Subjonctif Imparfait (Subjunctive Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb budgétiser
Introduction to the verb budgétiser
The English translation of the French verb budgétiser is “to budget.” It is pronounced as “boo-zhey-tee-zay” in the infinitive form.
Budgétiser comes from the French word budget, which originated from the Old French word bougette, meaning “purse.” It was first used in the 18th century to refer to a financial plan or estimate. In everyday French, budgétiser is commonly used in the Subjonctif Imparfait tense to express a hypothetical or uncertain action related to budgeting.
Examples:
-
Il fallait que je budgétisasse mes dépenses avant de partir en voyage. (I needed to budget my expenses before going on a trip.)
-
Elle nous conseillait de budgétisassions nos achats pour économiser de l’argent. (She advised us to budget our purchases to save money.)
-
Il était important que nous budgétisassions chaque mois pour éviter les dettes. (It was important for us to budget every month to avoid debts.)
English translations:
-
I had to budget my expenses before going on a trip.
-
She advised us to budget our purchases to save money.
-
It was important for us to budget every month to avoid debts.
Table of the Subjonctif Imparfait (Subjunctive Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of budgétiser
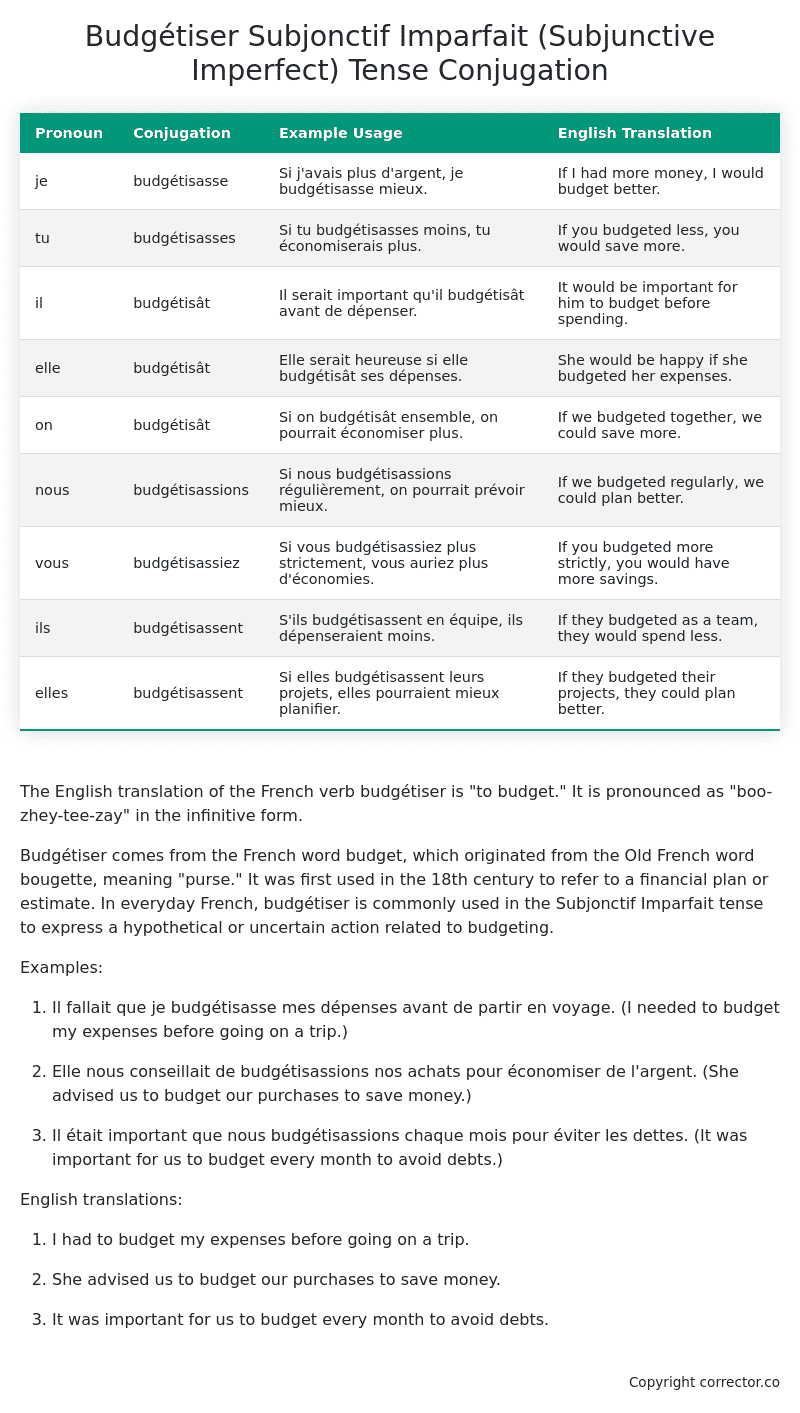
| Pronoun | Conjugation | Example Usage | English Translation |
|---|---|---|---|
| je | budgétisasse | Si j’avais plus d’argent, je budgétisasse mieux. | If I had more money, I would budget better. |
| tu | budgétisasses | Si tu budgétisasses moins, tu économiserais plus. | If you budgeted less, you would save more. |
| il | budgétisât | Il serait important qu’il budgétisât avant de dépenser. | It would be important for him to budget before spending. |
| elle | budgétisât | Elle serait heureuse si elle budgétisât ses dépenses. | She would be happy if she budgeted her expenses. |
| on | budgétisât | Si on budgétisât ensemble, on pourrait économiser plus. | If we budgeted together, we could save more. |
| nous | budgétisassions | Si nous budgétisassions régulièrement, on pourrait prévoir mieux. | If we budgeted regularly, we could plan better. |
| vous | budgétisassiez | Si vous budgétisassiez plus strictement, vous auriez plus d’économies. | If you budgeted more strictly, you would have more savings. |
| ils | budgétisassent | S’ils budgétisassent en équipe, ils dépenseraient moins. | If they budgeted as a team, they would spend less. |
