Plus-que-parfait (Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb harpailler
Introduction to the verb harpailler
The English translation of the French verb harpailler is “to squabble” or “to bicker”. It is pronounced as “ahr-pay-yay”.
The language origin of harpailler can be traced back to the Old French word “harpie”, which meant “to quarrel” or “to bicker”. Over time, this verb evolved into “harpailler” in modern French.
In every day French, harpailler is most often used in the Plus-que-parfait tense, which is the past perfect tense. This tense is used to describe an action that was completed before another past action.
Examples:
- Nous avions beaucoup harpaillé avant de finalement trouver un compromis. (We had squabbled a lot before finally reaching a compromise.)
- Ils avaient toujours harpaillé sur des sujets politiques, mais cette fois-ci, ils ont réussi à trouver un terrain d’entente. (They had always bickered about political issues, but this time, they managed to find common ground.)
- J’avais entendu mes voisins harpailler toute la nuit, c’était insupportable. (I had heard my neighbors squabbling all night, it was unbearable.)
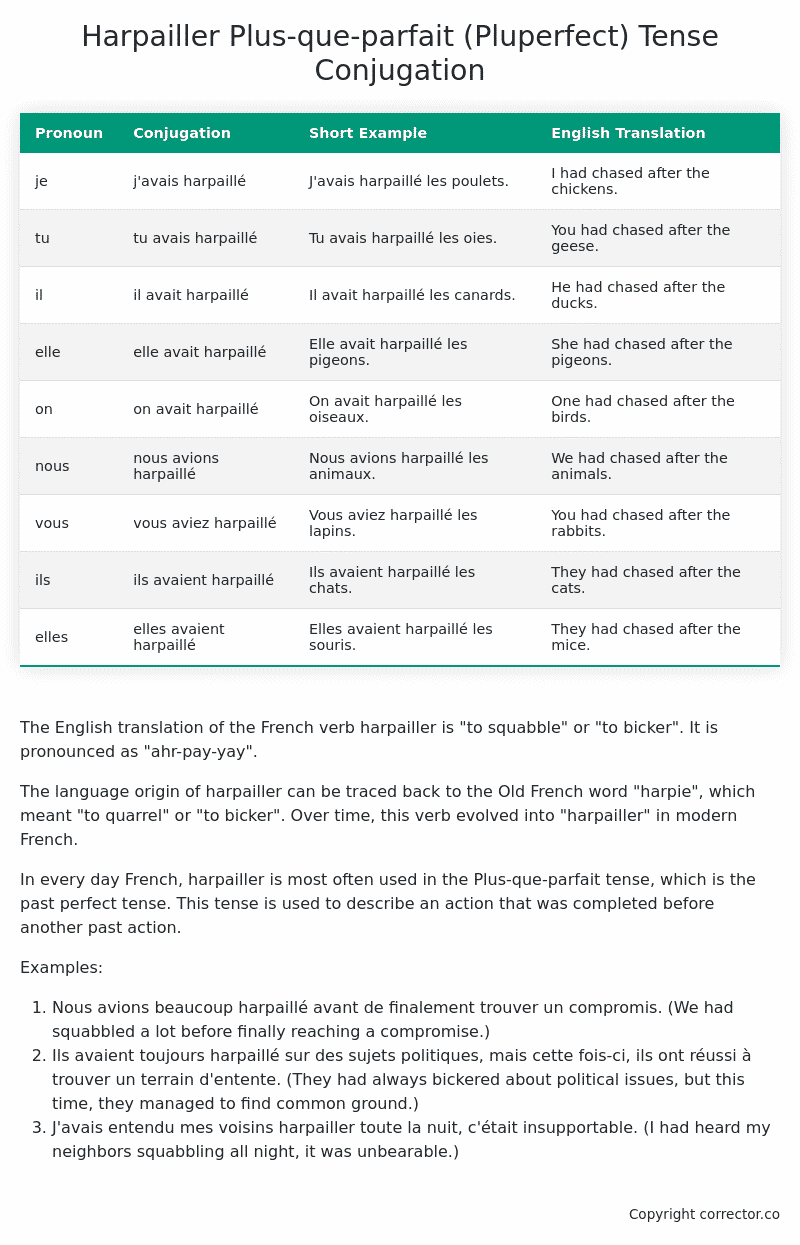
Table of the Plus-que-parfait (Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of harpailler
| Pronoun | Conjugation | Short Example | English Translation |
|---|---|---|---|
| je | j’avais harpaillé | J’avais harpaillé les poulets. | I had chased after the chickens. |
| tu | tu avais harpaillé | Tu avais harpaillé les oies. | You had chased after the geese. |
| il | il avait harpaillé | Il avait harpaillé les canards. | He had chased after the ducks. |
| elle | elle avait harpaillé | Elle avait harpaillé les pigeons. | She had chased after the pigeons. |
| on | on avait harpaillé | On avait harpaillé les oiseaux. | One had chased after the birds. |
| nous | nous avions harpaillé | Nous avions harpaillé les animaux. | We had chased after the animals. |
| vous | vous aviez harpaillé | Vous aviez harpaillé les lapins. | You had chased after the rabbits. |
| ils | ils avaient harpaillé | Ils avaient harpaillé les chats. | They had chased after the cats. |
| elles | elles avaient harpaillé | Elles avaient harpaillé les souris. | They had chased after the mice. |
Other Conjugations for Harpailler.
Le Present (Present Tense) Conjugation of the French Verb harpailler
Imparfait (Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb harpailler
Passé Simple (Simple Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb harpailler
Passé Composé (Present Perfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb harpailler
Futur Simple (Simple Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb harpailler
Futur Proche (Near Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb harpailler
Plus-que-parfait (Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb harpailler (this article)
Passé Antérieur (Past Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb harpailler
Futur Antérieur (Future Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb harpailler
Subjonctif Présent (Subjunctive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb harpailler
Subjonctif Passé (Subjunctive Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb harpailler
Subjonctif Imparfait (Subjunctive Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb harpailler
Subjonctif Plus-que-parfait (Subjunctive Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb harpailler
Conditionnel Présent (Conditional Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb harpailler
Conditionnel Passé (Conditional Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb harpailler
L’impératif Présent (Imperative Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb harpailler
L’infinitif Présent (Infinitive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb harpailler
Struggling with French verbs or the language in general? Why not use our free French Grammar Checker – no registration required!
Get a FREE Download Study Sheet of this Conjugation 🔥
Simply right click the image below, click “save image” and get your free reference for the harpailler Plus-que-parfait tense conjugation!
Harpailler – About the French Plus-que-parfait (Pluperfect) Tense
Tense Formation
Common everyday usage patterns
Sequencing of past events
Background information
Hypothetical or reported speech
Interactions with other tenses
Summary
I hope you enjoyed this article on the verb harpailler. Still in a learning mood? Check out another TOTALLY random French verb conjugation!


