Plus-que-parfait (Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb digitaliser
Introduction to the verb digitaliser
The English translation of the French verb digitaliser is “to digitize.” It is pronounced dee-je-tah-lee-zay in its infinitive form.
The word digitaliser is derived from the Latin word “digitus,” meaning “finger,” and the suffix “-iser,” which indicates the act of making something. In French, it is most often used in a technological context, referring to the process of converting information into a digital format.
In everyday French, the verb digitaliser is commonly used in the plus-que-parfait tense, which is the past perfect tense in English. This tense is used to talk about an action that was completed before another past action or point in time. Here are three simple examples of its usage in this tense:
-
J’avais déjà digitalisé toutes mes photos avant de les partager sur les réseaux sociaux. (I had already digitized all my photos before sharing them on social media.)
-
L’entreprise avait digitalisé ses archives pour faciliter la recherche d’informations. (The company had digitized its archives to facilitate information retrieval.)
-
Nous avions digitalisé tous nos documents administratifs afin de les stocker de manière sécurisée. (We had digitized all our administrative documents in order to store them securely.)
In these examples, we can see that the verb digitaliser is used to describe a completed action in the past, before another action or event took place. It is often used in a business or technological context, as shown in the examples above.
Table of the Plus-que-parfait (Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of digitaliser
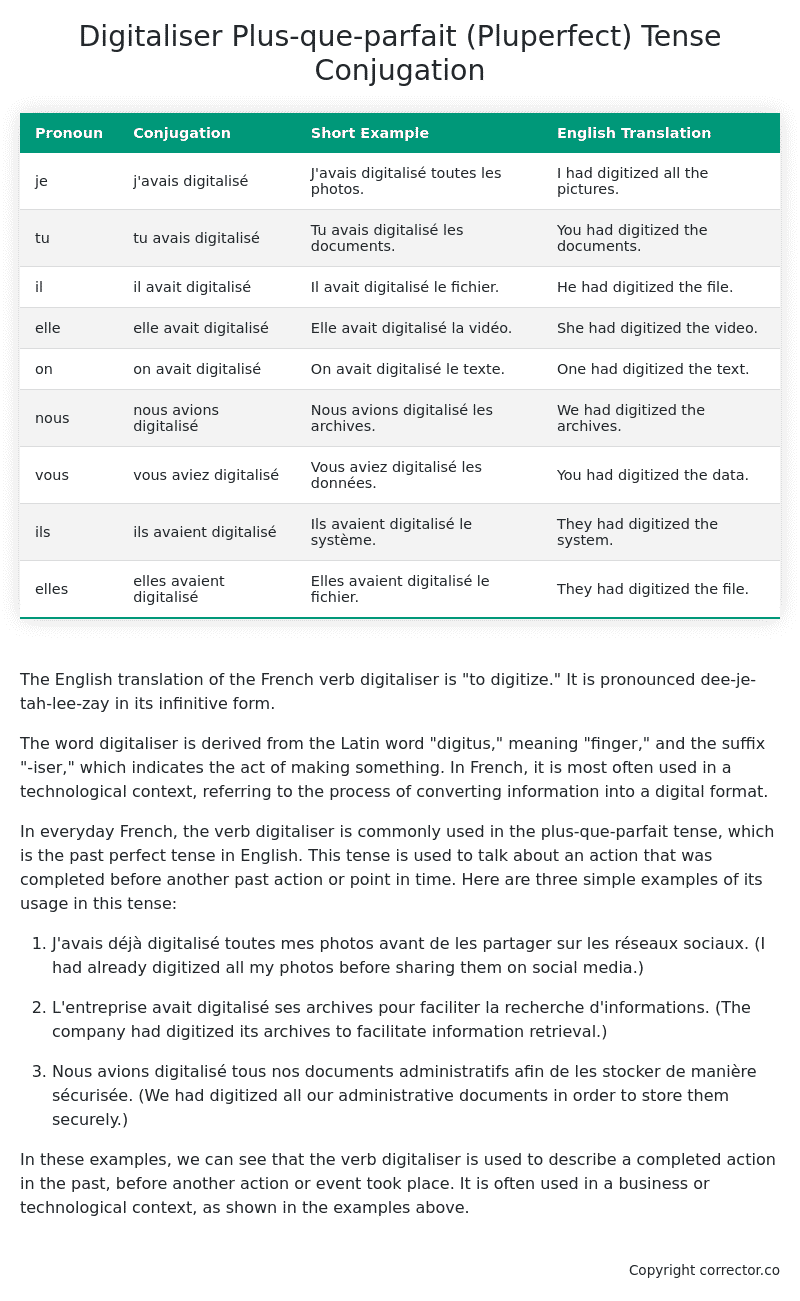
| Pronoun | Conjugation | Short Example | English Translation |
|---|---|---|---|
| je | j’avais digitalisé | J’avais digitalisé toutes les photos. | I had digitized all the pictures. |
| tu | tu avais digitalisé | Tu avais digitalisé les documents. | You had digitized the documents. |
| il | il avait digitalisé | Il avait digitalisé le fichier. | He had digitized the file. |
| elle | elle avait digitalisé | Elle avait digitalisé la vidéo. | She had digitized the video. |
| on | on avait digitalisé | On avait digitalisé le texte. | One had digitized the text. |
| nous | nous avions digitalisé | Nous avions digitalisé les archives. | We had digitized the archives. |
| vous | vous aviez digitalisé | Vous aviez digitalisé les données. | You had digitized the data. |
| ils | ils avaient digitalisé | Ils avaient digitalisé le système. | They had digitized the system. |
| elles | elles avaient digitalisé | Elles avaient digitalisé le fichier. | They had digitized the file. |
Other Conjugations for Digitaliser.
Le Present (Present Tense) Conjugation of the French Verb digitaliser
Imparfait (Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb digitaliser
Passé Simple (Simple Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb digitaliser
Passé Composé (Present Perfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb digitaliser
Futur Simple (Simple Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb digitaliser
Futur Proche (Near Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb digitaliser
Plus-que-parfait (Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb digitaliser (this article)
Passé Antérieur (Past Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb digitaliser
Futur Antérieur (Future Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb digitaliser
Subjonctif Présent (Subjunctive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb digitaliser
Subjonctif Passé (Subjunctive Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb digitaliser
Subjonctif Imparfait (Subjunctive Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb digitaliser
Conditionnel Présent (Conditional Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb digitaliser
Conditionnel Passé (Conditional Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb digitaliser
L’impératif Présent (Imperative Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb digitaliser
L’infinitif Présent (Infinitive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb digitaliser
Struggling with French verbs or the language in general? Why not use our free French Grammar Checker – no registration required!
Get a FREE Download Study Sheet of this Conjugation 🔥
Simply right click the image below, click “save image” and get your free reference for the digitaliser Plus-que-parfait tense conjugation!
Digitaliser – About the French Plus-que-parfait (Pluperfect) Tense
Tense Formation
Common everyday usage patterns
Sequencing of past events
Background information
Hypothetical or reported speech
Interactions with other tenses
Summary
I hope you enjoyed this article on the verb digitaliser. Still in a learning mood? Check out another TOTALLY random French verb conjugation!


