Passé Simple (Simple Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb affairer
Introduction to the verb affairer
The English translation of the French verb “affairer” is “to keep busy” or “to be busy.” The infinitive form, “affairer,” is pronounced as [a.fɛ.ʁe].
The verb “affairer” comes from the Old French word “aferir,” which means “to define” or “to give a legal status.” In everyday French, “affairer” is used to express the action of being busy or occupied with various tasks.
In the Passé Simple (Simple Past) tense, “affairer” is less commonly used in everyday spoken French, as it tends to be reserved for formal or written contexts. However, here are three simple examples of its usage in the Simple Past tense, along with their English translations:
-
Hier, ils affairèrent toute la journée à préparer la réunion.
(Yesterday, they kept busy all day preparing for the meeting.) -
Durant les vacances, nous nous affairâmes à ranger la maison.
(During the holidays, we kept ourselves busy tidying up the house.) -
Le directeur affaira ses employés pour terminer le projet à temps.
(The manager kept his employees busy to finish the project on time.)
Table of the Passé Simple (Simple Past) Tense Conjugation of affairer
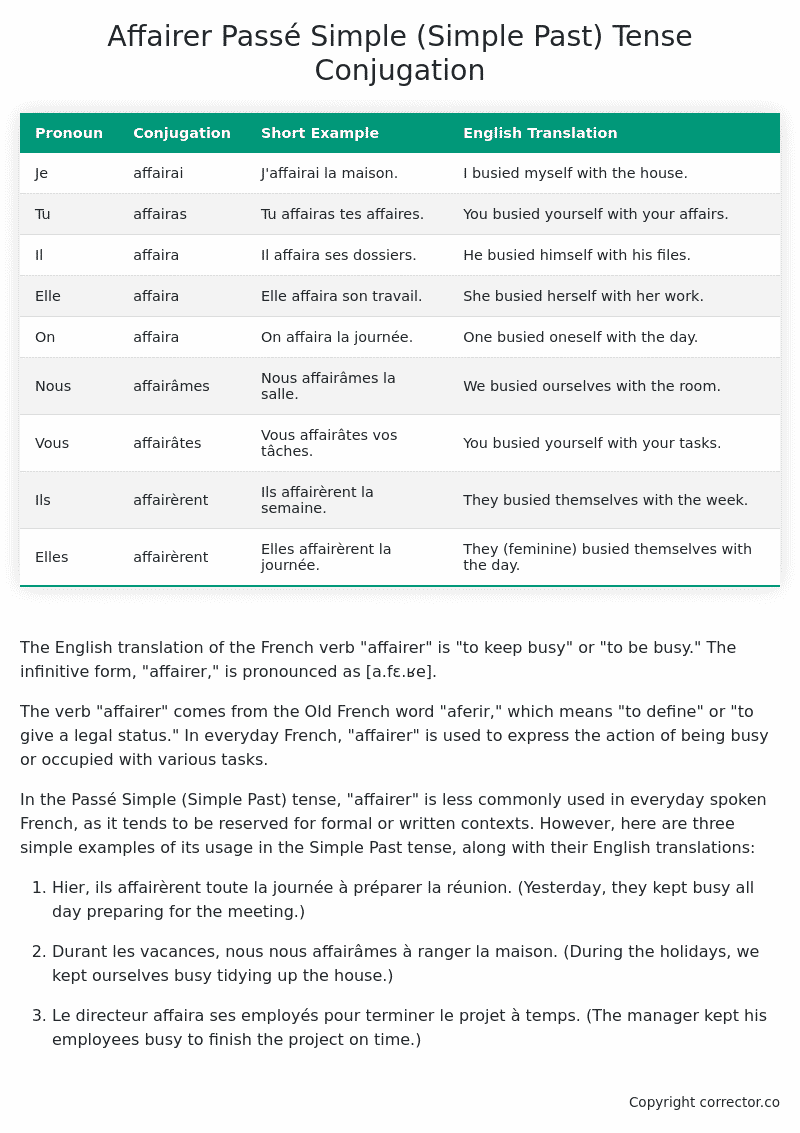
| Pronoun | Conjugation | Short Example | English Translation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Je | affairai | J’affairai la maison. | I busied myself with the house. |
| Tu | affairas | Tu affairas tes affaires. | You busied yourself with your affairs. |
| Il | affaira | Il affaira ses dossiers. | He busied himself with his files. |
| Elle | affaira | Elle affaira son travail. | She busied herself with her work. |
| On | affaira | On affaira la journée. | One busied oneself with the day. |
| Nous | affairâmes | Nous affairâmes la salle. | We busied ourselves with the room. |
| Vous | affairâtes | Vous affairâtes vos tâches. | You busied yourself with your tasks. |
| Ils | affairèrent | Ils affairèrent la semaine. | They busied themselves with the week. |
| Elles | affairèrent | Elles affairèrent la journée. | They (feminine) busied themselves with the day. |
Other Conjugations for Affairer.
Le Present (Present Tense) Conjugation of the French Verb affairer
Imparfait (Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb affairer
Passé Simple (Simple Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb affairer (You’re reading it right now!)
Passé Composé (Present Perfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb affairer
Futur Simple (Simple Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb affairer
Futur Proche (Near Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb affairer
Plus-que-parfait (Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb affairer
Passé Antérieur (Past Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb affairer
Futur Antérieur (Future Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb affairer
Subjonctif Présent (Subjunctive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb affairer
Subjonctif Passé (Subjunctive Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb affairer
Subjonctif Imparfait (Subjunctive Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb affairer
Subjonctif Plus-que-parfait (Subjunctive Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb affairer
Conditionnel Présent (Conditional Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb affairer
Conditionnel Passé (Conditional Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb affairer
Conditionnel Passé II (Conditional Past II) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb affairer
L’impératif Présent (Imperative Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb affairer
L’impératif Passé (Imperative Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb affairer
L’infinitif Présent (Infinitive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb affairer
L’infinitif Passé (Infinitive Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb affairer
Le Participe Présent (Present Participle) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb affairer
Le Participe Passé (Past Participle) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb affairer
Struggling with French verbs or the language in general? Why not use our free French Grammar Checker – no registration required!
Get a FREE Download Study Sheet of this Conjugation 🔥
Simply right click the image below, click “save image” and get your free reference for the affairer Passé Simple tense conjugation!
Affairer – About the French Passé Simple (Simple Past) Tense
Formation
Usage
Narration
Historical Context
Interactions with other tenses
Passé Composé
Imparfait
Conditional and Subjunctive
Summary
I hope you enjoyed this article on the verb affairer. Still in a learning mood? Check out another TOTALLY random French verb conjugation!


