L’impératif Présent (Imperative Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb embourrer
Introduction to the verb embourrer
The English translation of the French verb embourrer is “to stuff” or “to fill.” It is pronounced as “ahm-boo-reh.”
The word embourrer comes from the Old French word “embourrer” which means “to stuff” or “to fill.” It is most often used in everyday French in the L’impératif Présent tense, which is the imperative form used to give commands or orders.
Here are 3 examples of its usage in this tense, with the respective English translations:
- Embourre les oignons dans la dinde. (Stuff the onions into the turkey.)
- Embourrons le sac avec les vêtements. (Let’s stuff the bag with clothes.)
- N’embourrez pas trop la valise, il faut la fermer. (Don’t overstuff the suitcase, we need to close it.)
Table of the L’impératif Présent (Imperative Present) Tense Conjugation of embourrer
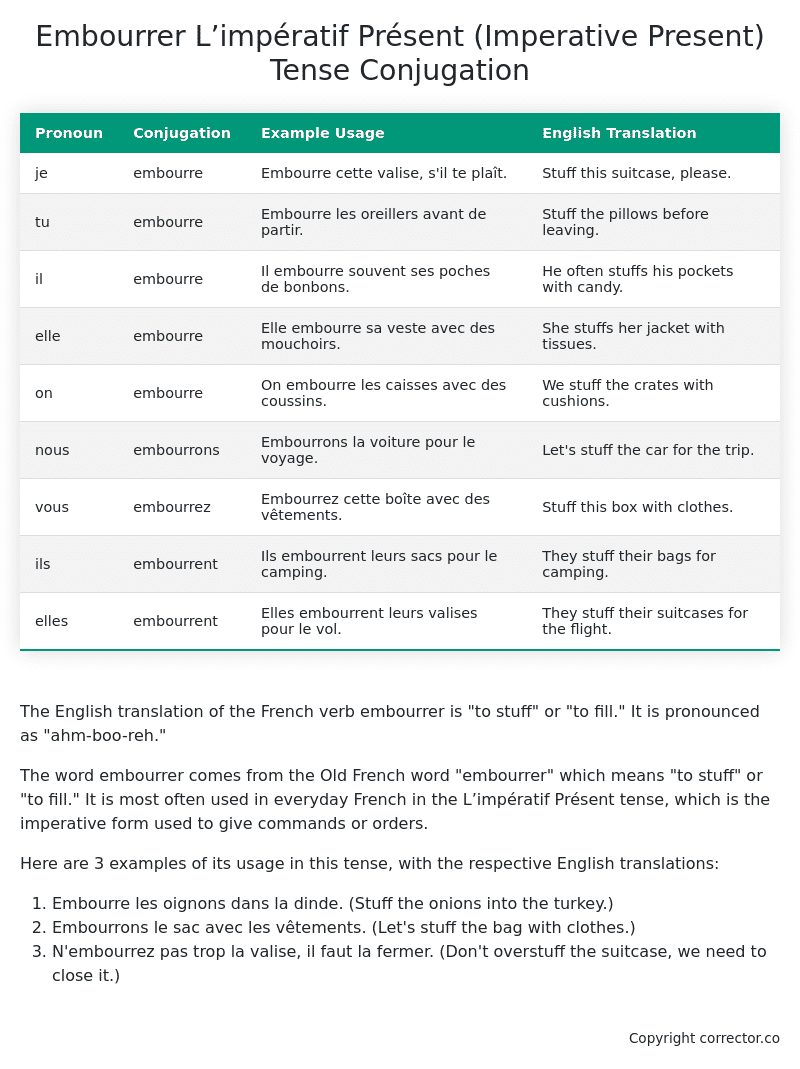
| Pronoun | Conjugation | Example Usage | English Translation |
|---|---|---|---|
| je | embourre | Embourre cette valise, s’il te plaît. | Stuff this suitcase, please. |
| tu | embourre | Embourre les oreillers avant de partir. | Stuff the pillows before leaving. |
| il | embourre | Il embourre souvent ses poches de bonbons. | He often stuffs his pockets with candy. |
| elle | embourre | Elle embourre sa veste avec des mouchoirs. | She stuffs her jacket with tissues. |
| on | embourre | On embourre les caisses avec des coussins. | We stuff the crates with cushions. |
| nous | embourrons | Embourrons la voiture pour le voyage. | Let’s stuff the car for the trip. |
| vous | embourrez | Embourrez cette boîte avec des vêtements. | Stuff this box with clothes. |
| ils | embourrent | Ils embourrent leurs sacs pour le camping. | They stuff their bags for camping. |
| elles | embourrent | Elles embourrent leurs valises pour le vol. | They stuff their suitcases for the flight. |
Other Conjugations for Embourrer.
Le Present (Present Tense) Conjugation of the French Verb embourrer
Imparfait (Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb embourrer
Passé Simple (Simple Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb embourrer
Passé Composé (Present Perfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb embourrer
Futur Simple (Simple Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb embourrer
Futur Proche (Near Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb embourrer
Plus-que-parfait (Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb embourrer
Passé Antérieur (Past Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb embourrer
Futur Antérieur (Future Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb embourrer
Subjonctif Présent (Subjunctive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb embourrer
Subjonctif Passé (Subjunctive Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb embourrer
Subjonctif Imparfait (Subjunctive Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb embourrer
Subjonctif Plus-que-parfait (Subjunctive Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb embourrer
Conditionnel Présent (Conditional Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb embourrer
Conditionnel Passé (Conditional Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb embourrer
L’impératif Présent (Imperative Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb embourrer (this article)
L’infinitif Présent (Infinitive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb embourrer
Struggling with French verbs or the language in general? Why not use our free French Grammar Checker – no registration required!
Get a FREE Download Study Sheet of this Conjugation 🔥
Simply right click the image below, click “save image” and get your free reference for the embourrer L’impératif Présent tense conjugation!
Embourrer – About the French L’impératif Présent (Imperative Present) Tense
Usage
Giving commands
Making requests
Offering advice
Expressing desires
Conjugation Formation
Interactions with other tenses
Want More?
I hope you enjoyed this article on the verb embourrer. Still in a learning mood? Check out another TOTALLY random French verb conjugation!


