Plus-que-parfait (Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb appeler
Introduction to the verb appeler
The English translation of the French verb appeler is “to call” or “to name.” It is pronounced “ah-peh-leh” in its infinitive form.
Appeler comes from the Latin word “appellare,” meaning “to accost” or “to address.” It entered the French language in the 12th century and has been used in everyday French since then.
In the Plus-que-parfait tense, appeler is used to express an action that had already been completed before another action in the past. It is formed by using the auxiliary verb avoir in the imperfect tense and adding the past participle “appelé.”
Example 1: J’avais appelé mon ami avant de partir. (I had called my friend before leaving.)
Example 2: Elle avait appelé son frère pour lui demander de l’aide. (She had called her brother to ask for his help.)
Example 3: Nous avions appelé la police dès que nous avons entendu du bruit. (We had called the police as soon as we heard some noise.)
In these examples, the action of calling had already been completed before another action in the past (leaving, asking for help, hearing a noise). The Plus-que-parfait tense is often used to add more detail or to show a sequence of events in the past.
Table of the Plus-que-parfait (Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of appeler
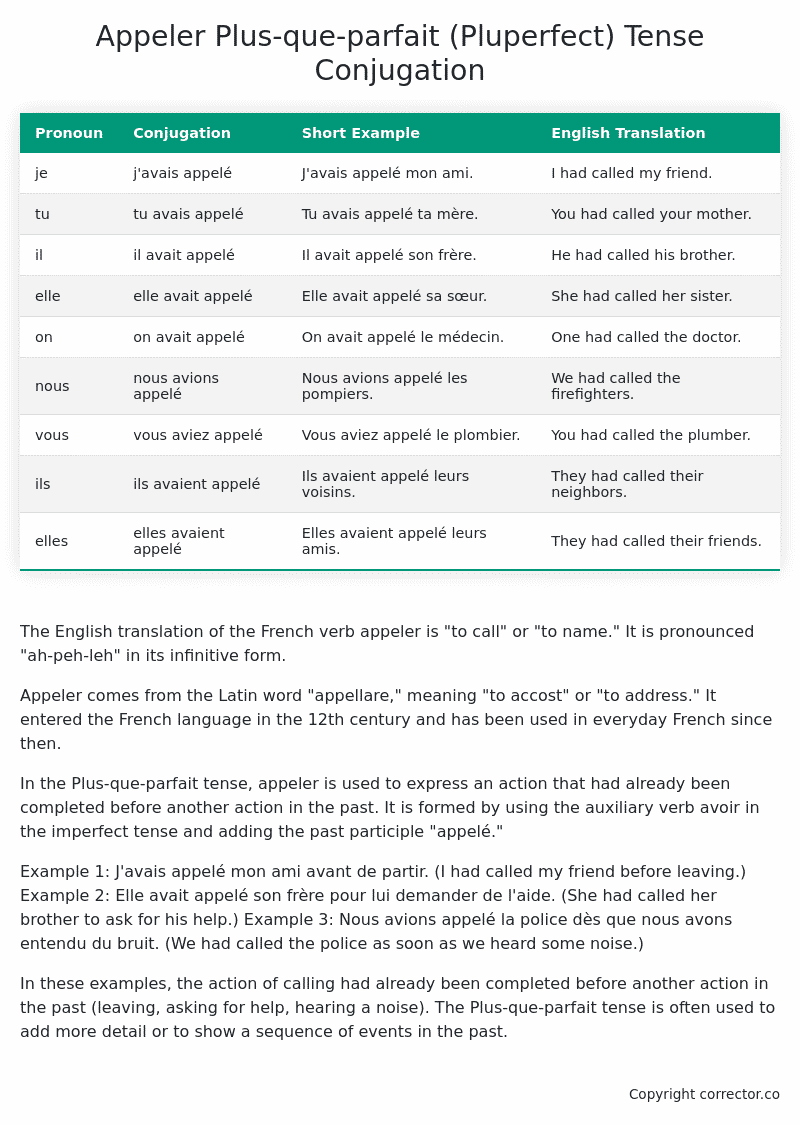
| Pronoun | Conjugation | Short Example | English Translation |
|---|---|---|---|
| je | j’avais appelé | J’avais appelé mon ami. | I had called my friend. |
| tu | tu avais appelé | Tu avais appelé ta mère. | You had called your mother. |
| il | il avait appelé | Il avait appelé son frère. | He had called his brother. |
| elle | elle avait appelé | Elle avait appelé sa sœur. | She had called her sister. |
| on | on avait appelé | On avait appelé le médecin. | One had called the doctor. |
| nous | nous avions appelé | Nous avions appelé les pompiers. | We had called the firefighters. |
| vous | vous aviez appelé | Vous aviez appelé le plombier. | You had called the plumber. |
| ils | ils avaient appelé | Ils avaient appelé leurs voisins. | They had called their neighbors. |
| elles | elles avaient appelé | Elles avaient appelé leurs amis. | They had called their friends. |
Other Conjugations for Appeler.
Le Present (Present Tense) Conjugation of the French Verb appeler
Imparfait (Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb appeler
Passé Simple (Simple Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb appeler
Passé Composé (Present Perfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb appeler
Futur Simple (Simple Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb appeler
Futur Proche (Near Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb appeler
Plus-que-parfait (Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb appeler (this article)
Passé Antérieur (Past Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb appeler
Futur Antérieur (Future Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb appeler
Subjonctif Présent (Subjunctive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb appeler
Subjonctif Passé (Subjunctive Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb appeler
Subjonctif Imparfait (Subjunctive Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb appeler
Subjonctif Plus-que-parfait (Subjunctive Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb appeler
Conditionnel Présent (Conditional Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb appeler
Conditionnel Passé (Conditional Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb appeler
L’impératif Présent (Imperative Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb appeler
L’infinitif Présent (Infinitive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb appeler
Struggling with French verbs or the language in general? Why not use our free French Grammar Checker – no registration required!
Get a FREE Download Study Sheet of this Conjugation 🔥
Simply right click the image below, click “save image” and get your free reference for the appeler Plus-que-parfait tense conjugation!
Appeler – About the French Plus-que-parfait (Pluperfect) Tense
Tense Formation
Common everyday usage patterns
Sequencing of past events
Background information
Hypothetical or reported speech
Interactions with other tenses
Summary
I hope you enjoyed this article on the verb appeler. Still in a learning mood? Check out another TOTALLY random French verb conjugation!


