Plus-que-parfait (Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb procrastiner
Introduction to the verb procrastiner
The English translation of the French verb procrastiner is “to procrastinate.” The infinitive form of the verb is pronounced “proh-krahs-tee-ne.”
The word procrastiner comes from the Latin word procrastinare, which means “to put off until tomorrow.” It is a combination of the prefix pro- meaning “forward” and crastinus meaning “of tomorrow.”
In everyday French, procrastiner is most often used in the Plus-que-parfait tense, which is the past perfect tense. This tense is used to describe an action that happened before another past action. For example, “I had procrastinated before I finally finished my project.”
Here are three simple examples of its usage in the Plus-que-parfait tense:
-
J’avais procrastiné pendant des jours avant de commencer à réviser pour l’examen. (I had procrastinated for days before starting to study for the exam.)
-
Tu avais procrastiné jusqu’au dernier moment et tu as dû rendre ton travail en retard. (You had procrastinated until the last moment and had to turn in your assignment late.)
-
Il avait procrastiné tout l’été et maintenant il doit se dépêcher pour trouver un travail. (He had procrastinated all summer and now he has to hurry to find a job.)
Table of the Plus-que-parfait (Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of procrastiner
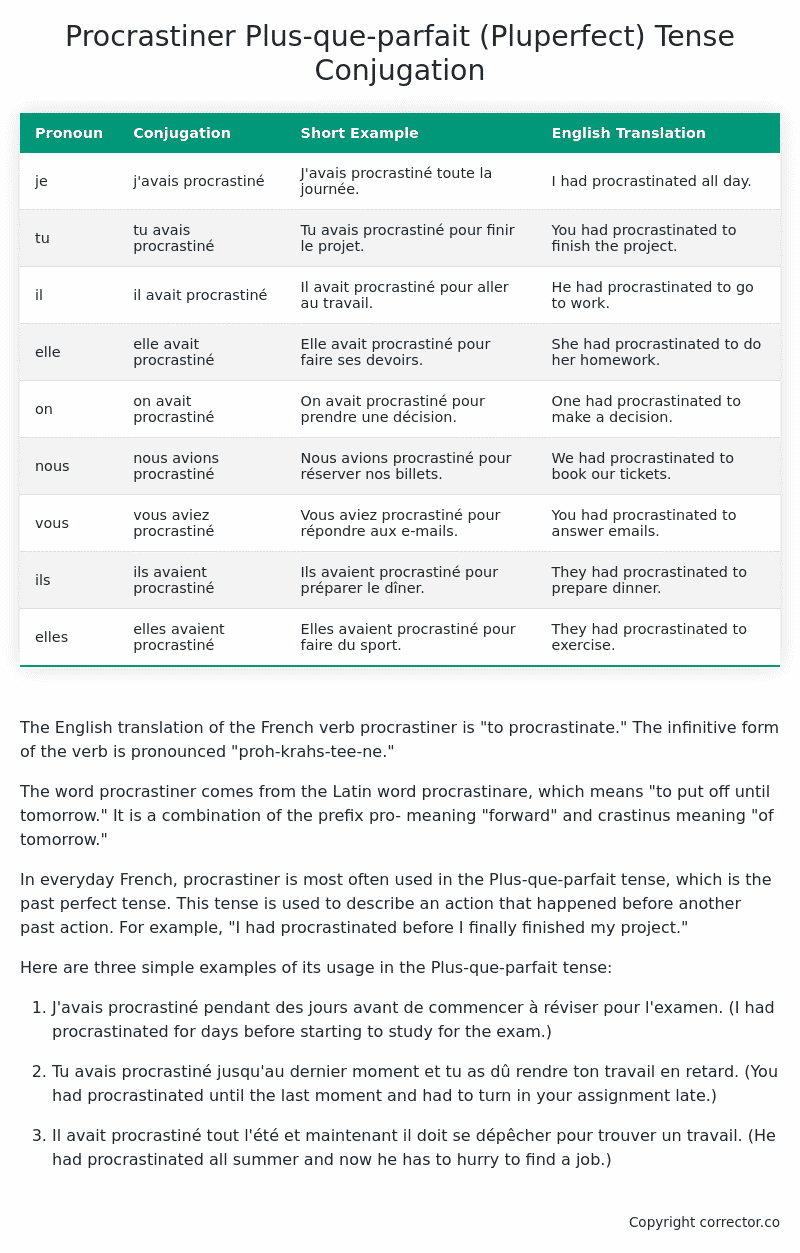
| Pronoun | Conjugation | Short Example | English Translation |
|---|---|---|---|
| je | j’avais procrastiné | J’avais procrastiné toute la journée. | I had procrastinated all day. |
| tu | tu avais procrastiné | Tu avais procrastiné pour finir le projet. | You had procrastinated to finish the project. |
| il | il avait procrastiné | Il avait procrastiné pour aller au travail. | He had procrastinated to go to work. |
| elle | elle avait procrastiné | Elle avait procrastiné pour faire ses devoirs. | She had procrastinated to do her homework. |
| on | on avait procrastiné | On avait procrastiné pour prendre une décision. | One had procrastinated to make a decision. |
| nous | nous avions procrastiné | Nous avions procrastiné pour réserver nos billets. | We had procrastinated to book our tickets. |
| vous | vous aviez procrastiné | Vous aviez procrastiné pour répondre aux e-mails. | You had procrastinated to answer emails. |
| ils | ils avaient procrastiné | Ils avaient procrastiné pour préparer le dîner. | They had procrastinated to prepare dinner. |
| elles | elles avaient procrastiné | Elles avaient procrastiné pour faire du sport. | They had procrastinated to exercise. |
Other Conjugations for Procrastiner.
Le Present (Present Tense) Conjugation of the French Verb procrastiner
Imparfait (Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb procrastiner
Passé Simple (Simple Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb procrastiner
Passé Composé (Present Perfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb procrastiner
Futur Simple (Simple Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb procrastiner
Futur Proche (Near Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb procrastiner
Plus-que-parfait (Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb procrastiner (this article)
Passé Antérieur (Past Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb procrastiner
Futur Antérieur (Future Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb procrastiner
Subjonctif Présent (Subjunctive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb procrastiner
Subjonctif Passé (Subjunctive Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb procrastiner
Subjonctif Imparfait (Subjunctive Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb procrastiner
Conditionnel Présent (Conditional Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb procrastiner
Conditionnel Passé (Conditional Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb procrastiner
L’impératif Présent (Imperative Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb procrastiner
L’infinitif Présent (Infinitive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb procrastiner
Struggling with French verbs or the language in general? Why not use our free French Grammar Checker – no registration required!
Get a FREE Download Study Sheet of this Conjugation 🔥
Simply right click the image below, click “save image” and get your free reference for the procrastiner Plus-que-parfait tense conjugation!
Procrastiner – About the French Plus-que-parfait (Pluperfect) Tense
Tense Formation
Common everyday usage patterns
Sequencing of past events
Background information
Hypothetical or reported speech
Interactions with other tenses
Summary
I hope you enjoyed this article on the verb procrastiner. Still in a learning mood? Check out another TOTALLY random French verb conjugation!


