Imparfait (Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb budgéter
Introduction to the verb budgéter
The English translation of the French verb “budgéter” is “to budget.” The infinitive form “budgéter” is pronounced as “byoo-zheh-teh.”
“Budgéter” originates from the noun “budget,” which comes from the Latin word “bulga” meaning “bag” or “purse.” It entered the French language in the 16th century, initially referring to a financial statement or an estimation of income and expenses.
In everyday French, “budgéter” is commonly used in the imparfait tense to describe actions or habits in the past. It conveys the idea of regularly or habitually budgeting during a specific period.
Here are three simple examples of “budgéter” in the imparfait tense:
- Chaque mois, je budgétais mes dépenses avec soin. (Every month, I used to budget my expenses carefully.)
- Nous budgétions toutes nos dépenses pour éviter les surprises. (We would budget all our expenses to avoid surprises.)
- Quand nous étions jeunes, nous budgétions notre argent de poche pour les sorties. (When we were young, we used to budget our pocket money for outings.)
English translations:
- Every month, I used to budget my expenses carefully.
- We would budget all our expenses to avoid surprises.
- When we were young, we used to budget our pocket money for outings.
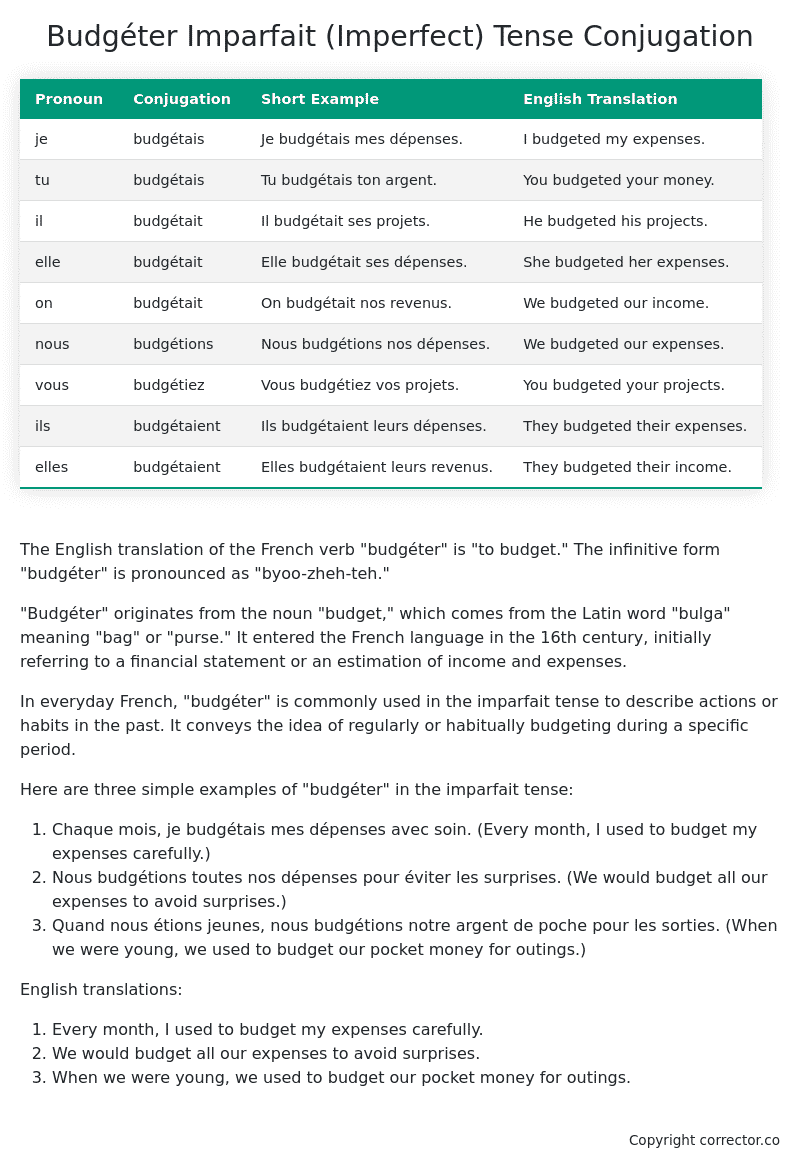
Table of the Imparfait (Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of budgéter
| Pronoun | Conjugation | Short Example | English Translation |
|---|---|---|---|
| je | budgétais | Je budgétais mes dépenses. | I budgeted my expenses. |
| tu | budgétais | Tu budgétais ton argent. | You budgeted your money. |
| il | budgétait | Il budgétait ses projets. | He budgeted his projects. |
| elle | budgétait | Elle budgétait ses dépenses. | She budgeted her expenses. |
| on | budgétait | On budgétait nos revenus. | We budgeted our income. |
| nous | budgétions | Nous budgétions nos dépenses. | We budgeted our expenses. |
| vous | budgétiez | Vous budgétiez vos projets. | You budgeted your projects. |
| ils | budgétaient | Ils budgétaient leurs dépenses. | They budgeted their expenses. |
| elles | budgétaient | Elles budgétaient leurs revenus. | They budgeted their income. |
Other Conjugations for Budgéter.
Le Present (Present Tense) Conjugation of the French Verb budgéter
Imparfait (Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb budgéter (You’re reading it right now!)
Passé Simple (Simple Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb budgéter
Passé Composé (Present Perfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb budgéter
Futur Simple (Simple Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb budgéter
Futur Proche (Near Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb budgéter
Plus-que-parfait (Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb budgéter
Passé Antérieur (Past Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb budgéter
Futur Antérieur (Future Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb budgéter
Subjonctif Présent (Subjunctive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb budgéter
Subjonctif Passé (Subjunctive Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb budgéter
Subjonctif Imparfait (Subjunctive Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb budgéter
Subjonctif Plus-que-parfait (Subjunctive Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb budgéter
Conditionnel Présent (Conditional Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb budgéter
Conditionnel Passé (Conditional Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb budgéter
Conditionnel Passé II (Conditional Past II) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb budgéter
L’impératif Présent (Imperative Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb budgéter
L’impératif Passé (Imperative Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb budgéter
L’infinitif Présent (Infinitive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb budgéter
L’infinitif Passé (Infinitive Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb budgéter
Le Participe Présent (Present Participle) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb budgéter
Le Participe Passé (Past Participle) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb budgéter
Struggling with French verbs or the language in general? Why not use our free French Grammar Checker – no registration required!
Get a FREE Download Study Sheet of this Conjugation 🔥
Simply right click the image below, click “save image” and get your free reference for the budgéter imparfait tense conjugation!
Budgéter – About the French Imparfait Tense
NOTE: To take a deep dive into all the French tenses then see our article on Mastering French Tense Conjugation.
Formation of the Imparfait Tense
For regular -er verbs:
For regular -ir verbs
For regular -re verbs
Common Everyday Usage Patterns
Description of Past Habits
Background Information
Mental and Emotional States
It’s employed to express emotions, thoughts, or physical sensations in the past. For example: “J’étais content quand il est arrivé.” (I was happy when he arrived.)
Ongoing Actions
Points to Note About the Imparfait Tense
Passé Composé vs. Imparfait
Conditional
Si Clauses
Narration
I hope you enjoyed this article on the verb budgéter. Still in a learning mood? Check out another TOTALLY random French verb imparfait conjugation!


