L’infinitif Présent (Infinitive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb badauder
Introduction to the verb badauder
The English translation of the French verb badauder is “to gawk” or “to stare”. It is pronounced as “bah-doh-deh”.
The word badauder has its origins in the Old French word “bauder”, meaning to tramp or wander. In modern French, it is most commonly used in everyday language in the L’infinitif Présent tense, which is the basic form of the verb.
Here are three examples of badauder being used in L’infinitif Présent tense:
- Je n’aime pas quand les gens badaudent dans ma chambre. (I don’t like it when people gawk in my room.)
- Arrête de badauder, concentre-toi sur ton travail ! (Stop staring, focus on your work!)
- Les touristes badaudent autour de la Tour Eiffel. (Tourists gawk around the Eiffel Tower.)
In all of these examples, badauder is used to describe someone who is staring or gawking at something or someone. It can also be used in a negative context to describe someone who is being nosy or intrusive.
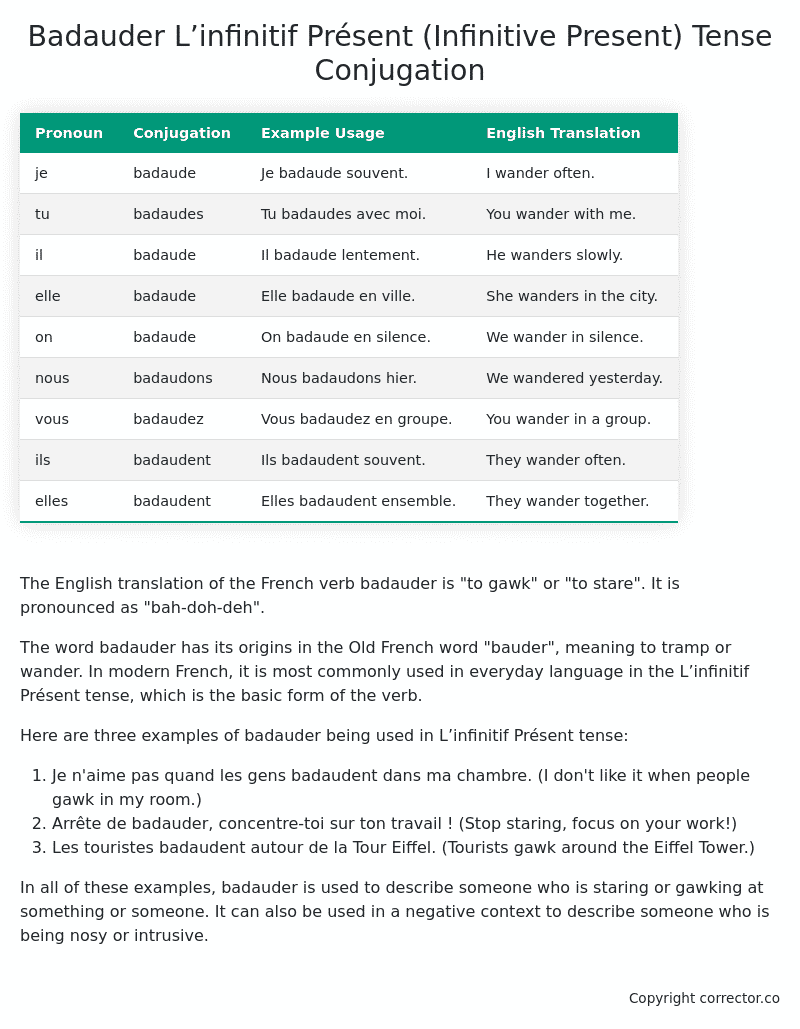
Table of the L’infinitif Présent (Infinitive Present) Tense Conjugation of badauder
| Pronoun | Conjugation | Example Usage | English Translation |
|---|---|---|---|
| je | badaude | Je badaude souvent. | I wander often. |
| tu | badaudes | Tu badaudes avec moi. | You wander with me. |
| il | badaude | Il badaude lentement. | He wanders slowly. |
| elle | badaude | Elle badaude en ville. | She wanders in the city. |
| on | badaude | On badaude en silence. | We wander in silence. |
| nous | badaudons | Nous badaudons hier. | We wandered yesterday. |
| vous | badaudez | Vous badaudez en groupe. | You wander in a group. |
| ils | badaudent | Ils badaudent souvent. | They wander often. |
| elles | badaudent | Elles badaudent ensemble. | They wander together. |
Other Conjugations for Badauder.
Le Present (Present Tense) Conjugation of the French Verb badauder
Imparfait (Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb badauder
Passé Simple (Simple Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb badauder
Passé Composé (Present Perfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb badauder
Futur Simple (Simple Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb badauder
Futur Proche (Near Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb badauder
Plus-que-parfait (Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb badauder
Passé Antérieur (Past Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb badauder
Futur Antérieur (Future Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb badauder
Subjonctif Présent (Subjunctive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb badauder
Subjonctif Passé (Subjunctive Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb badauder
Subjonctif Imparfait (Subjunctive Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb badauder
Subjonctif Plus-que-parfait (Subjunctive Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb badauder
Conditionnel Présent (Conditional Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb badauder
Conditionnel Passé (Conditional Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb badauder
L’impératif Présent (Imperative Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb badauder
L’infinitif Présent (Infinitive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb badauder (this article)
Struggling with French verbs or the language in general? Why not use our free French Grammar Checker – no registration required!
Get a FREE Download Study Sheet of this Conjugation 🔥
Simply right click the image below, click “save image” and get your free reference for the badauder L’infinitif Présent tense conjugation!
Badauder – About the French L’infinitif Présent (Infinitive Present) Tense
Forming the Infinitive Present
Common Everyday Usage Patterns
As a Verb’s Dictionary Form
After Modal Verbs
As an Imperative
In Infinitive Clauses
Interactions with Other Tenses
Present Tense
Future Tense
Conditional Tense
Passé Composé
Imperfect Tense
Subjunctive and Conditional Moods
Summary
Want More?
I hope you enjoyed this article on the verb badauder. Still in a learning mood? Check out another TOTALLY random French verb conjugation!


