Passé Simple (Simple Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb désembuer
Introduction to the verb désembuer
The English translation of the French verb désembuer is “to defog” or “to demist.” The pronunciation of the infinitive form désembuer is [deɪsɑ̃by].
Désembuer is derived from the combination of the prefix “dés-” (meaning “un-” or “de-“) and the verb “embuer” (meaning “to fog” or “to mist”). It is often used in everyday French to describe the action of removing fog or mist from a surface, such as car windows, mirrors, or eyeglasses.
In the Passé Simple tense (Simple Past), désembuer is less commonly used in everyday French conversation compared to other tenses. However, it can still be found in written literature and formal contexts. Here are three simple examples of its usage in the Passé Simple tense with their English translations:
- Je désembuai mes lunettes pour mieux voir. (I defogged my glasses to see better.)
- Il désembua le miroir avec une serviette. (He demisted the mirror with a towel.)
- Elle désembua les vitres de sa voiture avant de prendre la route. (She defogged the windows of her car before hitting the road.)
Please note that the Passé Simple tense is mostly used in formal writing, literature, and historical contexts in contemporary French. In everyday spoken French or informal writing, the Passé Composé tense is preferred to express past actions.
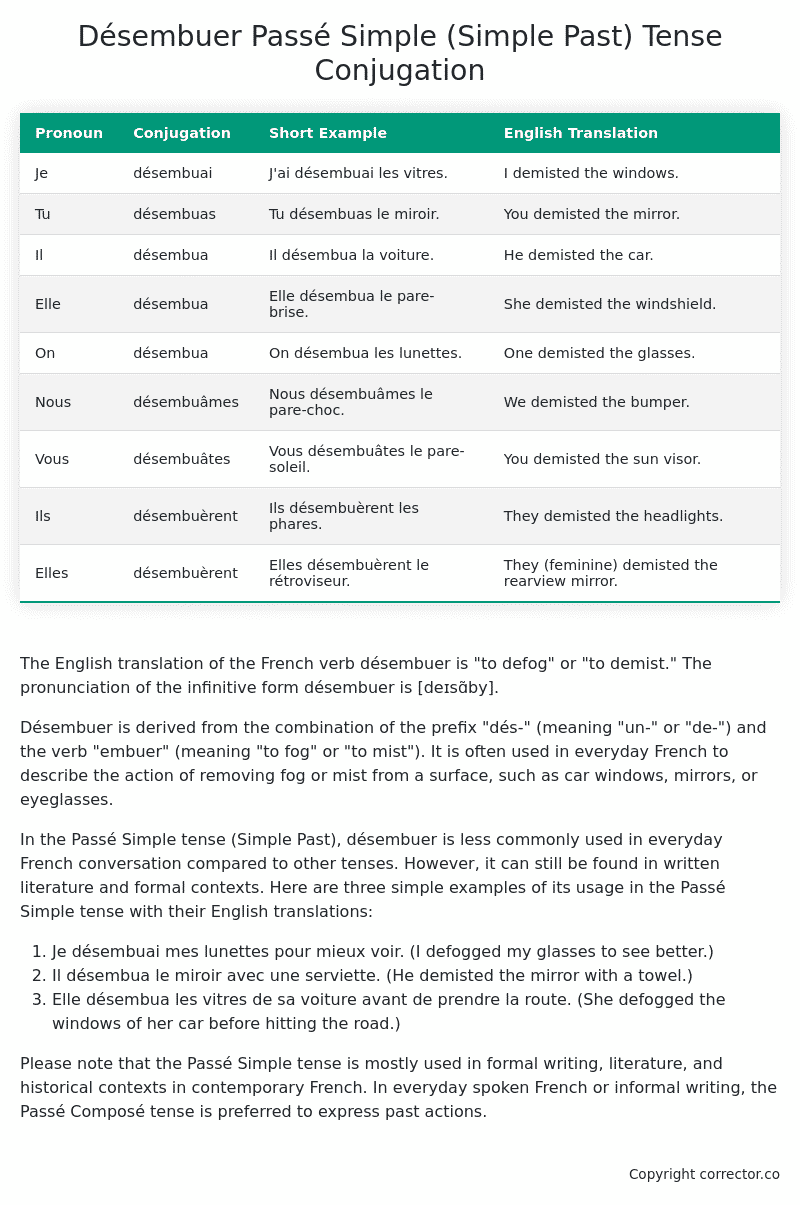
Table of the Passé Simple (Simple Past) Tense Conjugation of désembuer
| Pronoun | Conjugation | Short Example | English Translation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Je | désembuai | J’ai désembuai les vitres. | I demisted the windows. |
| Tu | désembuas | Tu désembuas le miroir. | You demisted the mirror. |
| Il | désembua | Il désembua la voiture. | He demisted the car. |
| Elle | désembua | Elle désembua le pare-brise. | She demisted the windshield. |
| On | désembua | On désembua les lunettes. | One demisted the glasses. |
| Nous | désembuâmes | Nous désembuâmes le pare-choc. | We demisted the bumper. |
| Vous | désembuâtes | Vous désembuâtes le pare-soleil. | You demisted the sun visor. |
| Ils | désembuèrent | Ils désembuèrent les phares. | They demisted the headlights. |
| Elles | désembuèrent | Elles désembuèrent le rétroviseur. | They (feminine) demisted the rearview mirror. |
Other Conjugations for Désembuer.
Le Present (Present Tense) Conjugation of the French Verb désembuer
Imparfait (Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb désembuer
Passé Simple (Simple Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb désembuer (You’re reading it right now!)
Passé Composé (Present Perfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb désembuer
Futur Simple (Simple Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb désembuer
Futur Proche (Near Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb désembuer
Plus-que-parfait (Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb désembuer
Passé Antérieur (Past Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb désembuer
Futur Antérieur (Future Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb désembuer
Subjonctif Présent (Subjunctive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb désembuer
Subjonctif Passé (Subjunctive Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb désembuer
Subjonctif Imparfait (Subjunctive Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb désembuer
Subjonctif Plus-que-parfait (Subjunctive Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb désembuer
Conditionnel Présent (Conditional Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb désembuer
Conditionnel Passé (Conditional Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb désembuer
Conditionnel Passé II (Conditional Past II) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb désembuer
L’impératif Présent (Imperative Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb désembuer
L’impératif Passé (Imperative Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb désembuer
L’infinitif Présent (Infinitive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb désembuer
L’infinitif Passé (Infinitive Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb désembuer
Le Participe Présent (Present Participle) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb désembuer
Le Participe Passé (Past Participle) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb désembuer
Struggling with French verbs or the language in general? Why not use our free French Grammar Checker – no registration required!
Get a FREE Download Study Sheet of this Conjugation 🔥
Simply right click the image below, click “save image” and get your free reference for the désembuer Passé Simple tense conjugation!
Désembuer – About the French Passé Simple (Simple Past) Tense
Formation
Usage
Narration
Historical Context
Interactions with other tenses
Passé Composé
Imparfait
Conditional and Subjunctive
Summary
I hope you enjoyed this article on the verb désembuer. Still in a learning mood? Check out another TOTALLY random French verb conjugation!


