L’infinitif Présent (Infinitive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb chromer
Introduction to the verb chromer
The English translation of the French verb chromer is “to chrome.” The infinitive form of the verb is pronounced as “kroh-may” in French.
The language origin of chromer comes from the English word “chrome,” which refers to a type of metal plating that gives a shiny and reflective finish. In French, chromer has the same meaning and is used to describe the action of applying chrome plating to an object.
In everyday French, chromer is most often used in the L’infinitif Présent tense. This tense is used to express actions that are currently happening or that will happen in the future.
Examples of chromer in L’infinitif Présent tense:
-
Je vais chromer ma voiture demain.
Translation: I am going to chrome my car tomorrow. -
Il faut que tu apprennes comment chromer correctement.
Translation: You need to learn how to chrome properly. -
Nous aimons chromer nos meubles pour qu’ils aient un aspect brillant.
Translation: We like to chrome our furniture to give them a shiny appearance.
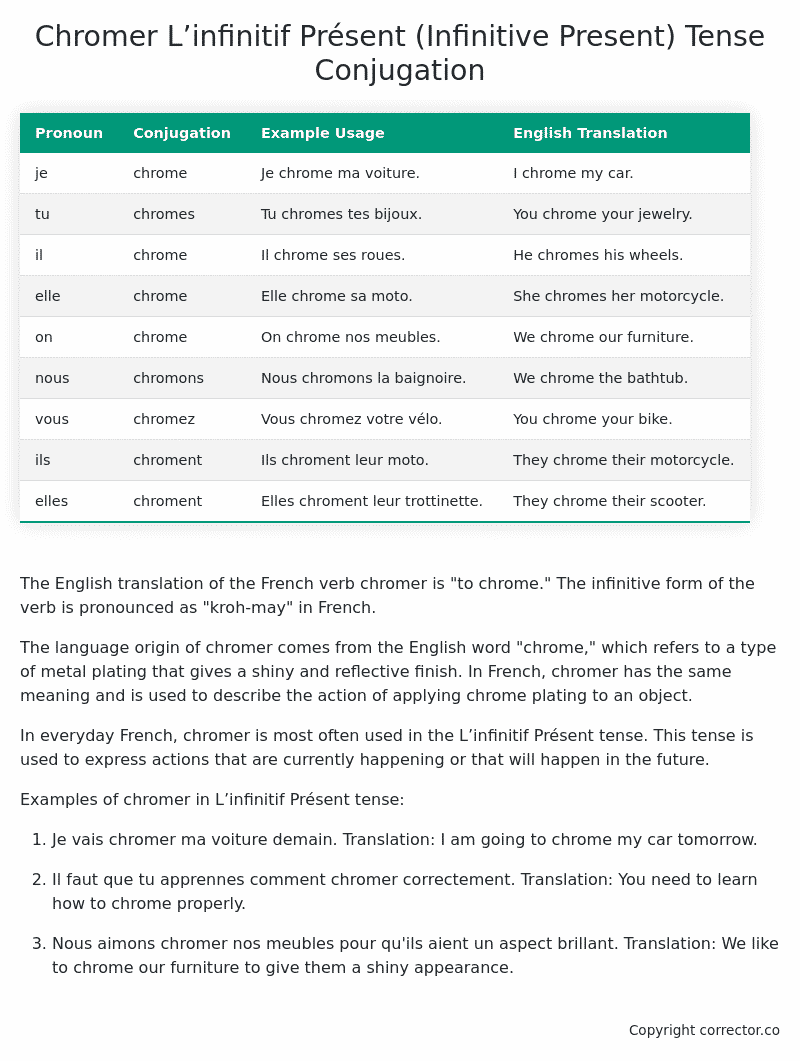
Table of the L’infinitif Présent (Infinitive Present) Tense Conjugation of chromer
| Pronoun | Conjugation | Example Usage | English Translation |
|---|---|---|---|
| je | chrome | Je chrome ma voiture. | I chrome my car. |
| tu | chromes | Tu chromes tes bijoux. | You chrome your jewelry. |
| il | chrome | Il chrome ses roues. | He chromes his wheels. |
| elle | chrome | Elle chrome sa moto. | She chromes her motorcycle. |
| on | chrome | On chrome nos meubles. | We chrome our furniture. |
| nous | chromons | Nous chromons la baignoire. | We chrome the bathtub. |
| vous | chromez | Vous chromez votre vélo. | You chrome your bike. |
| ils | chroment | Ils chroment leur moto. | They chrome their motorcycle. |
| elles | chroment | Elles chroment leur trottinette. | They chrome their scooter. |
Other Conjugations for Chromer.
Le Present (Present Tense) Conjugation of the French Verb chromer
Imparfait (Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb chromer
Passé Simple (Simple Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb chromer
Passé Composé (Present Perfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb chromer
Futur Simple (Simple Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb chromer
Futur Proche (Near Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb chromer
Plus-que-parfait (Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb chromer
Passé Antérieur (Past Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb chromer
Futur Antérieur (Future Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb chromer
Subjonctif Présent (Subjunctive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb chromer
Subjonctif Passé (Subjunctive Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb chromer
Subjonctif Imparfait (Subjunctive Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb chromer
Subjonctif Plus-que-parfait (Subjunctive Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb chromer
Conditionnel Présent (Conditional Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb chromer
Conditionnel Passé (Conditional Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb chromer
L’impératif Présent (Imperative Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb chromer
L’infinitif Présent (Infinitive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb chromer (this article)
Struggling with French verbs or the language in general? Why not use our free French Grammar Checker – no registration required!
Get a FREE Download Study Sheet of this Conjugation 🔥
Simply right click the image below, click “save image” and get your free reference for the chromer L’infinitif Présent tense conjugation!
Chromer – About the French L’infinitif Présent (Infinitive Present) Tense
Forming the Infinitive Present
Common Everyday Usage Patterns
As a Verb’s Dictionary Form
After Modal Verbs
As an Imperative
In Infinitive Clauses
Interactions with Other Tenses
Present Tense
Future Tense
Conditional Tense
Passé Composé
Imperfect Tense
Subjunctive and Conditional Moods
Summary
Want More?
I hope you enjoyed this article on the verb chromer. Still in a learning mood? Check out another TOTALLY random French verb conjugation!


