Plus-que-parfait (Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb accaparer
Introduction to the verb accaparer
The English translation of the French verb accaparer is “to monopolize.” The infinitive form of accaparer is pronounced “ah-kah-pah-reh.”
The word accaparer comes from the Old French word “capere,” meaning “to take.” It entered the French language in the 16th century and has its roots in the Latin word “capere,” with the same meaning. In everyday French, accaparer is most often used in the Plus-que-parfait tense, which is the past perfect tense.
Here are three examples of accaparer in the Plus-que-parfait tense:
- J’avais accaparé toute l’attention de la classe avec ma présentation. (I had monopolized all the attention of the class with my presentation.)
- Ils avaient accaparé toutes les ressources pour leur projet, laissant les autres équipes sans rien. (They had monopolized all the resources for their project, leaving the other teams with nothing.)
- Tu avais accaparé le micro toute la soirée, je n’ai pas eu l’occasion de parler. (You had monopolized the microphone all evening, I didn’t have a chance to speak.)
Overall, accaparer is used to describe the action of taking or monopolizing something, often to the detriment of others. In the Plus-que-parfait tense, it indicates that this action occurred in the past, before another action or event.
Table of the Plus-que-parfait (Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of accaparer
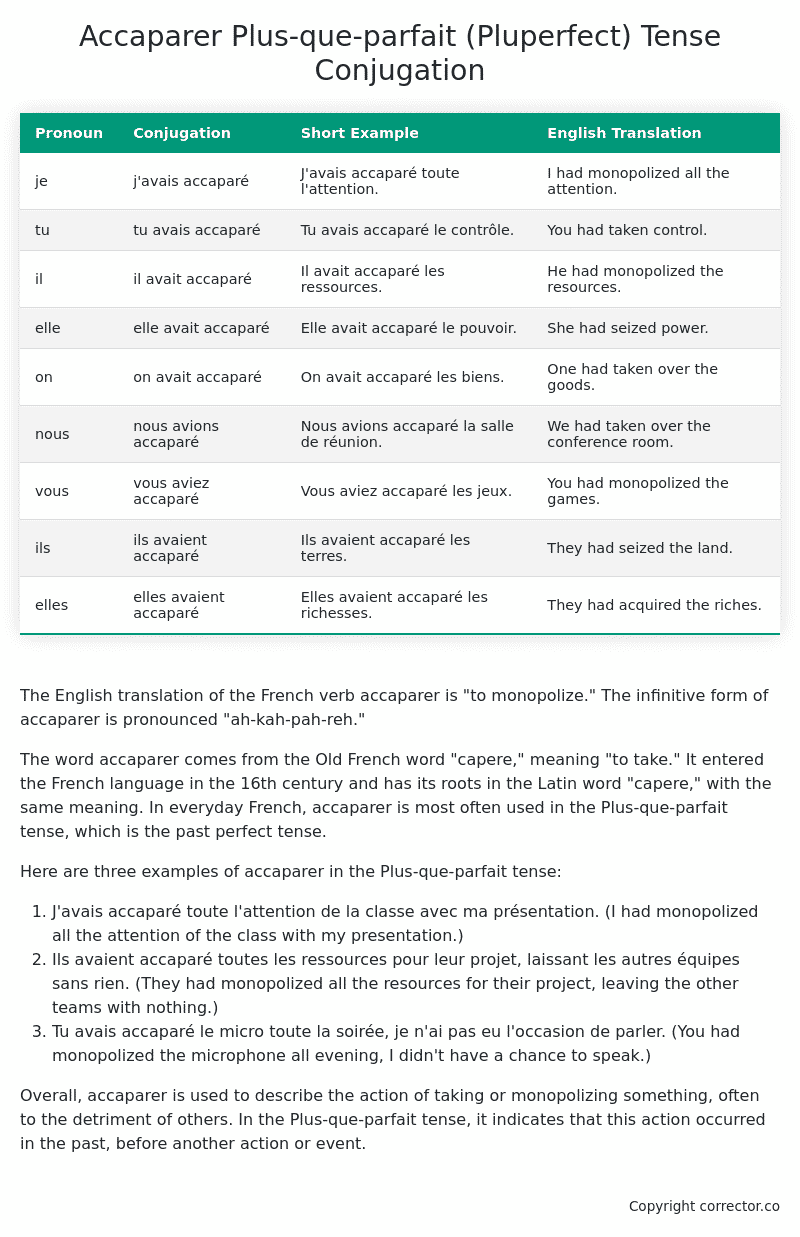
| Pronoun | Conjugation | Short Example | English Translation |
|---|---|---|---|
| je | j’avais accaparé | J’avais accaparé toute l’attention. | I had monopolized all the attention. |
| tu | tu avais accaparé | Tu avais accaparé le contrôle. | You had taken control. |
| il | il avait accaparé | Il avait accaparé les ressources. | He had monopolized the resources. |
| elle | elle avait accaparé | Elle avait accaparé le pouvoir. | She had seized power. |
| on | on avait accaparé | On avait accaparé les biens. | One had taken over the goods. |
| nous | nous avions accaparé | Nous avions accaparé la salle de réunion. | We had taken over the conference room. |
| vous | vous aviez accaparé | Vous aviez accaparé les jeux. | You had monopolized the games. |
| ils | ils avaient accaparé | Ils avaient accaparé les terres. | They had seized the land. |
| elles | elles avaient accaparé | Elles avaient accaparé les richesses. | They had acquired the riches. |
Other Conjugations for Accaparer.
Le Present (Present Tense) Conjugation of the French Verb accaparer
Imparfait (Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb accaparer
Passé Simple (Simple Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb accaparer
Passé Composé (Present Perfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb accaparer
Futur Simple (Simple Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb accaparer
Futur Proche (Near Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb accaparer
Plus-que-parfait (Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb accaparer (this article)
Passé Antérieur (Past Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb accaparer
Futur Antérieur (Future Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb accaparer
Subjonctif Présent (Subjunctive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb accaparer
Subjonctif Passé (Subjunctive Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb accaparer
Subjonctif Imparfait (Subjunctive Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb accaparer
Subjonctif Plus-que-parfait (Subjunctive Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb accaparer
Conditionnel Présent (Conditional Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb accaparer
Conditionnel Passé (Conditional Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb accaparer
L’impératif Présent (Imperative Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb accaparer
L’infinitif Présent (Infinitive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb accaparer
Struggling with French verbs or the language in general? Why not use our free French Grammar Checker – no registration required!
Get a FREE Download Study Sheet of this Conjugation 🔥
Simply right click the image below, click “save image” and get your free reference for the accaparer Plus-que-parfait tense conjugation!
Accaparer – About the French Plus-que-parfait (Pluperfect) Tense
Tense Formation
Common everyday usage patterns
Sequencing of past events
Background information
Hypothetical or reported speech
Interactions with other tenses
Summary
I hope you enjoyed this article on the verb accaparer. Still in a learning mood? Check out another TOTALLY random French verb conjugation!


