Passé Simple (Simple Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb fuser
Introduction to the verb fuser
The English translation of the French verb “fuser” is “to fuse” or “to blend.” The infinitive form of “fuser” is pronounced as “fyoo-zay.”
“Fuser” is derived from the Latin word “fuseus,” which means “to melt” or “to blend.” In everyday French, when used in the Passé Simple tense (Simple Past), “fuser” typically describes the action of two or more things melting or blending together.
Here are three simple examples of “fuser” in the Passé Simple tense, along with their English translations:
-
Les saveurs ont fusé dans ma bouche.
(The flavors fused in my mouth.) -
Les couleurs se sont fondues dans un magnifique coucher de soleil.
(The colors fused into a beautiful sunset.) -
Les cultures différentes ont fusionné pour créer un nouveau style musical.
(Different cultures fused to create a new musical style.)
In these examples, “fuser” describes the process of elements mixing, blending, or merging together in various contexts.
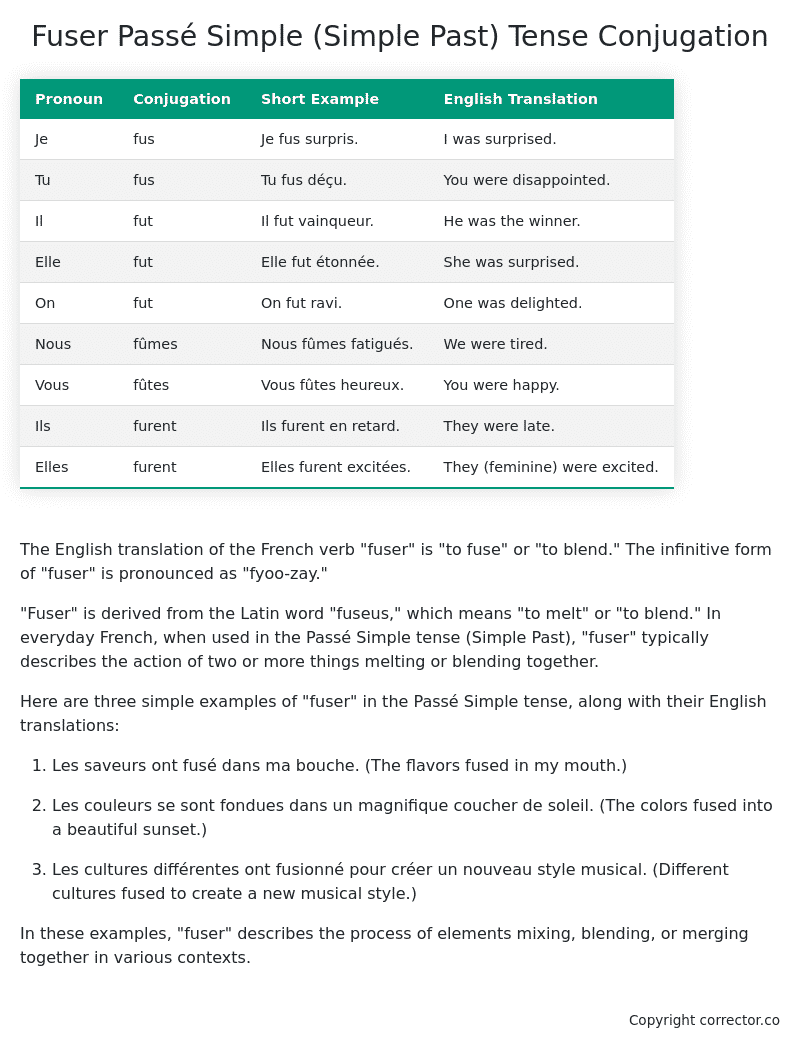
Table of the Passé Simple (Simple Past) Tense Conjugation of fuser
| Pronoun | Conjugation | Short Example | English Translation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Je | fus | Je fus surpris. | I was surprised. |
| Tu | fus | Tu fus déçu. | You were disappointed. |
| Il | fut | Il fut vainqueur. | He was the winner. |
| Elle | fut | Elle fut étonnée. | She was surprised. |
| On | fut | On fut ravi. | One was delighted. |
| Nous | fûmes | Nous fûmes fatigués. | We were tired. |
| Vous | fûtes | Vous fûtes heureux. | You were happy. |
| Ils | furent | Ils furent en retard. | They were late. |
| Elles | furent | Elles furent excitées. | They (feminine) were excited. |
Other Conjugations for Fuser.
Le Present (Present Tense) Conjugation of the French Verb fuser
Imparfait (Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb fuser
Passé Simple (Simple Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb fuser (You’re reading it right now!)
Passé Composé (Present Perfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb fuser
Futur Simple (Simple Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb fuser
Futur Proche (Near Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb fuser
Plus-que-parfait (Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb fuser
Passé Antérieur (Past Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb fuser
Futur Antérieur (Future Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb fuser
Subjonctif Présent (Subjunctive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb fuser
Subjonctif Passé (Subjunctive Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb fuser
Subjonctif Imparfait (Subjunctive Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb fuser
Subjonctif Plus-que-parfait (Subjunctive Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb fuser
Conditionnel Présent (Conditional Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb fuser
Conditionnel Passé (Conditional Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb fuser
Conditionnel Passé II (Conditional Past II) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb fuser
L’impératif Présent (Imperative Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb fuser
L’impératif Passé (Imperative Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb fuser
L’infinitif Présent (Infinitive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb fuser
L’infinitif Passé (Infinitive Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb fuser
Le Participe Présent (Present Participle) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb fuser
Le Participe Passé (Past Participle) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb fuser
Struggling with French verbs or the language in general? Why not use our free French Grammar Checker – no registration required!
Get a FREE Download Study Sheet of this Conjugation 🔥
Simply right click the image below, click “save image” and get your free reference for the fuser Passé Simple tense conjugation!
Fuser – About the French Passé Simple (Simple Past) Tense
Formation
Usage
Narration
Historical Context
Interactions with other tenses
Passé Composé
Imparfait
Conditional and Subjunctive
Summary
I hope you enjoyed this article on the verb fuser. Still in a learning mood? Check out another TOTALLY random French verb conjugation!