| elles | budgétisassent | Si elles budgétisassent leurs projets, elles pourraient mieux planifier. | If they budgeted their projects, they could plan better. |
Other Conjugations for Budgétiser.
Le Present (Present Tense) Conjugation of the French Verb budgétiser
Imparfait (Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb budgétiser
Passé Simple (Simple Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb budgétiser
Passé Composé (Present Perfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb budgétiser
Futur Simple (Simple Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb budgétiser
Futur Proche (Near Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb budgétiser
Plus-que-parfait (Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb budgétiser
Passé Antérieur (Past Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb budgétiser
Futur Antérieur (Future Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb budgétiser
Subjonctif Présent (Subjunctive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb budgétiser
Subjonctif Passé (Subjunctive Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb budgétiser
Subjonctif Imparfait (Subjunctive Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb budgétiser (this article)
Subjonctif Plus-que-parfait (Subjunctive Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb budgétiser
Conditionnel Présent (Conditional Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb budgétiser
Conditionnel Passé (Conditional Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb budgétiser
L’impératif Présent (Imperative Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb budgétiser
L’infinitif Présent (Infinitive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb budgétiser
Struggling with French verbs or the language in general? Why not use our free French Grammar Checker – no registration required!
Get a FREE Download Study Sheet of this Conjugation 🔥
Simply right click the image below, click “save image” and get your free reference for the budgétiser Subjonctif Imparfait tense conjugation!
Budgétiser – About the French Subjonctif Imparfait (Subjunctive Imperfect) Tense
Formation
Common Everyday Usage Patterns
Interactions with Other Tenses
Subjonctif Présent
Indicatif Passé Composé
Conditional
Conditional Perfect
Summary
I hope you enjoyed this article on the verb budgétiser. Still in a learning mood? Check out another TOTALLY random French verb conjugation!


