Imparfait (Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb coïncider
Introduction to the verb coïncider
The English translation of the French verb “coïncider” is “to coincide.” The infinitive form of “coïncider” is pronounced as “kwa~si.de”.
The term “coïncider” originates from the Latin word “coincidere,” which means “to happen at the same time.” In everyday French, “coïncider” is commonly used to express the idea of two or more events or circumstances happening simultaneously or in agreement.
Here are three examples of how “coïncider” is used in the imparfait tense, along with their English translations:
-
Pendant que je lisais, le téléphone a sonné et ça coïncidait avec l’arrivée du facteur.
(While I was reading, the phone rang, and it coincided with the mailman’s arrival.) -
Chaque fois que je sortais sans parapluie, il pleuvait. Cela coïncidait avec ma malchance habituelle.
(Every time I went out without an umbrella, it would rain. It coincided with my usual bad luck.) -
Quand nous étions voisins, nos vacances coïncidaient souvent, alors nous partions ensemble.
(When we were neighbors, our vacations would often coincide, so we would leave together.)
Please note that the verb “coïncider” can also be used in other tenses and moods, but for the purpose of your question, the examples provided are in the imparfait tense.
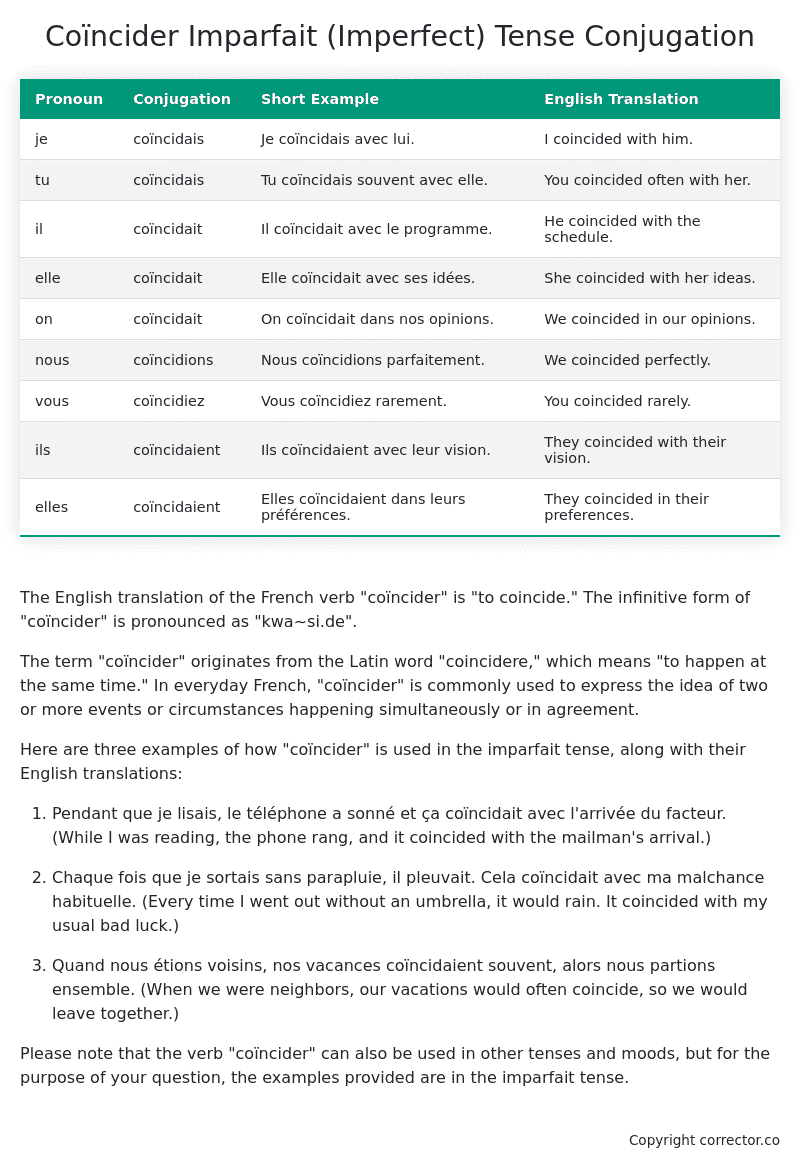
Table of the Imparfait (Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of coïncider
| Pronoun | Conjugation | Short Example | English Translation |
|---|---|---|---|
| je | coïncidais | Je coïncidais avec lui. | I coincided with him. |
| tu | coïncidais | Tu coïncidais souvent avec elle. | You coincided often with her. |
| il | coïncidait | Il coïncidait avec le programme. | He coincided with the schedule. |
| elle | coïncidait | Elle coïncidait avec ses idées. | She coincided with her ideas. |
| on | coïncidait | On coïncidait dans nos opinions. | We coincided in our opinions. |
| nous | coïncidions | Nous coïncidions parfaitement. | We coincided perfectly. |
| vous | coïncidiez | Vous coïncidiez rarement. | You coincided rarely. |
| ils | coïncidaient | Ils coïncidaient avec leur vision. | They coincided with their vision. |
| elles | coïncidaient | Elles coïncidaient dans leurs préférences. | They coincided in their preferences. |
Other Conjugations for Coïncider.
Le Present (Present Tense) Conjugation of the French Verb coïncider
Imparfait (Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb coïncider (You’re reading it right now!)
Passé Simple (Simple Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb coïncider
Passé Composé (Present Perfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb coïncider
Futur Simple (Simple Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb coïncider
Futur Proche (Near Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb coïncider
Plus-que-parfait (Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb coïncider
Passé Antérieur (Past Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb coïncider
Futur Antérieur (Future Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb coïncider
Subjonctif Présent (Subjunctive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb coïncider
Subjonctif Passé (Subjunctive Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb coïncider
Subjonctif Imparfait (Subjunctive Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb coïncider
Subjonctif Plus-que-parfait (Subjunctive Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb coïncider
Conditionnel Présent (Conditional Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb coïncider
Conditionnel Passé (Conditional Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb coïncider
Conditionnel Passé II (Conditional Past II) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb coïncider
L’impératif Présent (Imperative Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb coïncider
L’impératif Passé (Imperative Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb coïncider
L’infinitif Présent (Infinitive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb coïncider
L’infinitif Passé (Infinitive Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb coïncider
Le Participe Présent (Present Participle) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb coïncider
Le Participe Passé (Past Participle) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb coïncider
Struggling with French verbs or the language in general? Why not use our free French Grammar Checker – no registration required!
Get a FREE Download Study Sheet of this Conjugation 🔥
Simply right click the image below, click “save image” and get your free reference for the coïncider imparfait tense conjugation!
Coïncider – About the French Imparfait Tense
NOTE: To take a deep dive into all the French tenses then see our article on Mastering French Tense Conjugation.
Formation of the Imparfait Tense
For regular -er verbs:
For regular -ir verbs
For regular -re verbs
Common Everyday Usage Patterns
Description of Past Habits
Background Information
Mental and Emotional States
It’s employed to express emotions, thoughts, or physical sensations in the past. For example: “J’étais content quand il est arrivé.” (I was happy when he arrived.)
Ongoing Actions
Points to Note About the Imparfait Tense
Passé Composé vs. Imparfait
Conditional
Si Clauses
Narration
I hope you enjoyed this article on the verb coïncider. Still in a learning mood? Check out another TOTALLY random French verb imparfait conjugation!


