Passé Simple (Simple Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb assoner
Introduction to the verb assoner
The English translation of the French verb “assoner” is “to rhyme.” The infinitive form of “assoner” is pronounced as /a.sɔ.ne/.
The word “assoner” comes from the Old French verb “asoner,” which originated from the Latin word “adsonare,” meaning “to sound in response.” In everyday French, the passé simple tense is rarely used in spoken language but is found in written literature or formal contexts to express actions completed in the past.
Here are three examples of “assoner” used in the passé simple tense:
-
Les mots assonèrent parfaitement dans son poème.
(The words rhymed perfectly in his poem.) -
Hier, j’assonai mes vers avec habileté.
(Yesterday, I rhymed my verses skillfully.) -
Quand il écrivit cette chanson, il assona chaque couplet.
(When he wrote this song, he rhymed every verse.)
Table of the Passé Simple (Simple Past) Tense Conjugation of assoner
| Pronoun | Conjugation | Short Example | English Translation |
|---|---|---|---|
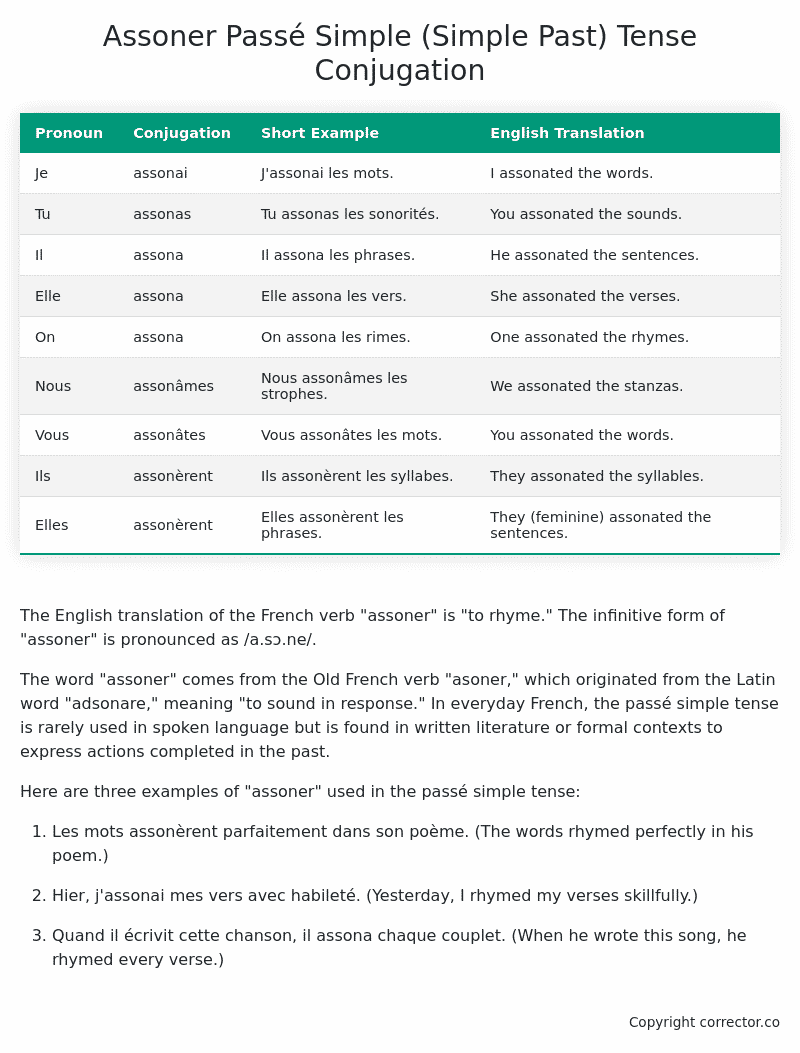
| Je | assonai | J’assonai les mots. | I assonated the words. |
| Tu | assonas | Tu assonas les sonorités. | You assonated the sounds. |
| Il | assona | Il assona les phrases. | He assonated the sentences. |
| Elle | assona | Elle assona les vers. | She assonated the verses. |
| On | assona | On assona les rimes. | One assonated the rhymes. |
| Nous | assonâmes | Nous assonâmes les strophes. | We assonated the stanzas. |
| Vous | assonâtes | Vous assonâtes les mots. | You assonated the words. |
| Ils | assonèrent | Ils assonèrent les syllabes. | They assonated the syllables. |
| Elles | assonèrent | Elles assonèrent les phrases. | They (feminine) assonated the sentences. |
Other Conjugations for Assoner.
Le Present (Present Tense) Conjugation of the French Verb assoner
Imparfait (Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb assoner
Passé Simple (Simple Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb assoner (You’re reading it right now!)
Passé Composé (Present Perfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb assoner
Futur Simple (Simple Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb assoner
Futur Proche (Near Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb assoner
Plus-que-parfait (Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb assoner
Passé Antérieur (Past Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb assoner
Futur Antérieur (Future Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb assoner
Subjonctif Présent (Subjunctive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb assoner
Subjonctif Passé (Subjunctive Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb assoner
Subjonctif Imparfait (Subjunctive Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb assoner
Subjonctif Plus-que-parfait (Subjunctive Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb assoner
Conditionnel Présent (Conditional Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb assoner
Conditionnel Passé (Conditional Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb assoner
Conditionnel Passé II (Conditional Past II) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb assoner
L’impératif Présent (Imperative Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb assoner
L’impératif Passé (Imperative Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb assoner
L’infinitif Présent (Infinitive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb assoner
L’infinitif Passé (Infinitive Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb assoner
Le Participe Présent (Present Participle) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb assoner
Le Participe Passé (Past Participle) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb assoner
Struggling with French verbs or the language in general? Why not use our free French Grammar Checker – no registration required!
Get a FREE Download Study Sheet of this Conjugation 🔥
Simply right click the image below, click “save image” and get your free reference for the assoner Passé Simple tense conjugation!
Assoner – About the French Passé Simple (Simple Past) Tense
Formation
Usage
Narration
Historical Context
Interactions with other tenses
Passé Composé
Imparfait
Conditional and Subjunctive
Summary
I hope you enjoyed this article on the verb assoner. Still in a learning mood? Check out another TOTALLY random French verb conjugation!


