Plus-que-parfait (Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb flâner
Introduction to the verb flâner
The English translation of the French verb flâner is “to stroll” or “to wander”. It is pronounced as “flah-nay”.
The word flâner comes from the French noun flâneur, which means “stroller” or “wanderer”. It originated in the 19th century and was popularized by French poet Charles Baudelaire. In everyday French, flâner is often used to describe the act of leisurely walking or strolling without a specific destination.
In the Plus-que-parfait tense, which is the past perfect tense in English, flâner is used to describe an action that had already been completed in the past. Here are three examples of its usage in this tense with the respective English translations:
- J’avais flâné dans les rues de Paris toute la journée avant de rentrer à l’hôtel. (I had strolled through the streets of Paris all day before returning to the hotel.)
- Ils avaient flâné dans le parc avant de se rendre au musée. (They had wandered around the park before going to the museum.)
- Tu avais flâné dans les magasins, mais tu n’as rien acheté. (You had strolled through the shops, but you didn’t buy anything.)
Table of the Plus-que-parfait (Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of flâner
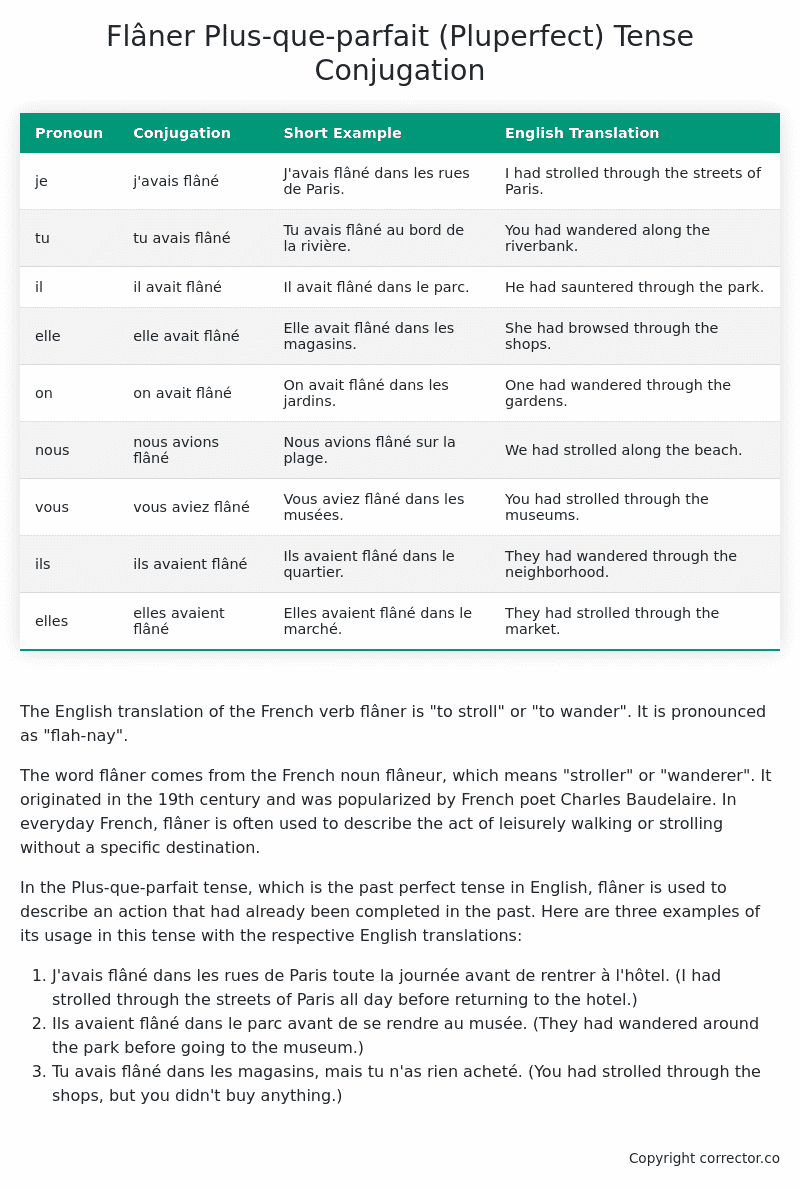
| Pronoun | Conjugation | Short Example | English Translation |
|---|---|---|---|
| je | j’avais flâné | J’avais flâné dans les rues de Paris. | I had strolled through the streets of Paris. |
| tu | tu avais flâné | Tu avais flâné au bord de la rivière. | You had wandered along the riverbank. |
| il | il avait flâné | Il avait flâné dans le parc. | He had sauntered through the park. |
| elle | elle avait flâné | Elle avait flâné dans les magasins. | She had browsed through the shops. |
| on | on avait flâné | On avait flâné dans les jardins. | One had wandered through the gardens. |
| nous | nous avions flâné | Nous avions flâné sur la plage. | We had strolled along the beach. |
| vous | vous aviez flâné | Vous aviez flâné dans les musées. | You had strolled through the museums. |
| ils | ils avaient flâné | Ils avaient flâné dans le quartier. | They had wandered through the neighborhood. |
| elles | elles avaient flâné | Elles avaient flâné dans le marché. | They had strolled through the market. |
Other Conjugations for Flâner.
Le Present (Present Tense) Conjugation of the French Verb flâner
Imparfait (Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb flâner
Passé Simple (Simple Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb flâner
Passé Composé (Present Perfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb flâner
Futur Simple (Simple Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb flâner
Futur Proche (Near Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb flâner
Plus-que-parfait (Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb flâner (this article)
Passé Antérieur (Past Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb flâner
Futur Antérieur (Future Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb flâner
Subjonctif Présent (Subjunctive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb flâner
Subjonctif Passé (Subjunctive Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb flâner
Subjonctif Imparfait (Subjunctive Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb flâner
Subjonctif Plus-que-parfait (Subjunctive Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb flâner
Conditionnel Présent (Conditional Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb flâner
Conditionnel Passé (Conditional Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb flâner
L’impératif Présent (Imperative Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb flâner
L’infinitif Présent (Infinitive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb flâner
Struggling with French verbs or the language in general? Why not use our free French Grammar Checker – no registration required!
Get a FREE Download Study Sheet of this Conjugation 🔥
Simply right click the image below, click “save image” and get your free reference for the flâner Plus-que-parfait tense conjugation!
Flâner – About the French Plus-que-parfait (Pluperfect) Tense
Tense Formation
Common everyday usage patterns
Sequencing of past events
Background information
Hypothetical or reported speech
Interactions with other tenses
Summary
I hope you enjoyed this article on the verb flâner. Still in a learning mood? Check out another TOTALLY random French verb conjugation!


