L’infinitif Présent (Infinitive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb entre-frapper
Introduction to the verb entre-frapper
The English translation of the French verb entre-frapper is “to knock between.” It is pronounced “ahn-truh-frah-peh” in its infinitive form.
The verb entre-frapper comes from the combination of the prefix “entre” meaning “between” and the verb “frapper” meaning “to knock.” It is most often used in everyday French to describe knocking on a door or window that is located between two other objects or buildings.
Examples:
-
Je vais entre-frapper à la fenêtre pour que tu m’entendes. (I will knock between the windows so that you can hear me.)
-
Le chat est coincé entre les deux murs, je vais entre-frapper pour qu’il puisse sortir. (The cat is stuck between the two walls, I will knock between them so it can get out.)
-
Nous avons vu une main qui entre-frappait à la porte du bâtiment abandonné. (We saw a hand knocking between the door of the abandoned building.)
Note: In these examples, the verb entre-frapper is conjugated in the l’infinitif présent tense, which is the equivalent of the English infinitive form.
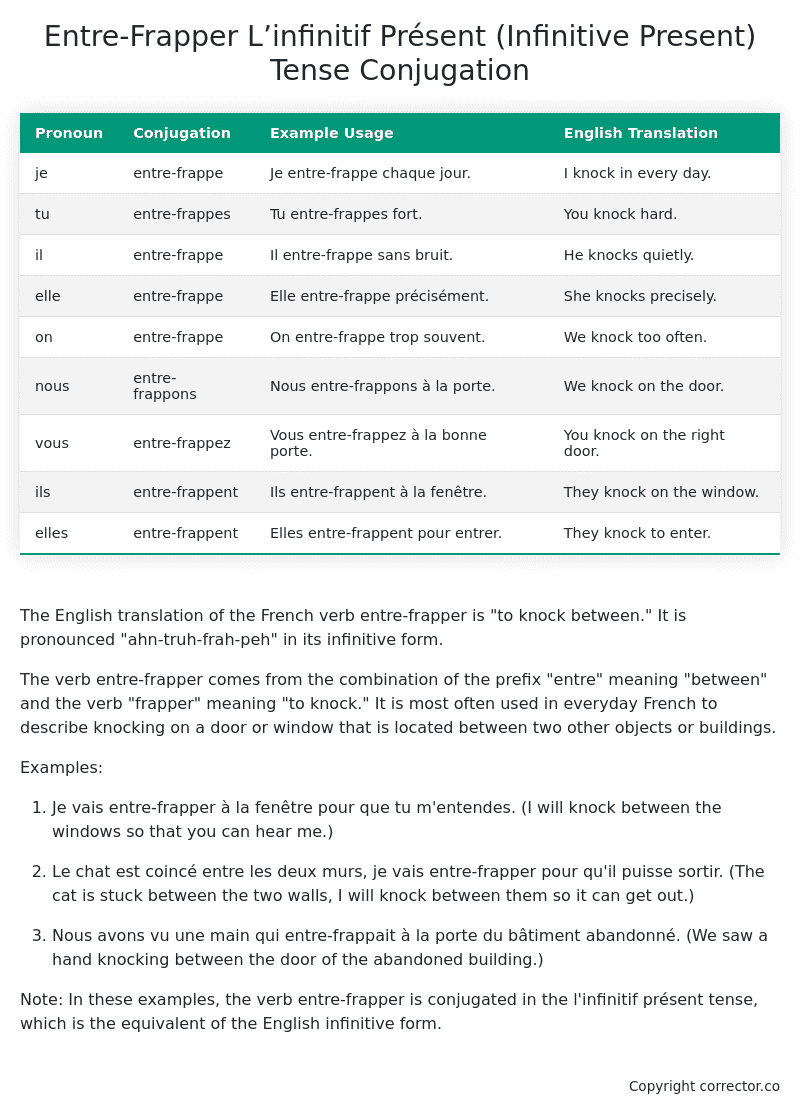
Table of the L’infinitif Présent (Infinitive Present) Tense Conjugation of entre-frapper
| Pronoun | Conjugation | Example Usage | English Translation |
|---|---|---|---|
| je | entre-frappe | Je entre-frappe chaque jour. | I knock in every day. |
| tu | entre-frappes | Tu entre-frappes fort. | You knock hard. |
| il | entre-frappe | Il entre-frappe sans bruit. | He knocks quietly. |
| elle | entre-frappe | Elle entre-frappe précisément. | She knocks precisely. |
| on | entre-frappe | On entre-frappe trop souvent. | We knock too often. |
| nous | entre-frappons | Nous entre-frappons à la porte. | We knock on the door. |
| vous | entre-frappez | Vous entre-frappez à la bonne porte. | You knock on the right door. |
| ils | entre-frappent | Ils entre-frappent à la fenêtre. | They knock on the window. |
| elles | entre-frappent | Elles entre-frappent pour entrer. | They knock to enter. |
Other Conjugations for Entre-Frapper.
Le Present (Present Tense) Conjugation of the French Verb entre-frapper
Imparfait (Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb entre-frapper
Passé Simple (Simple Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb entre-frapper
Passé Composé (Present Perfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb entre-frapper
Futur Simple (Simple Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb entre-frapper
Futur Proche (Near Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb entre-frapper
Plus-que-parfait (Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb entre-frapper
Passé Antérieur (Past Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb entre-frapper
Futur Antérieur (Future Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb entre-frapper
Subjonctif Présent (Subjunctive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb entre-frapper
Subjonctif Passé (Subjunctive Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb entre-frapper
Subjonctif Imparfait (Subjunctive Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb entre-frapper
Conditionnel Présent (Conditional Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb entre-frapper
Conditionnel Passé (Conditional Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb entre-frapper
L’impératif Présent (Imperative Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb entre-frapper
L’infinitif Présent (Infinitive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb entre-frapper (this article)
Struggling with French verbs or the language in general? Why not use our free French Grammar Checker – no registration required!
Get a FREE Download Study Sheet of this Conjugation 🔥
Simply right click the image below, click “save image” and get your free reference for the entre-frapper L’infinitif Présent tense conjugation!
Entre-Frapper – About the French L’infinitif Présent (Infinitive Present) Tense
Forming the Infinitive Present
Common Everyday Usage Patterns
As a Verb’s Dictionary Form
After Modal Verbs
As an Imperative
In Infinitive Clauses
Interactions with Other Tenses
Present Tense
Future Tense
Conditional Tense
Passé Composé
Imperfect Tense
Subjunctive and Conditional Moods
Summary
Want More?
I hope you enjoyed this article on the verb entre-frapper. Still in a learning mood? Check out another TOTALLY random French verb conjugation!


