Passé Simple (Simple Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb domicilier
Introduction to the verb domicilier
The English translation of the French verb “domicilier” is “to domicile” or “to register an address.” The infinitive form “domicilier” is pronounced as “doh-mee-see-lee-eh.”
The verb “domicilier” comes from the Latin word “domicilium,” which means “residence” or “dwelling place.” It is used in everyday French to describe the action of officially registering an address or declaring a residence. This verb is commonly used when someone moves to a new place and needs to update their official address with government authorities or organizations.
In the Passé Simple (Simple Past) tense, “domicilier” is conjugated as follows:
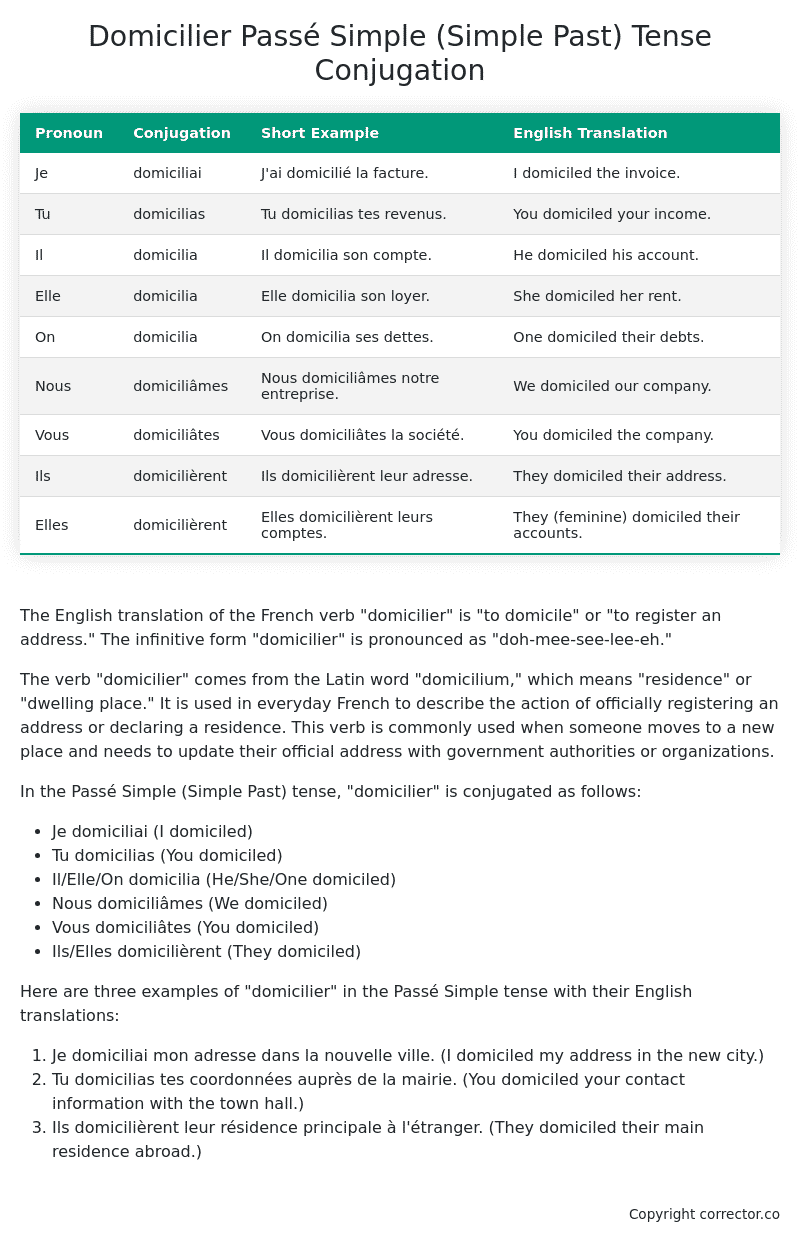
- Je domiciliai (I domiciled)
- Tu domicilias (You domiciled)
- Il/Elle/On domicilia (He/She/One domiciled)
- Nous domiciliâmes (We domiciled)
- Vous domiciliâtes (You domiciled)
- Ils/Elles domicilièrent (They domiciled)
Here are three examples of “domicilier” in the Passé Simple tense with their English translations:
- Je domiciliai mon adresse dans la nouvelle ville. (I domiciled my address in the new city.)
- Tu domicilias tes coordonnées auprès de la mairie. (You domiciled your contact information with the town hall.)
- Ils domicilièrent leur résidence principale à l’étranger. (They domiciled their main residence abroad.)
Table of the Passé Simple (Simple Past) Tense Conjugation of domicilier
| Pronoun | Conjugation | Short Example | English Translation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Je | domiciliai | J’ai domicilié la facture. | I domiciled the invoice. |
| Tu | domicilias | Tu domicilias tes revenus. | You domiciled your income. |
| Il | domicilia | Il domicilia son compte. | He domiciled his account. |
| Elle | domicilia | Elle domicilia son loyer. | She domiciled her rent. |
| On | domicilia | On domicilia ses dettes. | One domiciled their debts. |
| Nous | domiciliâmes | Nous domiciliâmes notre entreprise. | We domiciled our company. |
| Vous | domiciliâtes | Vous domiciliâtes la société. | You domiciled the company. |
| Ils | domicilièrent | Ils domicilièrent leur adresse. | They domiciled their address. |
| Elles | domicilièrent | Elles domicilièrent leurs comptes. | They (feminine) domiciled their accounts. |
Other Conjugations for Domicilier.
Le Present (Present Tense) Conjugation of the French Verb domicilier
Imparfait (Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb domicilier
Passé Simple (Simple Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb domicilier (You’re reading it right now!)
Passé Composé (Present Perfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb domicilier
Futur Simple (Simple Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb domicilier
Futur Proche (Near Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb domicilier
Plus-que-parfait (Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb domicilier
Passé Antérieur (Past Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb domicilier
Futur Antérieur (Future Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb domicilier
Subjonctif Présent (Subjunctive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb domicilier
Subjonctif Passé (Subjunctive Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb domicilier
Subjonctif Imparfait (Subjunctive Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb domicilier
Subjonctif Plus-que-parfait (Subjunctive Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb domicilier
Conditionnel Présent (Conditional Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb domicilier
Conditionnel Passé (Conditional Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb domicilier
Conditionnel Passé II (Conditional Past II) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb domicilier
L’impératif Présent (Imperative Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb domicilier
L’impératif Passé (Imperative Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb domicilier
L’infinitif Présent (Infinitive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb domicilier
L’infinitif Passé (Infinitive Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb domicilier
Le Participe Présent (Present Participle) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb domicilier
Le Participe Passé (Past Participle) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb domicilier
Struggling with French verbs or the language in general? Why not use our free French Grammar Checker – no registration required!
Get a FREE Download Study Sheet of this Conjugation 🔥
Simply right click the image below, click “save image” and get your free reference for the domicilier Passé Simple tense conjugation!
Domicilier – About the French Passé Simple (Simple Past) Tense
Formation
Usage
Narration
Historical Context
Interactions with other tenses
Passé Composé
Imparfait
Conditional and Subjunctive
Summary
I hope you enjoyed this article on the verb domicilier. Still in a learning mood? Check out another TOTALLY random French verb conjugation!


