Passé Simple (Simple Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb blasphémer
Introduction to the verb blasphémer
The English translation of the French verb blasphémer is “to blaspheme”. The pronunciation of the infinitive form “blasphémer” is [blas-feh-mey].
The word blasphémer originated from the Latin word “blasphemare”, which means “to speak evil of, to blaspheme”. It entered the French language during the Middle Ages. In everyday French, blasphémer is used to describe the act of uttering profane or disrespectful language or words against religious beliefs, deities, or sacred things.
In the Passé Simple tense (Simple Past), blasphémer is less commonly used in everyday spoken French and is mostly encountered in written or formal contexts. Here are three simple examples of the usage of blasphémer in the Passé Simple tense with their English translations:
- Il blasphéma contre les dieux. (He blasphemed against the gods.)
- Elle blasphéma de manière offensante lors de la cérémonie. (She blasphemed offensively during the ceremony.)
- Les disciples ne blasphémèrent jamais malgré les épreuves. (The disciples never blasphemed despite the hardships.)
Note: The Passé Simple tense is primarily used in literature, historical accounts, or formal writing in French. In spoken French, the Passé Composé is more commonly used to express the past tense.
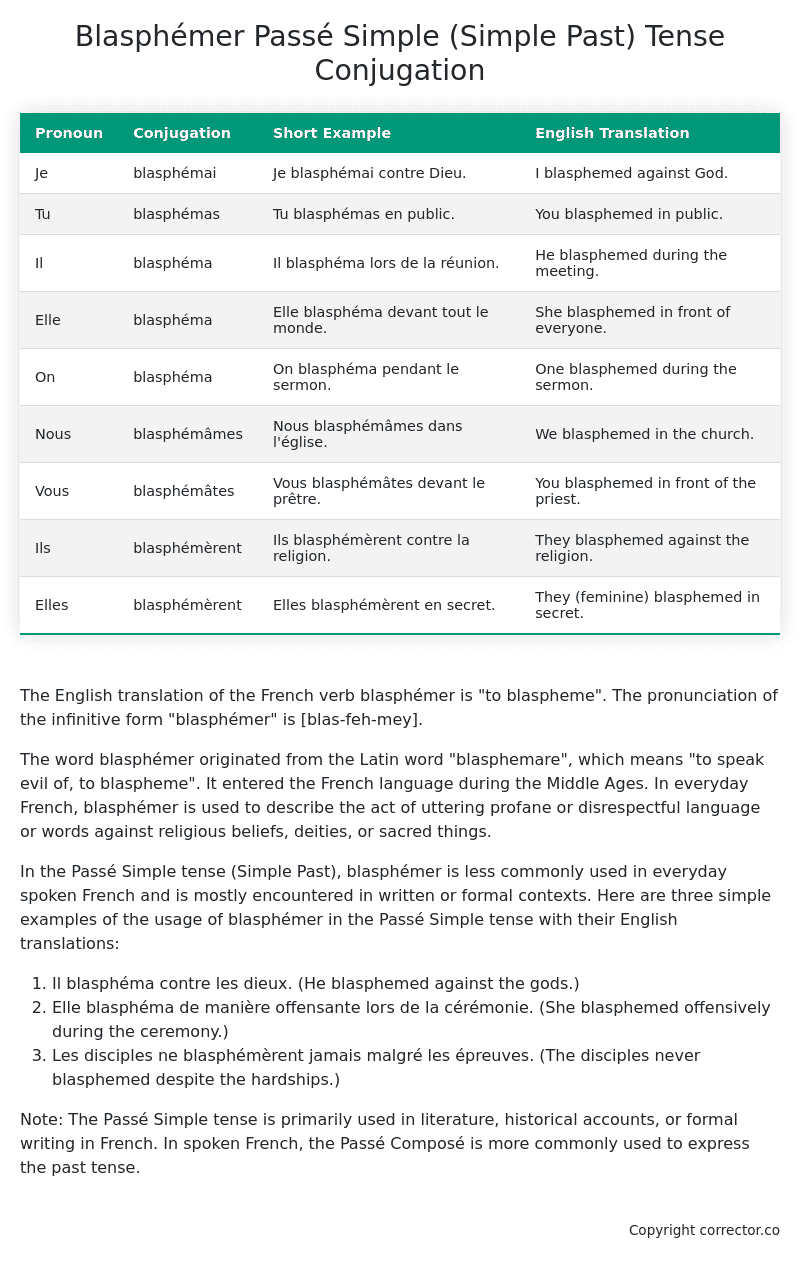
Table of the Passé Simple (Simple Past) Tense Conjugation of blasphémer
| Pronoun | Conjugation | Short Example | English Translation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Je | blasphémai | Je blasphémai contre Dieu. | I blasphemed against God. |
| Tu | blasphémas | Tu blasphémas en public. | You blasphemed in public. |
| Il | blasphéma | Il blasphéma lors de la réunion. | He blasphemed during the meeting. |
| Elle | blasphéma | Elle blasphéma devant tout le monde. | She blasphemed in front of everyone. |
| On | blasphéma | On blasphéma pendant le sermon. | One blasphemed during the sermon. |
| Nous | blasphémâmes | Nous blasphémâmes dans l’église. | We blasphemed in the church. |
| Vous | blasphémâtes | Vous blasphémâtes devant le prêtre. | You blasphemed in front of the priest. |
| Ils | blasphémèrent | Ils blasphémèrent contre la religion. | They blasphemed against the religion. |
| Elles | blasphémèrent | Elles blasphémèrent en secret. | They (feminine) blasphemed in secret. |
Other Conjugations for Blasphémer.
Le Present (Present Tense) Conjugation of the French Verb blasphémer
Imparfait (Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb blasphémer
Passé Simple (Simple Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb blasphémer (You’re reading it right now!)
Passé Composé (Present Perfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb blasphémer
Futur Simple (Simple Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb blasphémer
Futur Proche (Near Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb blasphémer
Plus-que-parfait (Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb blasphémer
Passé Antérieur (Past Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb blasphémer
Futur Antérieur (Future Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb blasphémer
Subjonctif Présent (Subjunctive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb blasphémer
Subjonctif Passé (Subjunctive Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb blasphémer
Subjonctif Imparfait (Subjunctive Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb blasphémer
Subjonctif Plus-que-parfait (Subjunctive Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb blasphémer
Conditionnel Présent (Conditional Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb blasphémer
Conditionnel Passé (Conditional Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb blasphémer
Conditionnel Passé II (Conditional Past II) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb blasphémer
L’impératif Présent (Imperative Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb blasphémer
L’impératif Passé (Imperative Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb blasphémer
L’infinitif Présent (Infinitive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb blasphémer
L’infinitif Passé (Infinitive Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb blasphémer
Le Participe Présent (Present Participle) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb blasphémer
Le Participe Passé (Past Participle) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb blasphémer
Struggling with French verbs or the language in general? Why not use our free French Grammar Checker – no registration required!
Get a FREE Download Study Sheet of this Conjugation 🔥
Simply right click the image below, click “save image” and get your free reference for the blasphémer Passé Simple tense conjugation!
Blasphémer – About the French Passé Simple (Simple Past) Tense
Formation
Usage
Narration
Historical Context
Interactions with other tenses
Passé Composé
Imparfait
Conditional and Subjunctive
Summary
I hope you enjoyed this article on the verb blasphémer. Still in a learning mood? Check out another TOTALLY random French verb conjugation!


