L’infinitif Présent (Infinitive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb ancrer
Introduction to the verb ancrer
The English translation of the French verb ancrer is “to anchor.” In French, it is pronounced as “ahn-kreh.”
The language origin of ancrer can be traced back to the Latin word “ancora,” meaning “anchor.” It is used in everyday French in the L’infinitif Présent tense to express the action of securing or stabilizing something, both physically and figuratively.
Three simple examples of its usage in this tense with their English translations are:
-
Je dois ancrer le bateau avant la tempête. (I have to anchor the boat before the storm.)
-
Il faut ancrer ses valeurs pour rester fidèle à soi-même. (One must anchor their values to stay true to oneself.)
-
Nous devons nous ancrer dans le présent et arrêter de regarder en arrière. (We must anchor ourselves in the present and stop looking back.)
Table of the L’infinitif Présent (Infinitive Present) Tense Conjugation of ancrer
| Pronoun | Conjugation | Example Usage | English Translation |
|---|---|---|---|
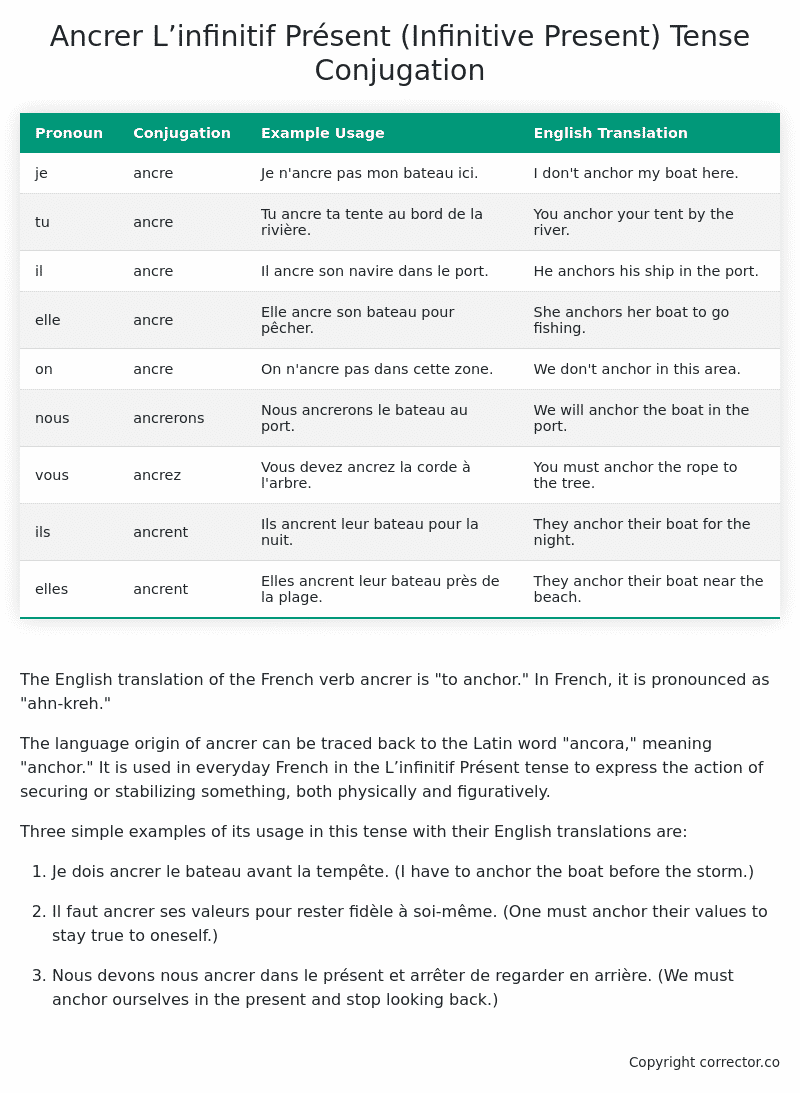
| je | ancre | Je n’ancre pas mon bateau ici. | I don’t anchor my boat here. |
| tu | ancre | Tu ancre ta tente au bord de la rivière. | You anchor your tent by the river. |
| il | ancre | Il ancre son navire dans le port. | He anchors his ship in the port. |
| elle | ancre | Elle ancre son bateau pour pêcher. | She anchors her boat to go fishing. |
| on | ancre | On n’ancre pas dans cette zone. | We don’t anchor in this area. |
| nous | ancrerons | Nous ancrerons le bateau au port. | We will anchor the boat in the port. |
| vous | ancrez | Vous devez ancrez la corde à l’arbre. | You must anchor the rope to the tree. |
| ils | ancrent | Ils ancrent leur bateau pour la nuit. | They anchor their boat for the night. |
| elles | ancrent | Elles ancrent leur bateau près de la plage. | They anchor their boat near the beach. |
Other Conjugations for Ancrer.
Le Present (Present Tense) Conjugation of the French Verb ancrer
Imparfait (Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb ancrer
Passé Simple (Simple Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb ancrer
Passé Composé (Present Perfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb ancrer
Futur Simple (Simple Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb ancrer
Futur Proche (Near Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb ancrer
Plus-que-parfait (Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb ancrer
Passé Antérieur (Past Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb ancrer
Futur Antérieur (Future Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb ancrer
Subjonctif Présent (Subjunctive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb ancrer
Subjonctif Passé (Subjunctive Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb ancrer
Subjonctif Imparfait (Subjunctive Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb ancrer
Subjonctif Plus-que-parfait (Subjunctive Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb ancrer
Conditionnel Présent (Conditional Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb ancrer
Conditionnel Passé (Conditional Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb ancrer
L’impératif Présent (Imperative Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb ancrer
L’infinitif Présent (Infinitive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb ancrer (this article)
Struggling with French verbs or the language in general? Why not use our free French Grammar Checker – no registration required!
Get a FREE Download Study Sheet of this Conjugation 🔥
Simply right click the image below, click “save image” and get your free reference for the ancrer L’infinitif Présent tense conjugation!
Ancrer – About the French L’infinitif Présent (Infinitive Present) Tense
Forming the Infinitive Present
Common Everyday Usage Patterns
As a Verb’s Dictionary Form
After Modal Verbs
As an Imperative
In Infinitive Clauses
Interactions with Other Tenses
Present Tense
Future Tense
Conditional Tense
Passé Composé
Imperfect Tense
Subjunctive and Conditional Moods
Summary
Want More?
I hope you enjoyed this article on the verb ancrer. Still in a learning mood? Check out another TOTALLY random French verb conjugation!


