L’infinitif Présent (Infinitive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb emporter
Introduction to the verb emporter
The English translation of the French verb emporter is “to take away” or “to bring.” The infinitive form of emporter is pronounced as “ahm-por-tay.”
The word emporter comes from the Old French root “emporter,” which is derived from the Latin “in” (in) and “portare” (to carry). It is most commonly used as a transitive verb, meaning that it requires a direct object.
In everyday French, emporter is often used to describe physically taking something with you or bringing something to a specific location. For example:
- Je vais emporter mon parapluie car il va pleuvoir. (I am going to take my umbrella because it’s going to rain.)
- Nous avons oublié d’emporter notre passeport pour le voyage. (We forgot to bring our passport for the trip.)
- Est-ce que tu peux emporter ces livres à la bibliothèque ? (Can you take these books to the library?)
In these examples, emporter is used in its infinitive present form to express an immediate action or a future plan. The subject of the sentence is the person who will perform the action of taking or bringing something.
Overall, emporter is a useful verb to know in French as it is commonly used in daily conversations. It can also be used in different tenses, such as the past tense “emporté” or the future tense “emporterai,” to express various actions related to taking or bringing something.
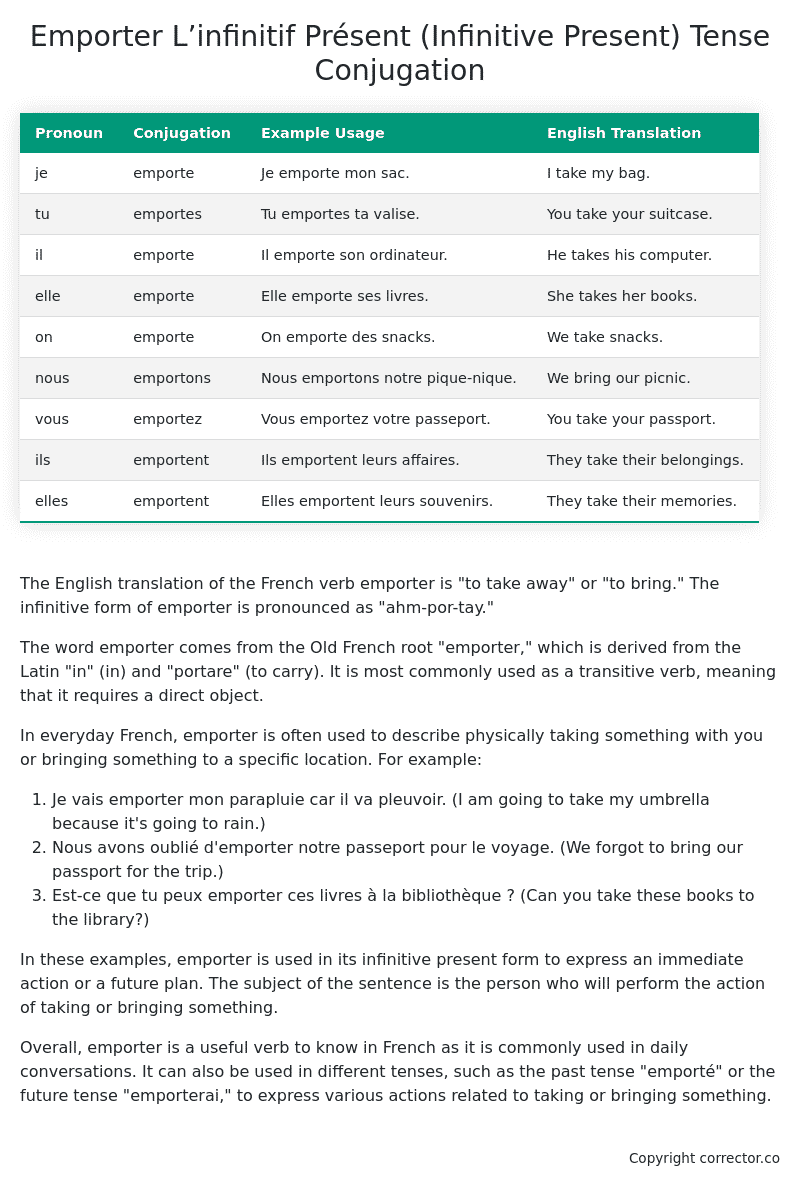
Table of the L’infinitif Présent (Infinitive Present) Tense Conjugation of emporter
| Pronoun | Conjugation | Example Usage | English Translation |
|---|---|---|---|
| je | emporte | Je emporte mon sac. | I take my bag. |
| tu | emportes | Tu emportes ta valise. | You take your suitcase. |
| il | emporte | Il emporte son ordinateur. | He takes his computer. |
| elle | emporte | Elle emporte ses livres. | She takes her books. |
| on | emporte | On emporte des snacks. | We take snacks. |
| nous | emportons | Nous emportons notre pique-nique. | We bring our picnic. |
| vous | emportez | Vous emportez votre passeport. | You take your passport. |
| ils | emportent | Ils emportent leurs affaires. | They take their belongings. |
| elles | emportent | Elles emportent leurs souvenirs. | They take their memories. |
Other Conjugations for Emporter.
Le Present (Present Tense) Conjugation of the French Verb emporter
Imparfait (Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb emporter
Passé Simple (Simple Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb emporter
Passé Composé (Present Perfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb emporter
Futur Simple (Simple Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb emporter
Futur Proche (Near Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb emporter
Plus-que-parfait (Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb emporter
Passé Antérieur (Past Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb emporter
Futur Antérieur (Future Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb emporter
Subjonctif Présent (Subjunctive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb emporter
Subjonctif Passé (Subjunctive Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb emporter
Subjonctif Imparfait (Subjunctive Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb emporter
Subjonctif Plus-que-parfait (Subjunctive Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb emporter
Conditionnel Présent (Conditional Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb emporter
Conditionnel Passé (Conditional Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb emporter
L’impératif Présent (Imperative Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb emporter
L’infinitif Présent (Infinitive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb emporter (this article)
Struggling with French verbs or the language in general? Why not use our free French Grammar Checker – no registration required!
Get a FREE Download Study Sheet of this Conjugation 🔥
Simply right click the image below, click “save image” and get your free reference for the emporter L’infinitif Présent tense conjugation!
Emporter – About the French L’infinitif Présent (Infinitive Present) Tense
Forming the Infinitive Present
Common Everyday Usage Patterns
As a Verb’s Dictionary Form
After Modal Verbs
As an Imperative
In Infinitive Clauses
Interactions with Other Tenses
Present Tense
Future Tense
Conditional Tense
Passé Composé
Imperfect Tense
Subjunctive and Conditional Moods
Summary
Want More?
I hope you enjoyed this article on the verb emporter. Still in a learning mood? Check out another TOTALLY random French verb conjugation!


