Subjonctif Imparfait (Subjunctive Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb bâcher
Introduction to the verb bâcher
The English translation of the French verb bâcher is “to cover” or “to tarp” in English. The infinitive form is pronounced as “ba-shay.”
The verb bâcher comes from the Old French word “bâcher,” which means “to cover.” It originated from the verb “bachier,” which means “to cover with a cloth.” Bâcher is most often used in everyday French in the Subjonctif Imparfait tense, which is the past subjunctive tense used to express actions or events that are hypothetical, uncertain, or contrary to reality.
Three simple examples of bâcher in Subjonctif Imparfait tense are:
- Il fallait que je bâchasse la voiture pour la protéger de la pluie. (It was necessary for me to cover the car to protect it from the rain.)
- Nous souhaitions que vous bâchiez le toit avant qu’il ne pleuve. (We wanted you to tarp the roof before it rained.)
- Il était important que vous bâchiez les meubles avant de partir en vacances. (It was important for you to cover the furniture before going on vacation.)
Overall, bâcher is commonly used in the Subjonctif Imparfait tense to express the need or desire for something to be covered or protected in a hypothetical or uncertain situation.
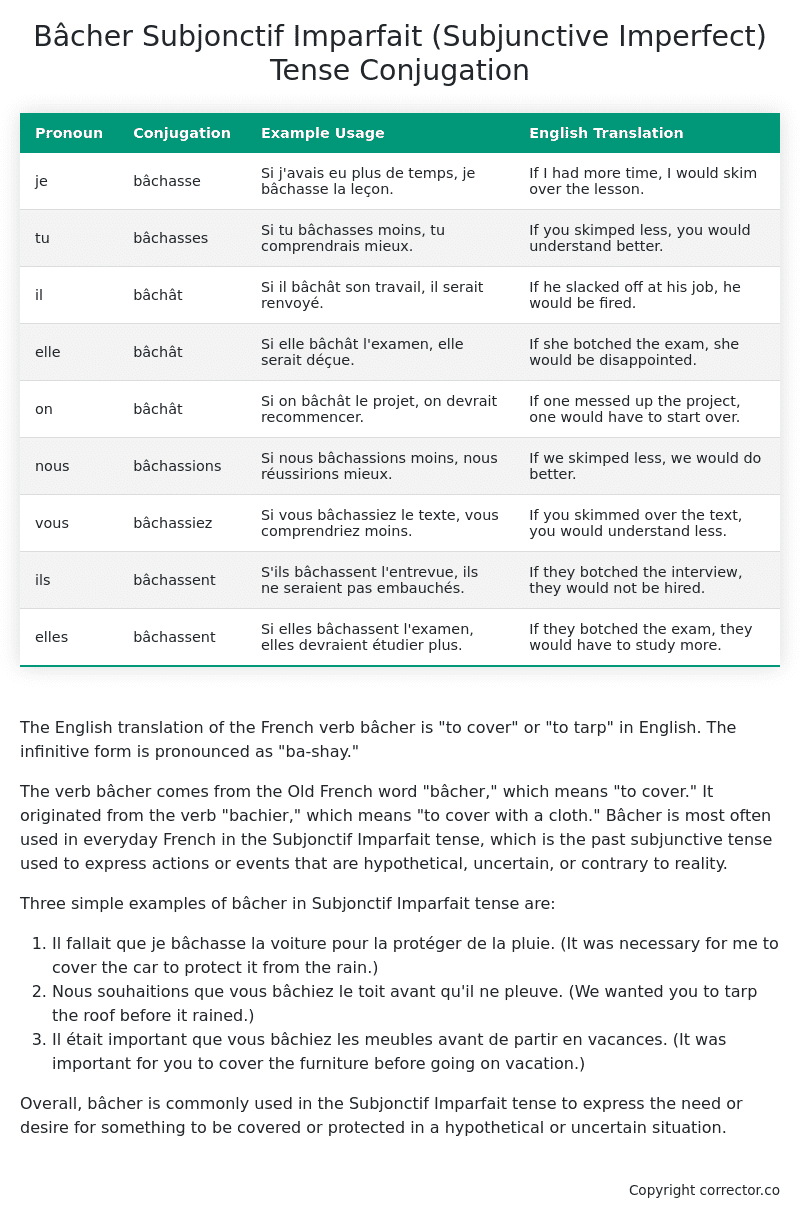
Table of the Subjonctif Imparfait (Subjunctive Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of bâcher
| Pronoun | Conjugation | Example Usage | English Translation |
|---|---|---|---|
| je | bâchasse | Si j’avais eu plus de temps, je bâchasse la leçon. | If I had more time, I would skim over the lesson. |
| tu | bâchasses | Si tu bâchasses moins, tu comprendrais mieux. | If you skimped less, you would understand better. |
| il | bâchât | Si il bâchât son travail, il serait renvoyé. | If he slacked off at his job, he would be fired. |
| elle | bâchât | Si elle bâchât l’examen, elle serait déçue. | If she botched the exam, she would be disappointed. |
| on | bâchât | Si on bâchât le projet, on devrait recommencer. | If one messed up the project, one would have to start over. |
| nous | bâchassions | Si nous bâchassions moins, nous réussirions mieux. | If we skimped less, we would do better. |
| vous | bâchassiez | Si vous bâchassiez le texte, vous comprendriez moins. | If you skimmed over the text, you would understand less. |
| ils | bâchassent | S’ils bâchassent l’entrevue, ils ne seraient pas embauchés. | If they botched the interview, they would not be hired. |
| elles | bâchassent | Si elles bâchassent l’examen, elles devraient étudier plus. | If they botched the exam, they would have to study more. |
Other Conjugations for Bâcher.
Le Present (Present Tense) Conjugation of the French Verb bâcher
Imparfait (Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb bâcher
Passé Simple (Simple Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb bâcher
Passé Composé (Present Perfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb bâcher
Futur Simple (Simple Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb bâcher
Futur Proche (Near Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb bâcher
Plus-que-parfait (Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb bâcher
Passé Antérieur (Past Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb bâcher
Futur Antérieur (Future Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb bâcher
Subjonctif Présent (Subjunctive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb bâcher
Subjonctif Passé (Subjunctive Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb bâcher
Subjonctif Imparfait (Subjunctive Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb bâcher (this article)
Subjonctif Plus-que-parfait (Subjunctive Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb bâcher
Conditionnel Présent (Conditional Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb bâcher
Conditionnel Passé (Conditional Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb bâcher
L’impératif Présent (Imperative Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb bâcher
L’infinitif Présent (Infinitive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb bâcher
Struggling with French verbs or the language in general? Why not use our free French Grammar Checker – no registration required!
Get a FREE Download Study Sheet of this Conjugation 🔥
Simply right click the image below, click “save image” and get your free reference for the bâcher Subjonctif Imparfait tense conjugation!
Bâcher – About the French Subjonctif Imparfait (Subjunctive Imperfect) Tense
Formation
Common Everyday Usage Patterns
Interactions with Other Tenses
Subjonctif Présent
Indicatif Passé Composé
Conditional
Conditional Perfect
Summary
I hope you enjoyed this article on the verb bâcher. Still in a learning mood? Check out another TOTALLY random French verb conjugation!


