L’impératif Présent (Imperative Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb déshuiler
Introduction to the verb déshuiler
The English translation of the French verb déshuiler is “to degrease” or “to remove oil.” It is pronounced as “day-shwee-leh.”
The word déshuiler comes from the combination of the prefix “dé-” which means “to remove” and the noun “huile” which means “oil.” This verb is most often used in everyday French in the imperative present tense, which is used to give commands or directives.
- Déshuilez la poêle avant de faire cuire les légumes. (Degrease the pan before cooking the vegetables.)
- Déshuile-le avant de l’utiliser pour ta recette. (Degrease it before using it for your recipe.)
- Ne déshuile pas trop la viande, sinon elle sera trop sèche. (Don’t degrease the meat too much, otherwise it will be too dry.)
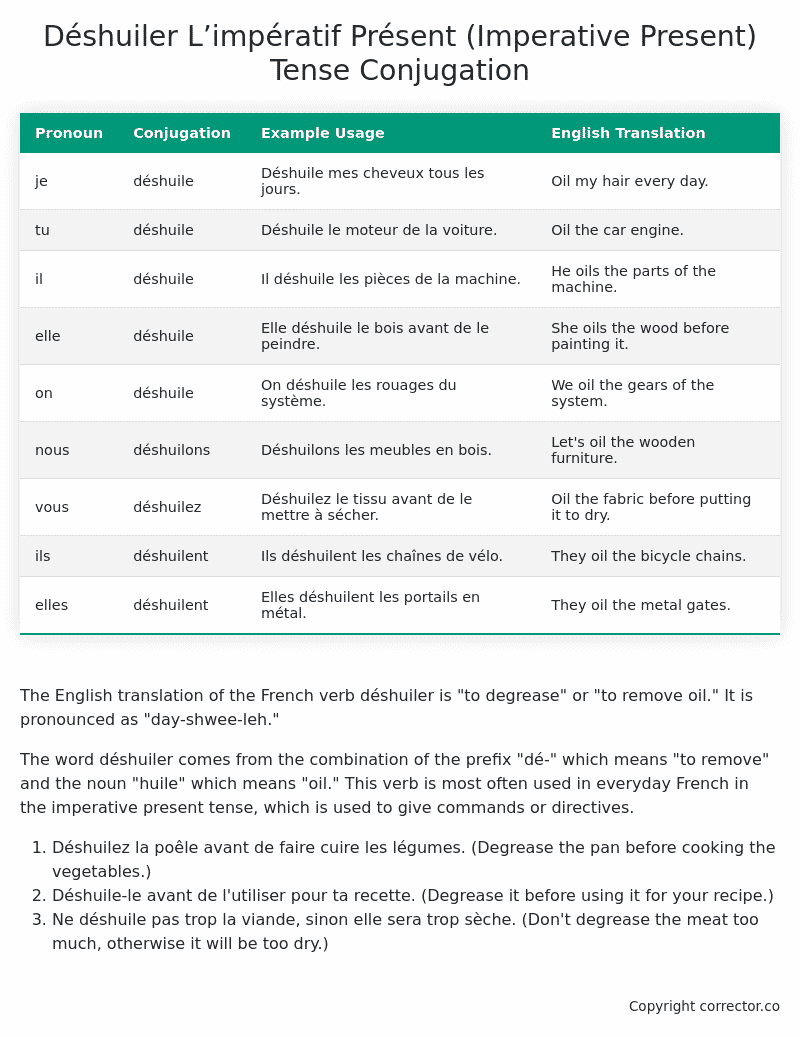
Table of the L’impératif Présent (Imperative Present) Tense Conjugation of déshuiler
| Pronoun | Conjugation | Example Usage | English Translation |
|---|---|---|---|
| je | déshuile | Déshuile mes cheveux tous les jours. | Oil my hair every day. |
| tu | déshuile | Déshuile le moteur de la voiture. | Oil the car engine. |
| il | déshuile | Il déshuile les pièces de la machine. | He oils the parts of the machine. |
| elle | déshuile | Elle déshuile le bois avant de le peindre. | She oils the wood before painting it. |
| on | déshuile | On déshuile les rouages du système. | We oil the gears of the system. |
| nous | déshuilons | Déshuilons les meubles en bois. | Let’s oil the wooden furniture. |
| vous | déshuilez | Déshuilez le tissu avant de le mettre à sécher. | Oil the fabric before putting it to dry. |
| ils | déshuilent | Ils déshuilent les chaînes de vélo. | They oil the bicycle chains. |
| elles | déshuilent | Elles déshuilent les portails en métal. | They oil the metal gates. |
Other Conjugations for Déshuiler.
Le Present (Present Tense) Conjugation of the French Verb déshuiler
Imparfait (Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb déshuiler
Passé Simple (Simple Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb déshuiler
Passé Composé (Present Perfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb déshuiler
Futur Simple (Simple Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb déshuiler
Futur Proche (Near Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb déshuiler
Plus-que-parfait (Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb déshuiler
Passé Antérieur (Past Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb déshuiler
Futur Antérieur (Future Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb déshuiler
Subjonctif Présent (Subjunctive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb déshuiler
Subjonctif Passé (Subjunctive Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb déshuiler
Subjonctif Imparfait (Subjunctive Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb déshuiler
Subjonctif Plus-que-parfait (Subjunctive Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb déshuiler
Conditionnel Présent (Conditional Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb déshuiler
Conditionnel Passé (Conditional Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb déshuiler
L’impératif Présent (Imperative Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb déshuiler (this article)
L’infinitif Présent (Infinitive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb déshuiler
Struggling with French verbs or the language in general? Why not use our free French Grammar Checker – no registration required!
Get a FREE Download Study Sheet of this Conjugation 🔥
Simply right click the image below, click “save image” and get your free reference for the déshuiler L’impératif Présent tense conjugation!
Déshuiler – About the French L’impératif Présent (Imperative Present) Tense
Usage
Giving commands
Making requests
Offering advice
Expressing desires
Conjugation Formation
Interactions with other tenses
Want More?
I hope you enjoyed this article on the verb déshuiler. Still in a learning mood? Check out another TOTALLY random French verb conjugation!


