Passé Simple (Simple Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb aspirer
Introduction to the verb aspirer
The English translation of the French verb “aspirer” is “to aspire” or “to inhale”. The infinitive form “aspirer” is pronounced as /a.spi.ʁe/.
The verb “aspirer” comes from the Latin word “aspirare”, which means “to breathe, inhale”. In everyday French, it is commonly used to express the idea of aspiring to achieve something or inhaling something.
In the Passé Simple (Simple Past) tense, “aspirer” is not frequently used in everyday French. However, here are three examples of its usage in this tense along with their English translations:
- J’aspirai à devenir un grand artiste. (I aspired to become a great artist.)
- Elle aspira profondément l’air frais de la montagne. (She inhaled deeply the fresh air of the mountain.)
- Nous aspirâmes les fumées toxiques involontairement. (We inadvertently inhaled the toxic fumes.)
Please note that the Passé Simple tense is primarily used in formal or literary writing, and in spoken language, the Passé Composé or other compound tenses are more commonly used to express actions in the past.
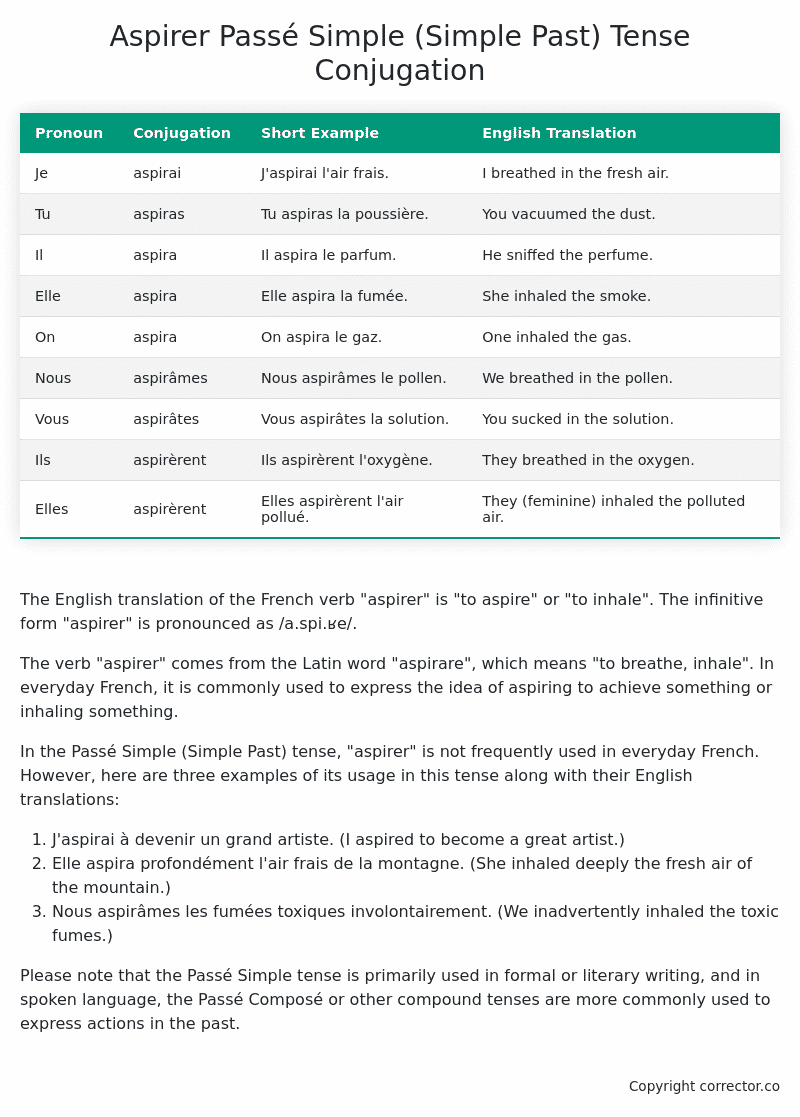
Table of the Passé Simple (Simple Past) Tense Conjugation of aspirer
| Pronoun | Conjugation | Short Example | English Translation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Je | aspirai | J’aspirai l’air frais. | I breathed in the fresh air. |
| Tu | aspiras | Tu aspiras la poussière. | You vacuumed the dust. |
| Il | aspira | Il aspira le parfum. | He sniffed the perfume. |
| Elle | aspira | Elle aspira la fumée. | She inhaled the smoke. |
| On | aspira | On aspira le gaz. | One inhaled the gas. |
| Nous | aspirâmes | Nous aspirâmes le pollen. | We breathed in the pollen. |
| Vous | aspirâtes | Vous aspirâtes la solution. | You sucked in the solution. |
| Ils | aspirèrent | Ils aspirèrent l’oxygène. | They breathed in the oxygen. |
| Elles | aspirèrent | Elles aspirèrent l’air pollué. | They (feminine) inhaled the polluted air. |
Other Conjugations for Aspirer.
Le Present (Present Tense) Conjugation of the French Verb aspirer
Imparfait (Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb aspirer
Passé Simple (Simple Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb aspirer (You’re reading it right now!)
Passé Composé (Present Perfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb aspirer
Futur Simple (Simple Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb aspirer
Futur Proche (Near Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb aspirer
Plus-que-parfait (Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb aspirer
Passé Antérieur (Past Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb aspirer
Futur Antérieur (Future Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb aspirer
Subjonctif Présent (Subjunctive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb aspirer
Subjonctif Passé (Subjunctive Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb aspirer
Subjonctif Imparfait (Subjunctive Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb aspirer
Subjonctif Plus-que-parfait (Subjunctive Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb aspirer
Conditionnel Présent (Conditional Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb aspirer
Conditionnel Passé (Conditional Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb aspirer
Conditionnel Passé II (Conditional Past II) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb aspirer
L’impératif Présent (Imperative Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb aspirer
L’impératif Passé (Imperative Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb aspirer
L’infinitif Présent (Infinitive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb aspirer
L’infinitif Passé (Infinitive Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb aspirer
Le Participe Présent (Present Participle) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb aspirer
Le Participe Passé (Past Participle) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb aspirer
Struggling with French verbs or the language in general? Why not use our free French Grammar Checker – no registration required!
Get a FREE Download Study Sheet of this Conjugation 🔥
Simply right click the image below, click “save image” and get your free reference for the aspirer Passé Simple tense conjugation!
Aspirer – About the French Passé Simple (Simple Past) Tense
Formation
Usage
Narration
Historical Context
Interactions with other tenses
Passé Composé
Imparfait
Conditional and Subjunctive
Summary
I hope you enjoyed this article on the verb aspirer. Still in a learning mood? Check out another TOTALLY random French verb conjugation!


