Plus-que-parfait (Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb mégoter
Introduction to the verb mégoter
The English translation of the French verb mégoter is “to haggle” or “to quibble.” It is pronounced “may-go-tay” in the infinitive form.
The word mégoter comes from the Old French verb magoter, which meant “to babble” or “to prattle.” Over time, its meaning evolved to refer to someone who is overly concerned with small details, especially when it comes to money and negotiations.
In everyday French, mégoter is most often used in the Plus-que-parfait tense, which indicates an action that happened before another action in the past. It is used to talk about past events that were already completed at a specific point in the past.
Here are three examples of how mégoter is used in the Plus-que-parfait tense:
-
J’avais déjà acheté la voiture, mais le vendeur a mégoté sur le prix. (I had already bought the car, but the salesman had haggled on the price.)
-
Nous avions signé le contrat, mais l’autre partie a mégoté sur certains détails. (We had signed the contract, but the other party had quibbled over certain details.)
-
Vous aviez promis de ne pas mégoter sur les dépenses, mais vous avez quand même essayé de négocier un meilleur prix. (You had promised not to haggle over expenses, but you still tried to negotiate a better price.)
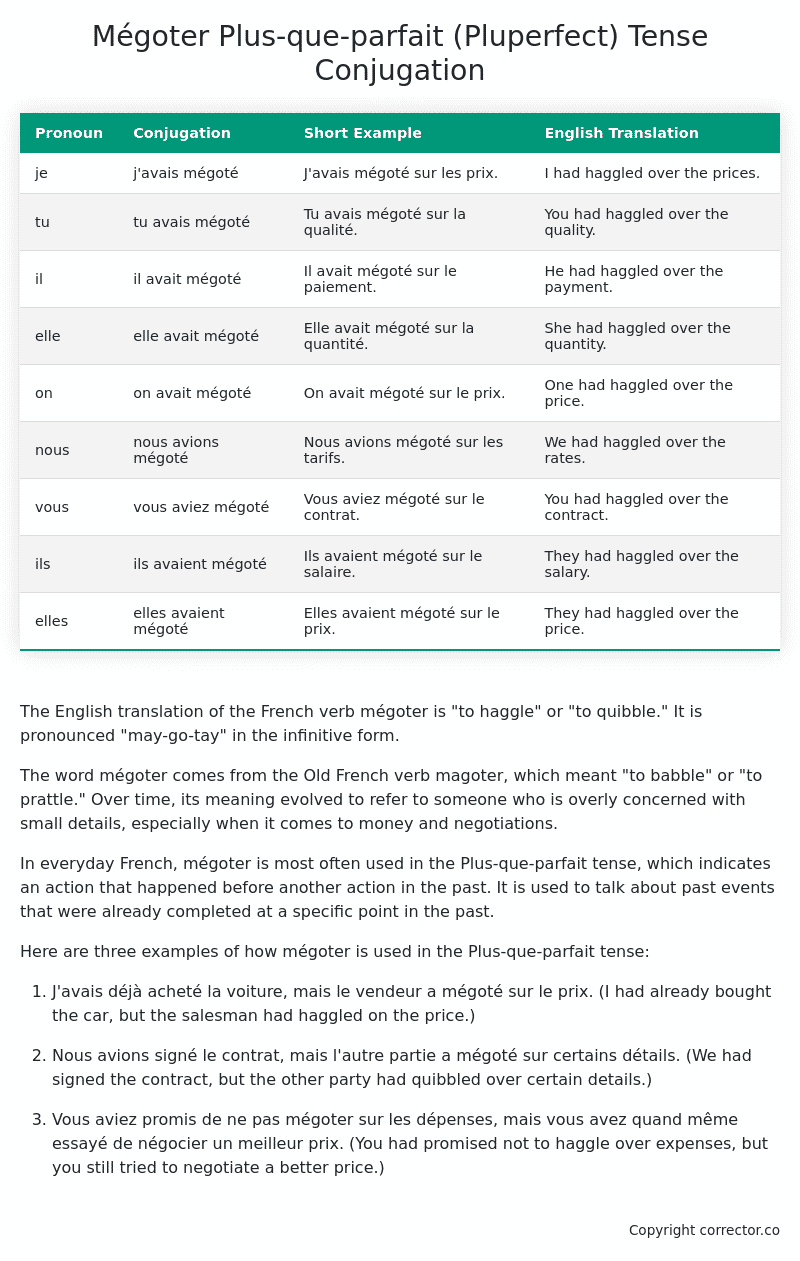
Table of the Plus-que-parfait (Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of mégoter
| Pronoun | Conjugation | Short Example | English Translation |
|---|---|---|---|
| je | j’avais mégoté | J’avais mégoté sur les prix. | I had haggled over the prices. |
| tu | tu avais mégoté | Tu avais mégoté sur la qualité. | You had haggled over the quality. |
| il | il avait mégoté | Il avait mégoté sur le paiement. | He had haggled over the payment. |
| elle | elle avait mégoté | Elle avait mégoté sur la quantité. | She had haggled over the quantity. |
| on | on avait mégoté | On avait mégoté sur le prix. | One had haggled over the price. |
| nous | nous avions mégoté | Nous avions mégoté sur les tarifs. | We had haggled over the rates. |
| vous | vous aviez mégoté | Vous aviez mégoté sur le contrat. | You had haggled over the contract. |
| ils | ils avaient mégoté | Ils avaient mégoté sur le salaire. | They had haggled over the salary. |
| elles | elles avaient mégoté | Elles avaient mégoté sur le prix. | They had haggled over the price. |
Other Conjugations for Mégoter.
Le Present (Present Tense) Conjugation of the French Verb mégoter
Imparfait (Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb mégoter
Passé Simple (Simple Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb mégoter
Passé Composé (Present Perfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb mégoter
Futur Simple (Simple Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb mégoter
Futur Proche (Near Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb mégoter
Plus-que-parfait (Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb mégoter (this article)
Passé Antérieur (Past Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb mégoter
Futur Antérieur (Future Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb mégoter
Subjonctif Présent (Subjunctive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb mégoter
Subjonctif Passé (Subjunctive Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb mégoter
Subjonctif Imparfait (Subjunctive Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb mégoter
Subjonctif Plus-que-parfait (Subjunctive Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb mégoter
Conditionnel Présent (Conditional Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb mégoter
Conditionnel Passé (Conditional Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb mégoter
L’impératif Présent (Imperative Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb mégoter
L’infinitif Présent (Infinitive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb mégoter
Struggling with French verbs or the language in general? Why not use our free French Grammar Checker – no registration required!
Get a FREE Download Study Sheet of this Conjugation 🔥
Simply right click the image below, click “save image” and get your free reference for the mégoter Plus-que-parfait tense conjugation!
Mégoter – About the French Plus-que-parfait (Pluperfect) Tense
Tense Formation
Common everyday usage patterns
Sequencing of past events
Background information
Hypothetical or reported speech
Interactions with other tenses
Summary
I hope you enjoyed this article on the verb mégoter. Still in a learning mood? Check out another TOTALLY random French verb conjugation!


