L’impératif Présent (Imperative Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb goutter
Introduction to the verb goutter
The English translation of the French verb goutter is “to taste” or “to drip”. In its infinitive form, it is pronounced “goo-tay.”
The word goutter comes from the Latin word “gutta” which means “drop”. It entered the French language in the 12th century and was originally used to refer to the action of water dripping from a roof or a tree.
In everyday French, goutter is most often used in the L’impératif Présent tense, which is the command form of the verb. This tense is commonly used to give orders, make requests, or give advice.
Example 1: Goutez ce gâteau, il est délicieux ! (Taste this cake, it’s delicious!)
Example 2: Ne gouttez pas à cette sauce, elle n’est pas encore prête. (Don’t taste this sauce, it’s not ready yet.)
Example 3: Goutte un peu de ce vin, il est excellent. (Try a bit of this wine, it’s excellent.)
In these examples, goutter is used to give a command or make a request. The subject is implied and the verb is conjugated in the imperative form. The English translations also show the different meanings of goutter, as it can refer to tasting food or drinks and also to the action of dripping.
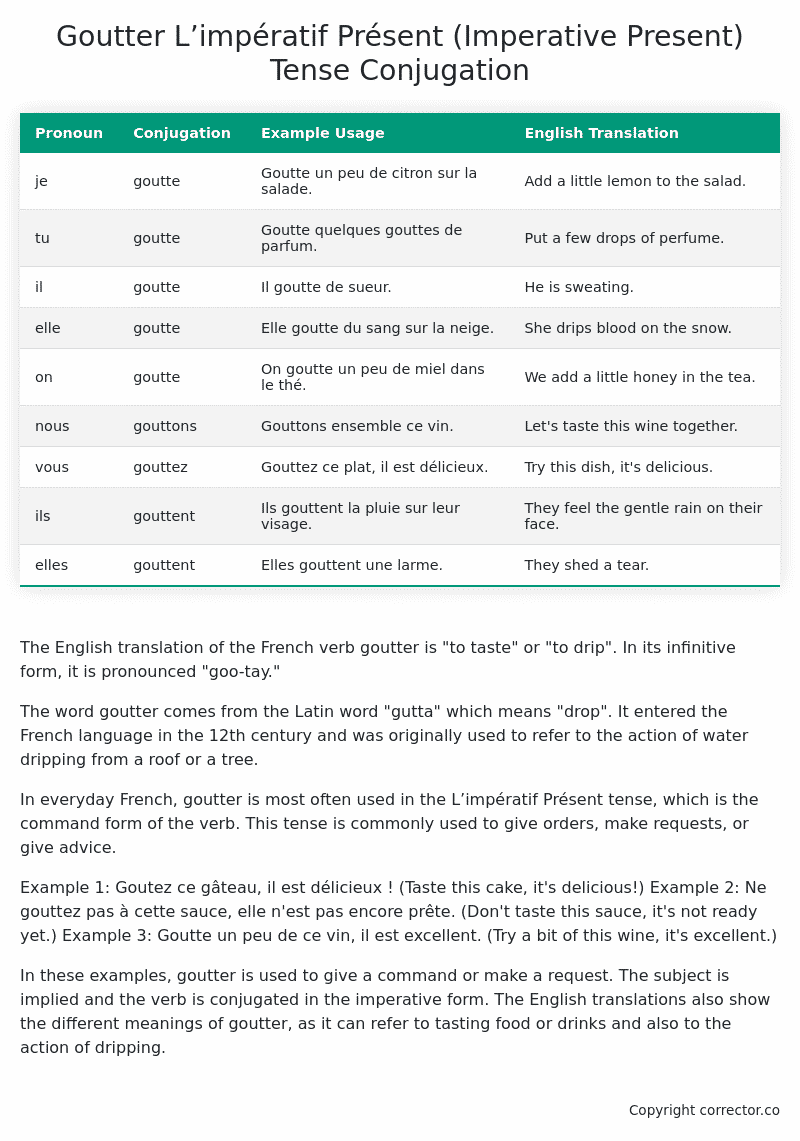
Table of the L’impératif Présent (Imperative Present) Tense Conjugation of goutter
| Pronoun | Conjugation | Example Usage | English Translation |
|---|---|---|---|
| je | goutte | Goutte un peu de citron sur la salade. | Add a little lemon to the salad. |
| tu | goutte | Goutte quelques gouttes de parfum. | Put a few drops of perfume. |
| il | goutte | Il goutte de sueur. | He is sweating. |
| elle | goutte | Elle goutte du sang sur la neige. | She drips blood on the snow. |
| on | goutte | On goutte un peu de miel dans le thé. | We add a little honey in the tea. |
| nous | gouttons | Gouttons ensemble ce vin. | Let’s taste this wine together. |
| vous | gouttez | Gouttez ce plat, il est délicieux. | Try this dish, it’s delicious. |
| ils | gouttent | Ils gouttent la pluie sur leur visage. | They feel the gentle rain on their face. |
| elles | gouttent | Elles gouttent une larme. | They shed a tear. |
Other Conjugations for Goutter.
Le Present (Present Tense) Conjugation of the French Verb goutter
Imparfait (Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb goutter
Passé Simple (Simple Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb goutter
Passé Composé (Present Perfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb goutter
Futur Simple (Simple Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb goutter
Futur Proche (Near Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb goutter
Plus-que-parfait (Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb goutter
Passé Antérieur (Past Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb goutter
Futur Antérieur (Future Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb goutter
Subjonctif Présent (Subjunctive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb goutter
Subjonctif Passé (Subjunctive Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb goutter
Subjonctif Imparfait (Subjunctive Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb goutter
Subjonctif Plus-que-parfait (Subjunctive Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb goutter
Conditionnel Présent (Conditional Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb goutter
Conditionnel Passé (Conditional Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb goutter
L’impératif Présent (Imperative Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb goutter (this article)
L’infinitif Présent (Infinitive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb goutter
Struggling with French verbs or the language in general? Why not use our free French Grammar Checker – no registration required!
Get a FREE Download Study Sheet of this Conjugation 🔥
Simply right click the image below, click “save image” and get your free reference for the goutter L’impératif Présent tense conjugation!
Goutter – About the French L’impératif Présent (Imperative Present) Tense
Usage
Giving commands
Making requests
Offering advice
Expressing desires
Conjugation Formation
Interactions with other tenses
Want More?
I hope you enjoyed this article on the verb goutter. Still in a learning mood? Check out another TOTALLY random French verb conjugation!


