Passé Antérieur (Past Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb disqualifier
Introduction to the verb disqualifier
The English translation of the French verb disqualifier is “to disqualify.” The infinitive form, disqualifier, is pronounced as “dee-skah-lee-fee-yay.”
The word disqualifier comes from the Latin word disqualificare, which consists of the prefix dis- meaning “apart” or “away,” and the word qualifier, meaning “to make eligible.” In everyday French, disqualifier is used to describe the act of rendering someone or something ineligible or unsuitable for a particular purpose or position.
In the Passé Antérieur tense, which is used to describe actions that occurred before another past action, disqualifier is conjugated as follows:
- J’eus disqualifié (I had disqualified)
- Tu eus disqualifié (You had disqualified)
- Il/Elle eut disqualifié (He/She had disqualified)
- Nous eûmes disqualifié (We had disqualified)
- Vous eûtes disqualifié (You had disqualified)
- Ils/Elles eurent disqualifié (They had disqualified)
Here are three simple examples of disqualifier in the Passé Antérieur tense, with their respective English translations:
-
J’eus disqualifié l’équipe adverse avant la finale. (I had disqualified the opposing team before the final match.)
-
Tu eus disqualifié ton coéquipier en trichant. (You had disqualified your teammate by cheating.)
-
Ils eurent disqualifié le joueur pour comportement antisportif. (They had disqualified the player for unsportsmanlike behavior.)
Table of the Passé Antérieur (Past Anterior) Tense Conjugation of disqualifier
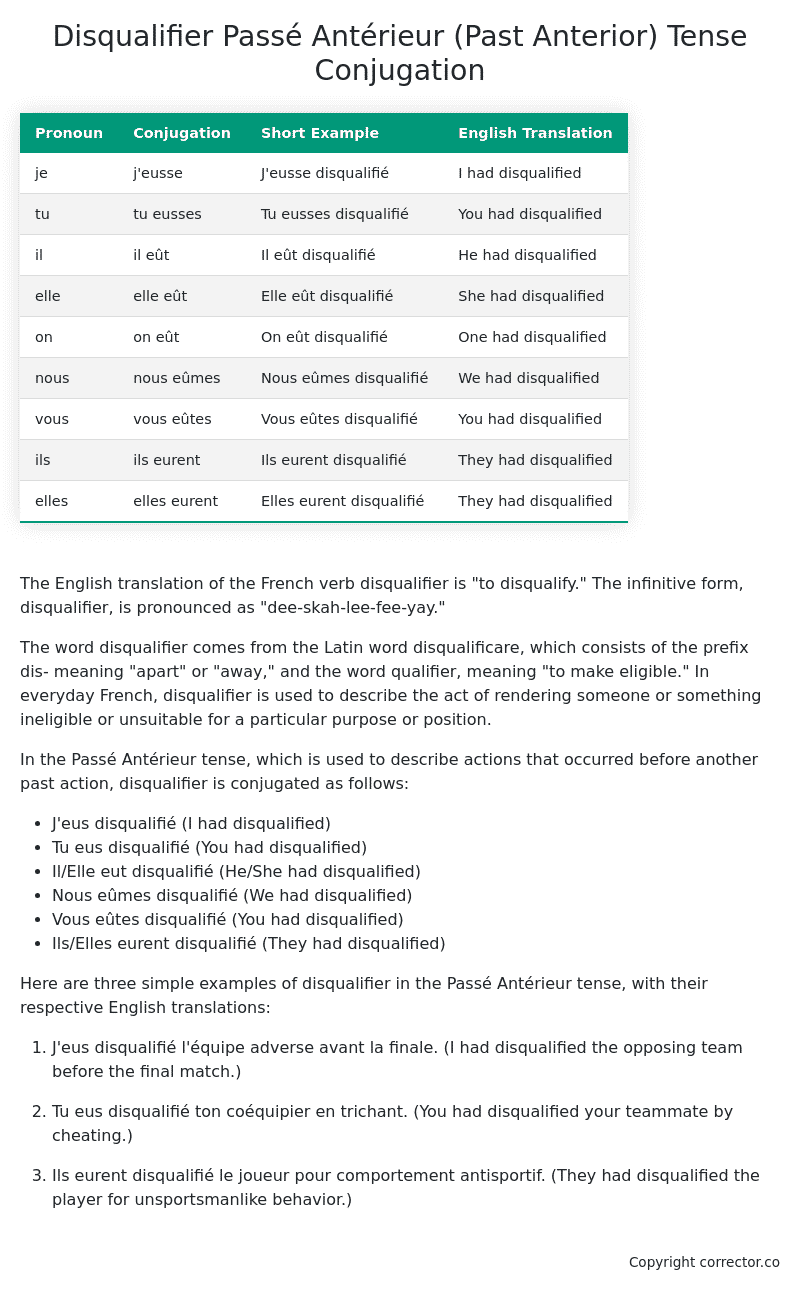
| Pronoun | Conjugation | Short Example | English Translation |
|---|---|---|---|
| je | j’eusse | J’eusse disqualifié | I had disqualified |
| tu | tu eusses | Tu eusses disqualifié | You had disqualified |
| il | il eût | Il eût disqualifié | He had disqualified |
| elle | elle eût | Elle eût disqualifié | She had disqualified |
| on | on eût | On eût disqualifié | One had disqualified |
| nous | nous eûmes | Nous eûmes disqualifié | We had disqualified |
| vous | vous eûtes | Vous eûtes disqualifié | You had disqualified |
| ils | ils eurent | Ils eurent disqualifié | They had disqualified |
| elles | elles eurent | Elles eurent disqualifié | They had disqualified |
Other Conjugations for Disqualifier.
Le Present (Present Tense) Conjugation of the French Verb disqualifier
Imparfait (Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb disqualifier
Passé Simple (Simple Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb disqualifier
Passé Composé (Present Perfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb disqualifier
Futur Simple (Simple Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb disqualifier
Futur Proche (Near Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb disqualifier
Plus-que-parfait (Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb disqualifier
Passé Antérieur (Past Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb disqualifier (this article)
Futur Antérieur (Future Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb disqualifier
Subjonctif Présent (Subjunctive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb disqualifier
Subjonctif Passé (Subjunctive Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb disqualifier
Subjonctif Imparfait (Subjunctive Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb disqualifier
Conditionnel Présent (Conditional Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb disqualifier
Conditionnel Passé (Conditional Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb disqualifier
L’impératif Présent (Imperative Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb disqualifier
L’infinitif Présent (Infinitive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb disqualifier
Struggling with French verbs or the language in general? Why not use our free French Grammar Checker – no registration required!
Get a FREE Download Study Sheet of this Conjugation 🔥
Simply right click the image below, click “save image” and get your free reference for the disqualifier Passé Antérieur tense conjugation!
Disqualifier – About the French Passé Antérieur (Past Anterior) Tense
Formation of the Passé Antérieur
Common Usage Patterns
Literature
Historical Texts
Formal Writing
Interactions with Other Tenses
Passé Composé (Present Perfect)
Imparfait (Imperfect)
Futur Antérieur (Future Perfect)
Summary
I hope you enjoyed this article on the verb disqualifier. Still in a learning mood? Check out another TOTALLY random French verb conjugation!


