Subjonctif Imparfait (Subjunctive Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb bonimenter
Introduction to the verb bonimenter
The English translation of the French verb bonimenter is “to embellish/to tell tall tales.” It is pronounced as boh-nee-mon-tay.
The word bonimenter comes from the French word “boniment,” which means “tale/story.” It is a combination of the words “bon” (good) and “mentir” (to lie), which reflects the idea of creating exaggerated or false stories.
In everyday French, bonimenter is most often used in the Subjonctif Imparfait tense to express a hypothetical or uncertain action in the past. This tense is formed by using the auxiliary verb “avoir” in the imperfect form, followed by the past participle of bonimenter (bonimenté).
3 examples of bonimenter in the Subjonctif Imparfait tense are:
-
Il aurait bonimenté pour impressionner ses amis.
(He would have told tall tales to impress his friends.) -
J’aurais bonimenté si j’avais été seul avec elle.
(I would have embellished if I had been alone with her.) -
Elle aurait bonimenté si elle avait su que j’étais là.
(She would have lied if she had known I was there.)
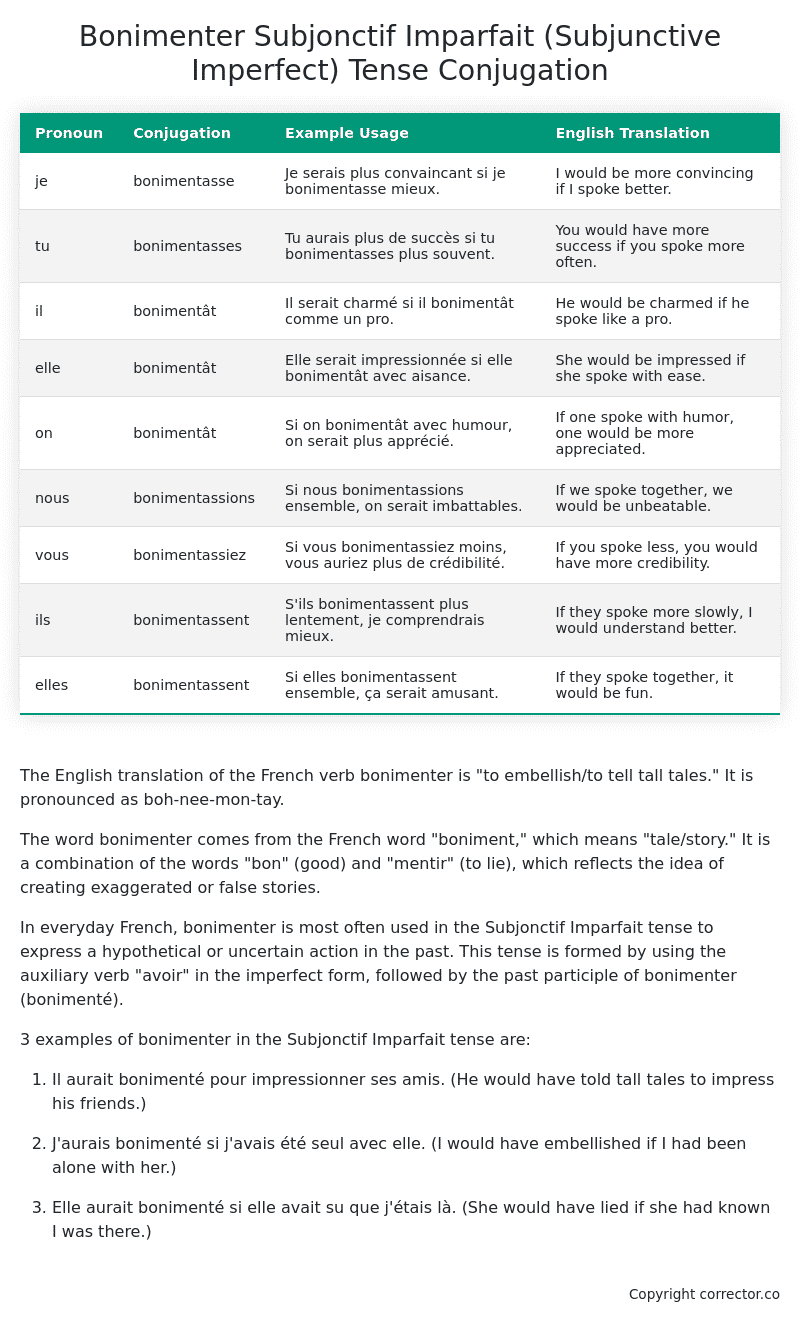
Table of the Subjonctif Imparfait (Subjunctive Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of bonimenter
| Pronoun | Conjugation | Example Usage | English Translation |
|---|---|---|---|
| je | bonimentasse | Je serais plus convaincant si je bonimentasse mieux. | I would be more convincing if I spoke better. |
| tu | bonimentasses | Tu aurais plus de succès si tu bonimentasses plus souvent. | You would have more success if you spoke more often. |
| il | bonimentât | Il serait charmé si il bonimentât comme un pro. | He would be charmed if he spoke like a pro. |
| elle | bonimentât | Elle serait impressionnée si elle bonimentât avec aisance. | She would be impressed if she spoke with ease. |
| on | bonimentât | Si on bonimentât avec humour, on serait plus apprécié. | If one spoke with humor, one would be more appreciated. |
| nous | bonimentassions | Si nous bonimentassions ensemble, on serait imbattables. | If we spoke together, we would be unbeatable. |
| vous | bonimentassiez | Si vous bonimentassiez moins, vous auriez plus de crédibilité. | If you spoke less, you would have more credibility. |
| ils | bonimentassent | S’ils bonimentassent plus lentement, je comprendrais mieux. | If they spoke more slowly, I would understand better. |
| elles | bonimentassent | Si elles bonimentassent ensemble, ça serait amusant. | If they spoke together, it would be fun. |
Other Conjugations for Bonimenter.
Le Present (Present Tense) Conjugation of the French Verb bonimenter
Imparfait (Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb bonimenter
Passé Simple (Simple Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb bonimenter
Passé Composé (Present Perfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb bonimenter
Futur Simple (Simple Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb bonimenter
Futur Proche (Near Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb bonimenter
Plus-que-parfait (Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb bonimenter
Passé Antérieur (Past Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb bonimenter
Futur Antérieur (Future Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb bonimenter
Subjonctif Présent (Subjunctive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb bonimenter
Subjonctif Passé (Subjunctive Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb bonimenter
Subjonctif Imparfait (Subjunctive Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb bonimenter (this article)
Subjonctif Plus-que-parfait (Subjunctive Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb bonimenter
Conditionnel Présent (Conditional Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb bonimenter
Conditionnel Passé (Conditional Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb bonimenter
L’impératif Présent (Imperative Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb bonimenter
L’infinitif Présent (Infinitive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb bonimenter
Struggling with French verbs or the language in general? Why not use our free French Grammar Checker – no registration required!
Get a FREE Download Study Sheet of this Conjugation 🔥
Simply right click the image below, click “save image” and get your free reference for the bonimenter Subjonctif Imparfait tense conjugation!
Bonimenter – About the French Subjonctif Imparfait (Subjunctive Imperfect) Tense
Formation
Common Everyday Usage Patterns
Interactions with Other Tenses
Subjonctif Présent
Indicatif Passé Composé
Conditional
Conditional Perfect
Summary
I hope you enjoyed this article on the verb bonimenter. Still in a learning mood? Check out another TOTALLY random French verb conjugation!


