Passé Simple (Simple Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb baguenauder
Introduction to the verb baguenauder
The English translation of the French verb “baguenauder” is “to wander aimlessly” or “to stroll around.” The pronunciation of the infinitive form “baguenauder” in French is [ba-ge-nô-de].
The verb “baguenauder” has its origins in the Old French word “baguener,” meaning “to walk in a zigzag manner.” It is derived from “baguenod,” which refers to someone who walks unsteadily or with an unsteady gait. In everyday French, the verb is used in the Passé Simple tense (Simple Past) to describe actions that occurred and were completed in the past. However, it is worth noting that the Passé Simple is rarely used in spoken French and is mostly reserved for formal or literary writing.
Here are three examples of “baguenauder” in the Passé Simple tense along with their English translations:
-
Je baguenaudai dans les rues de Paris.
(I wandered aimlessly in the streets of Paris.) -
Nous baguenaudâmes le long de la plage.
(We strolled along the beach.) -
Ils baguenaudèrent dans le parc toute la journée.
(They wandered aimlessly in the park all day.)
Please note that these examples showcase the usage of “baguenauder” in the Passé Simple tense, which is not commonly employed in everyday spoken French.
Table of the Passé Simple (Simple Past) Tense Conjugation of baguenauder
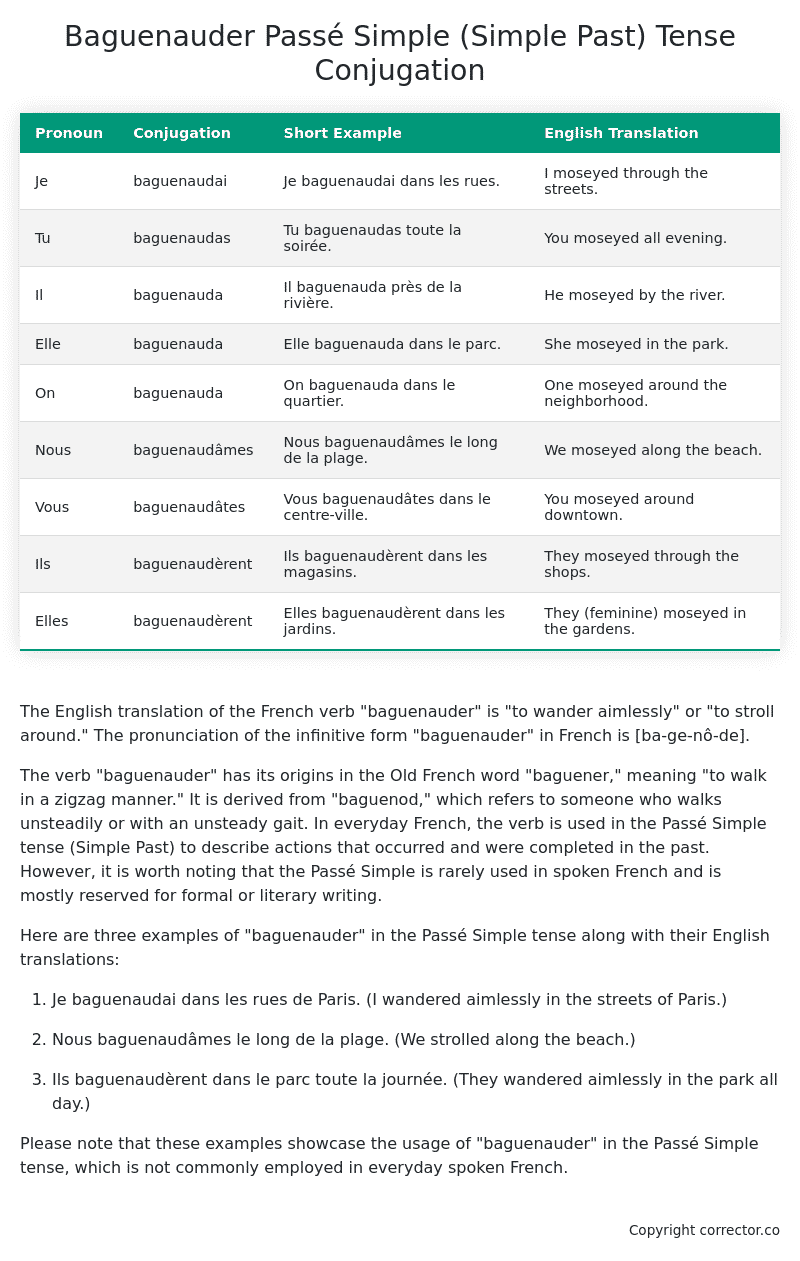
| Pronoun | Conjugation | Short Example | English Translation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Je | baguenaudai | Je baguenaudai dans les rues. | I moseyed through the streets. |
| Tu | baguenaudas | Tu baguenaudas toute la soirée. | You moseyed all evening. |
| Il | baguenauda | Il baguenauda près de la rivière. | He moseyed by the river. |
| Elle | baguenauda | Elle baguenauda dans le parc. | She moseyed in the park. |
| On | baguenauda | On baguenauda dans le quartier. | One moseyed around the neighborhood. |
| Nous | baguenaudâmes | Nous baguenaudâmes le long de la plage. | We moseyed along the beach. |
| Vous | baguenaudâtes | Vous baguenaudâtes dans le centre-ville. | You moseyed around downtown. |
| Ils | baguenaudèrent | Ils baguenaudèrent dans les magasins. | They moseyed through the shops. |
| Elles | baguenaudèrent | Elles baguenaudèrent dans les jardins. | They (feminine) moseyed in the gardens. |
Other Conjugations for Baguenauder.
Le Present (Present Tense) Conjugation of the French Verb baguenauder
Imparfait (Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb baguenauder
Passé Simple (Simple Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb baguenauder (You’re reading it right now!)
Passé Composé (Present Perfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb baguenauder
Futur Simple (Simple Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb baguenauder
Futur Proche (Near Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb baguenauder
Plus-que-parfait (Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb baguenauder
Passé Antérieur (Past Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb baguenauder
Futur Antérieur (Future Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb baguenauder
Subjonctif Présent (Subjunctive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb baguenauder
Subjonctif Passé (Subjunctive Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb baguenauder
Subjonctif Imparfait (Subjunctive Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb baguenauder
Conditionnel Présent (Conditional Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb baguenauder
Conditionnel Passé (Conditional Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb baguenauder
Conditionnel Passé II (Conditional Past II) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb baguenauder
L’impératif Présent (Imperative Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb baguenauder
L’impératif Passé (Imperative Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb baguenauder
L’infinitif Présent (Infinitive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb baguenauder
L’infinitif Passé (Infinitive Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb baguenauder
Le Participe Présent (Present Participle) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb baguenauder
Le Participe Passé (Past Participle) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb baguenauder
Struggling with French verbs or the language in general? Why not use our free French Grammar Checker – no registration required!
Get a FREE Download Study Sheet of this Conjugation 🔥
Simply right click the image below, click “save image” and get your free reference for the baguenauder Passé Simple tense conjugation!
Baguenauder – About the French Passé Simple (Simple Past) Tense
Formation
Usage
Narration
Historical Context
Interactions with other tenses
Passé Composé
Imparfait
Conditional and Subjunctive
Summary
I hope you enjoyed this article on the verb baguenauder. Still in a learning mood? Check out another TOTALLY random French verb conjugation!


