Subjonctif Imparfait (Subjunctive Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb aimanter
Introduction to the verb aimanter
The English translation of the French verb aimanter is “to magnetize” or “to attract.” The infinitive form of aimanter is pronounced like “eh-mahn-tay.”
Aimanter comes from the Latin word “ad manum” which means “to the hand.” It was first used in the 13th century to refer to the process of making iron magnetic by rubbing it with a lodestone. Over time, the word evolved to also mean “to attract” in a figurative sense.
In everyday French, aimanter is most often used in the Subjonctif Imparfait tense to express a hypothetical or uncertain action in the past. Here are three examples of its usage in this tense, with their English translations:
- J’aurais aimanté cette barre de fer si j’avais eu un aimant plus puissant. (I would have magnetized this iron bar if I had a stronger magnet.)
- Il se demandait si elle l’aimantait encore après toutes ces années. (He wondered if she still attracted him after all these years.)
- Nous aurions aimanté plus de clients si notre publicité avait été mieux ciblée. (We would have attracted more customers if our advertising had been more targeted.)
Table of the Subjonctif Imparfait (Subjunctive Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of aimanter
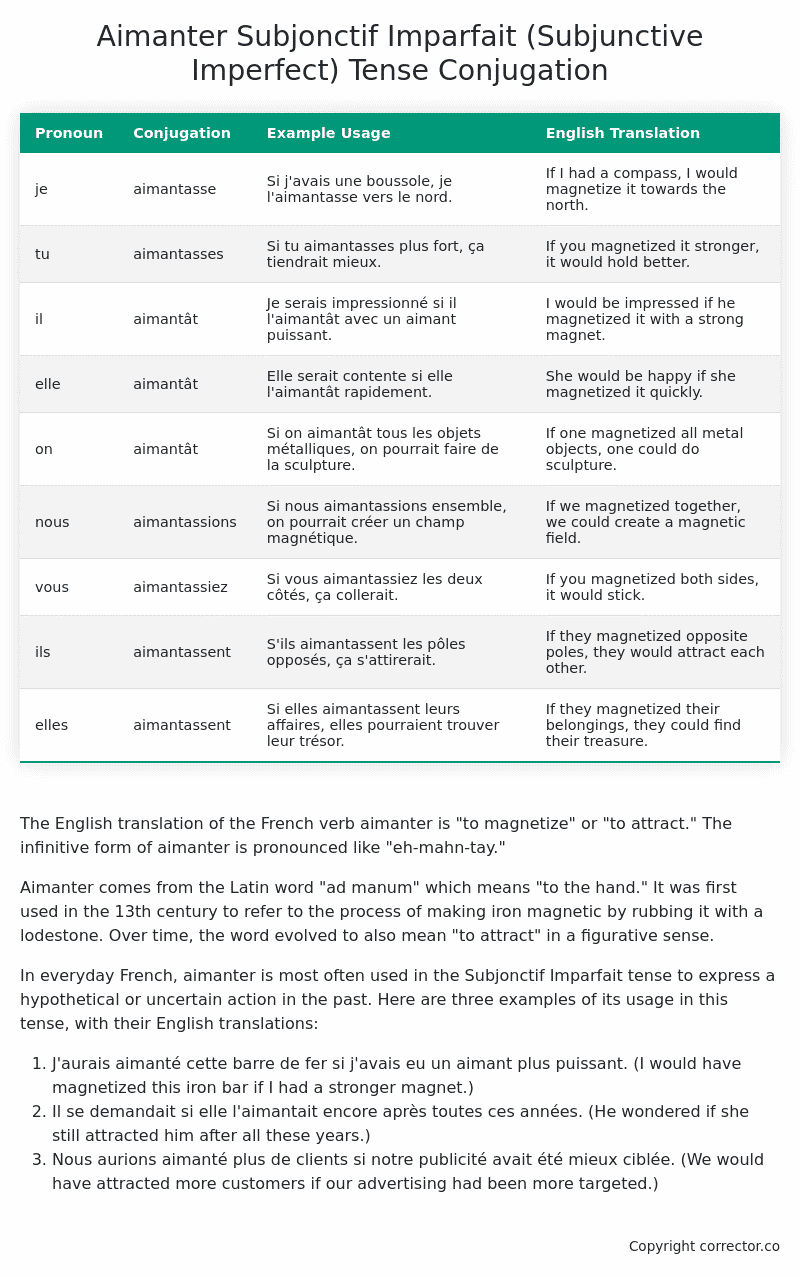
| Pronoun | Conjugation | Example Usage | English Translation |
|---|---|---|---|
| je | aimantasse | Si j’avais une boussole, je l’aimantasse vers le nord. | If I had a compass, I would magnetize it towards the north. |
| tu | aimantasses | Si tu aimantasses plus fort, ça tiendrait mieux. | If you magnetized it stronger, it would hold better. |
| il | aimantât | Je serais impressionné si il l’aimantât avec un aimant puissant. | I would be impressed if he magnetized it with a strong magnet. |
| elle | aimantât | Elle serait contente si elle l’aimantât rapidement. | She would be happy if she magnetized it quickly. |
| on | aimantât | Si on aimantât tous les objets métalliques, on pourrait faire de la sculpture. | If one magnetized all metal objects, one could do sculpture. |
| nous | aimantassions | Si nous aimantassions ensemble, on pourrait créer un champ magnétique. | If we magnetized together, we could create a magnetic field. |
| vous | aimantassiez | Si vous aimantassiez les deux côtés, ça collerait. | If you magnetized both sides, it would stick. |
| ils | aimantassent | S’ils aimantassent les pôles opposés, ça s’attirerait. | If they magnetized opposite poles, they would attract each other. |
| elles | aimantassent | Si elles aimantassent leurs affaires, elles pourraient trouver leur trésor. | If they magnetized their belongings, they could find their treasure. |
Other Conjugations for Aimanter.
Le Present (Present Tense) Conjugation of the French Verb aimanter
Imparfait (Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb aimanter
Passé Simple (Simple Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb aimanter
Passé Composé (Present Perfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb aimanter
Futur Simple (Simple Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb aimanter
Futur Proche (Near Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb aimanter
Plus-que-parfait (Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb aimanter
Passé Antérieur (Past Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb aimanter
Futur Antérieur (Future Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb aimanter
Subjonctif Présent (Subjunctive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb aimanter
Subjonctif Passé (Subjunctive Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb aimanter
Subjonctif Imparfait (Subjunctive Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb aimanter (this article)
Subjonctif Plus-que-parfait (Subjunctive Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb aimanter
Conditionnel Présent (Conditional Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb aimanter
Conditionnel Passé (Conditional Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb aimanter
L’impératif Présent (Imperative Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb aimanter
L’infinitif Présent (Infinitive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb aimanter
Struggling with French verbs or the language in general? Why not use our free French Grammar Checker – no registration required!
Get a FREE Download Study Sheet of this Conjugation 🔥
Simply right click the image below, click “save image” and get your free reference for the aimanter Subjonctif Imparfait tense conjugation!
Aimanter – About the French Subjonctif Imparfait (Subjunctive Imperfect) Tense
Formation
Common Everyday Usage Patterns
Interactions with Other Tenses
Subjonctif Présent
Indicatif Passé Composé
Conditional
Conditional Perfect
Summary
I hope you enjoyed this article on the verb aimanter. Still in a learning mood? Check out another TOTALLY random French verb conjugation!


