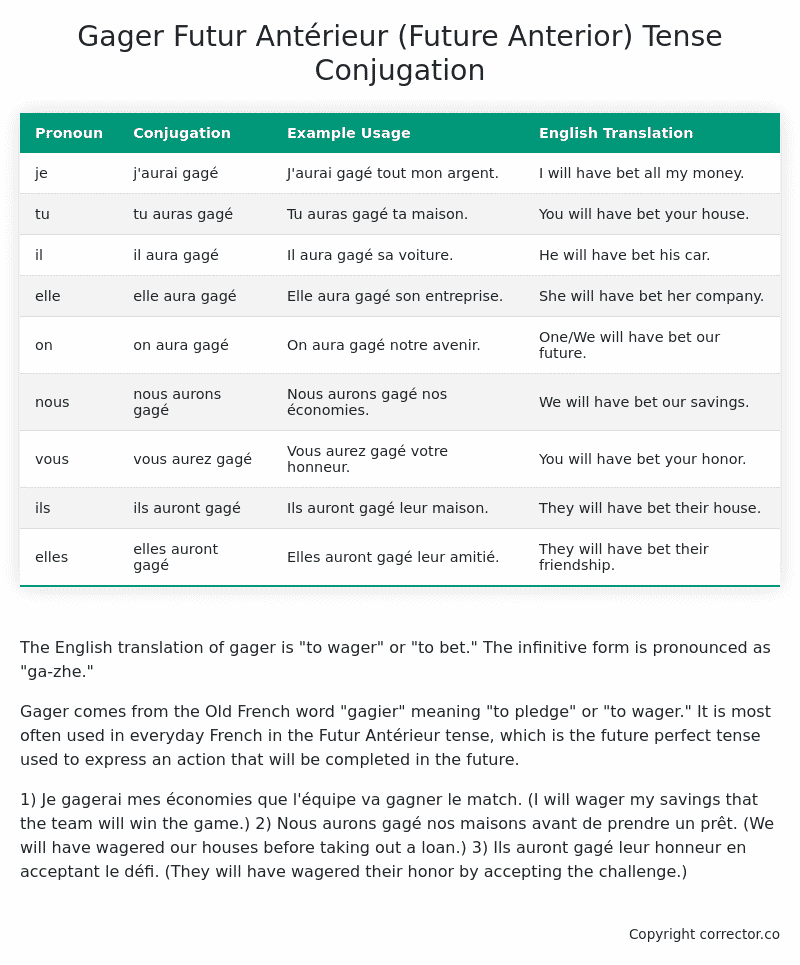
Table of the Futur Antérieur (Future Anterior) Tense Conjugation of gager
| Pronoun | Conjugation | Example Usage | English Translation |
|---|---|---|---|
| je | j’aurai gagé | J’aurai gagé tout mon argent. | I will have bet all my money. |
| tu | tu auras gagé | Tu auras gagé ta maison. | You will have bet your house. |
| il | il aura gagé | Il aura gagé sa voiture. | He will have bet his car. |
| elle | elle aura gagé | Elle aura gagé son entreprise. | She will have bet her company. |
| on | on aura gagé | On aura gagé notre avenir. | One/We will have bet our future. |
| nous | nous aurons gagé | Nous aurons gagé nos économies. | We will have bet our savings. |
| vous | vous aurez gagé | Vous aurez gagé votre honneur. | You will have bet your honor. |
| ils | ils auront gagé | Ils auront gagé leur maison. | They will have bet their house. |
| elles | elles auront gagé | Elles auront gagé leur amitié. | They will have bet their friendship. |
Other Conjugations for Gager.
Le Present (Present Tense) Conjugation of the French Verb gager
Imparfait (Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb gager
Passé Simple (Simple Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb gager
Passé Composé (Present Perfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb gager
Futur Simple (Simple Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb gager
Futur Proche (Near Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb gager
Plus-que-parfait (Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb gager
Passé Antérieur (Past Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb gager
Futur Antérieur (Future Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb gager (this article)
Subjonctif Présent (Subjunctive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb gager
Subjonctif Passé (Subjunctive Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb gager
Subjonctif Imparfait (Subjunctive Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb gager
Subjonctif Plus-que-parfait (Subjunctive Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb gager
Conditionnel Présent (Conditional Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb gager
Conditionnel Passé (Conditional Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb gager
L’impératif Présent (Imperative Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb gager
L’infinitif Présent (Infinitive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb gager
Struggling with French verbs or the language in general? Why not use our free French Grammar Checker – no registration required!
Get a FREE Download Study Sheet of this Conjugation 🔥
Simply right click the image below, click “save image” and get your free reference for the gager Futur Antérieur tense conjugation!
Gager – About the French Futur Antérieur (Future Anterior) Tense
Construction
Common Everyday Usage Patterns
Interactions with Other Tenses
For example
Summary
I hope you enjoyed this article on the verb gager. Still in a learning mood? Check out another TOTALLY random French verb conjugation!


