Plus-que-parfait (Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb bouleverser
Introduction to the verb bouleverser
The English translation of the French verb bouleverser is “to overturn” or “to upset.” The infinitive form, bouleverser, is pronounced as “boo-luh-vair-seh.”
The word bouleverser is derived from the combination of two French words: “boule” meaning “ball” and “verser” meaning “to pour.” It originated in the 16th century and has evolved to mean “to turn upside down” or “to cause disorder or confusion.”
In everyday French, bouleverser is commonly used in the Plus-que-parfait tense, which is the past perfect tense in English. This tense is used to talk about an action that was completed before another action in the past. Here are three examples of its usage in this tense:
- J’avais bouleversé la pièce avant que mes parents reviennent. (I had overturned the room before my parents came back.)
- Elle était bouleversée quand elle a découvert la vérité. (She was upset when she discovered the truth.)
- Nous avions été bouleversés par la nouvelle du décès de notre grand-mère. (We had been devastated by the news of our grandmother’s death.)
In these examples, bouleverser is used to express a sudden and intense change or disruption. It is often used to describe emotional or physical upheaval. In the Plus-que-parfait tense, it emphasizes that the action was completed before another event in the past.
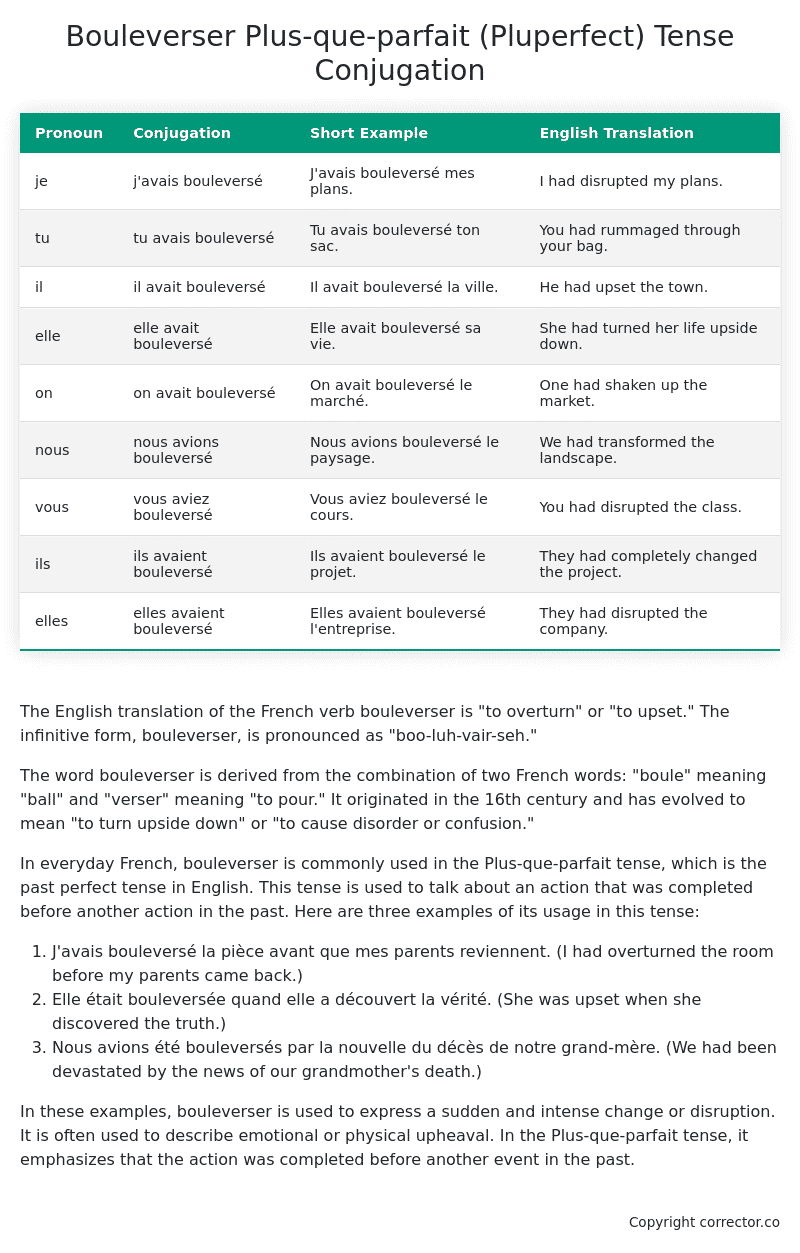
Table of the Plus-que-parfait (Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of bouleverser
| Pronoun | Conjugation | Short Example | English Translation |
|---|---|---|---|
| je | j’avais bouleversé | J’avais bouleversé mes plans. | I had disrupted my plans. |
| tu | tu avais bouleversé | Tu avais bouleversé ton sac. | You had rummaged through your bag. |
| il | il avait bouleversé | Il avait bouleversé la ville. | He had upset the town. |
| elle | elle avait bouleversé | Elle avait bouleversé sa vie. | She had turned her life upside down. |
| on | on avait bouleversé | On avait bouleversé le marché. | One had shaken up the market. |
| nous | nous avions bouleversé | Nous avions bouleversé le paysage. | We had transformed the landscape. |
| vous | vous aviez bouleversé | Vous aviez bouleversé le cours. | You had disrupted the class. |
| ils | ils avaient bouleversé | Ils avaient bouleversé le projet. | They had completely changed the project. |
| elles | elles avaient bouleversé | Elles avaient bouleversé l’entreprise. | They had disrupted the company. |
Other Conjugations for Bouleverser.
Le Present (Present Tense) Conjugation of the French Verb bouleverser
Imparfait (Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb bouleverser
Passé Simple (Simple Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb bouleverser
Passé Composé (Present Perfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb bouleverser
Futur Simple (Simple Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb bouleverser
Futur Proche (Near Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb bouleverser
Plus-que-parfait (Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb bouleverser (this article)
Passé Antérieur (Past Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb bouleverser
Futur Antérieur (Future Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb bouleverser
Subjonctif Présent (Subjunctive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb bouleverser
Subjonctif Passé (Subjunctive Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb bouleverser
Subjonctif Imparfait (Subjunctive Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb bouleverser
Conditionnel Présent (Conditional Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb bouleverser
Conditionnel Passé (Conditional Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb bouleverser
L’impératif Présent (Imperative Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb bouleverser
L’infinitif Présent (Infinitive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb bouleverser
Struggling with French verbs or the language in general? Why not use our free French Grammar Checker – no registration required!
Get a FREE Download Study Sheet of this Conjugation 🔥
Simply right click the image below, click “save image” and get your free reference for the bouleverser Plus-que-parfait tense conjugation!
Bouleverser – About the French Plus-que-parfait (Pluperfect) Tense
Tense Formation
Common everyday usage patterns
Sequencing of past events
Background information
Hypothetical or reported speech
Interactions with other tenses
Summary
I hope you enjoyed this article on the verb bouleverser. Still in a learning mood? Check out another TOTALLY random French verb conjugation!


