L’impératif Présent (Imperative Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb biper
Introduction to the verb biper
The English translation of the French verb biper is “to beep” or “to honk”. The infinitive form of biper is pronounced as “bee-pay”.
The word biper comes from the onomatopoeic sound “bip” which is the sound made by electronic devices such as pagers or beepers. In everyday French, biper is most often used to describe the sound made by car horns or electronic devices.
In the L’impératif Présent tense, biper is used as a command form and is conjugated as “bipe” for the singular form and “bipez” for the plural form. Here are three simple examples of its usage in this tense:
- Bipe le klaxon pour avertir les autres conducteurs. (Beep the horn to warn other drivers.)
- Ne bipe pas à chaque fois que tu doubles quelqu’un. (Don’t honk every time you pass someone.)
- Bipez si vous voulez que je vous ouvre la porte. (Honk if you want me to open the door for you.)
Table of the L’impératif Présent (Imperative Present) Tense Conjugation of biper
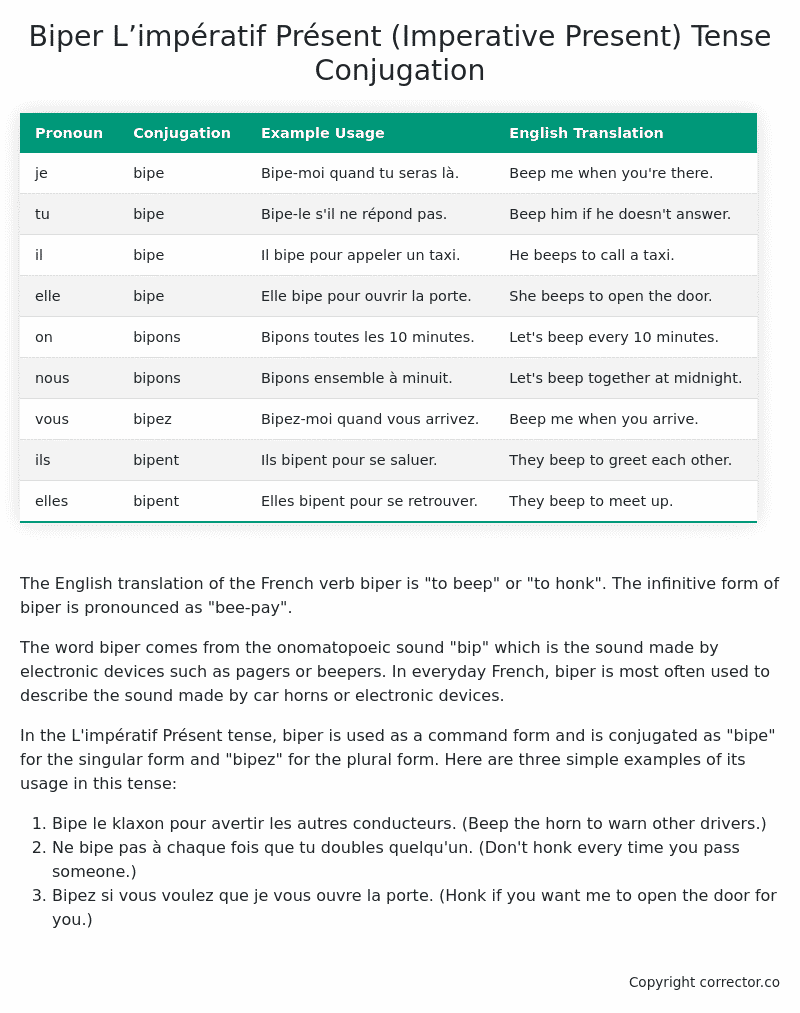
| Pronoun | Conjugation | Example Usage | English Translation |
|---|---|---|---|
| je | bipe | Bipe-moi quand tu seras là. | Beep me when you’re there. |
| tu | bipe | Bipe-le s’il ne répond pas. | Beep him if he doesn’t answer. |
| il | bipe | Il bipe pour appeler un taxi. | He beeps to call a taxi. |
| elle | bipe | Elle bipe pour ouvrir la porte. | She beeps to open the door. |
| on | bipons | Bipons toutes les 10 minutes. | Let’s beep every 10 minutes. |
| nous | bipons | Bipons ensemble à minuit. | Let’s beep together at midnight. |
| vous | bipez | Bipez-moi quand vous arrivez. | Beep me when you arrive. |
| ils | bipent | Ils bipent pour se saluer. | They beep to greet each other. |
| elles | bipent | Elles bipent pour se retrouver. | They beep to meet up. |
Other Conjugations for Biper.
Le Present (Present Tense) Conjugation of the French Verb biper
Imparfait (Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb biper
Passé Simple (Simple Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb biper
Passé Composé (Present Perfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb biper
Futur Simple (Simple Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb biper
Futur Proche (Near Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb biper
Plus-que-parfait (Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb biper
Passé Antérieur (Past Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb biper
Futur Antérieur (Future Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb biper
Subjonctif Présent (Subjunctive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb biper
Subjonctif Passé (Subjunctive Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb biper
Subjonctif Imparfait (Subjunctive Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb biper
Subjonctif Plus-que-parfait (Subjunctive Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb biper
Conditionnel Présent (Conditional Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb biper
Conditionnel Passé (Conditional Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb biper
L’impératif Présent (Imperative Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb biper (this article)
L’infinitif Présent (Infinitive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb biper
Struggling with French verbs or the language in general? Why not use our free French Grammar Checker – no registration required!
Get a FREE Download Study Sheet of this Conjugation 🔥
Simply right click the image below, click “save image” and get your free reference for the biper L’impératif Présent tense conjugation!
Biper – About the French L’impératif Présent (Imperative Present) Tense
Usage
Giving commands
Making requests
Offering advice
Expressing desires
Conjugation Formation
Interactions with other tenses
Want More?
I hope you enjoyed this article on the verb biper. Still in a learning mood? Check out another TOTALLY random French verb conjugation!


