Subjonctif Imparfait (Subjunctive Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb capéer
Introduction to the verb capéer
The English translation of the French verb capéer is “to capsize.” It is pronounced as “ka-pey-eh” in the infinitive form.
The origin of the verb capéer can be traced back to the Latin word “capere” meaning “to take, to seize.” In everyday French, it is most commonly used in the Subjonctif Imparfait tense, which expresses a hypothetical or uncertain action in the past.
Three simple examples of its usage in the Subjonctif Imparfait tense with their respective English translations are:
- Il fallait qu’elle capétât le bateau avant que la tempête ne s’aggrave. (She had to capsize the boat before the storm got worse.)
- J’aurais aimé que vous ne capetiez pas le canot lors de votre dernière sortie en mer. (I wish you hadn’t capsized the canoe during your last outing at sea.)
- Si tu capéais le navire, on pourrait tous se retrouver à la mer en un instant. (If you were to capsize the ship, we could all end up in the sea in an instant.)
Table of the Subjonctif Imparfait (Subjunctive Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of capéer
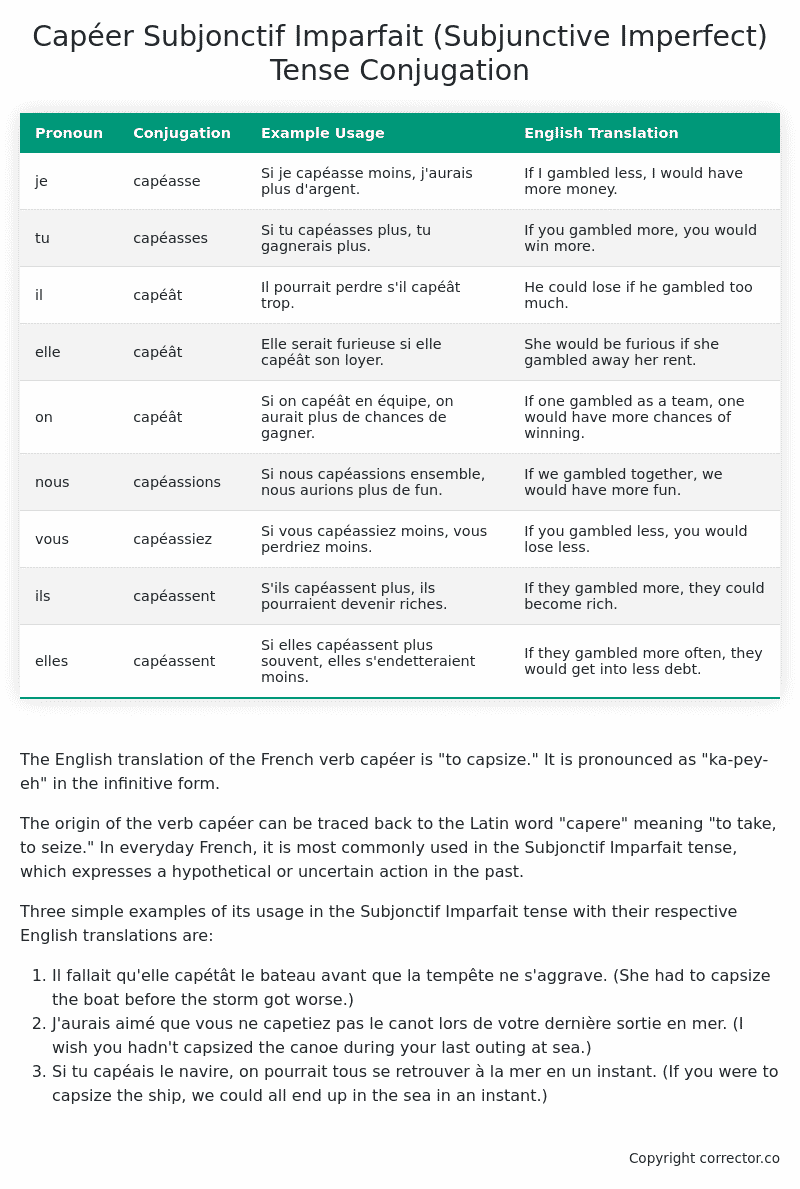
| Pronoun | Conjugation | Example Usage | English Translation |
|---|---|---|---|
| je | capéasse | Si je capéasse moins, j’aurais plus d’argent. | If I gambled less, I would have more money. |
| tu | capéasses | Si tu capéasses plus, tu gagnerais plus. | If you gambled more, you would win more. |
| il | capéât | Il pourrait perdre s’il capéât trop. | He could lose if he gambled too much. |
| elle | capéât | Elle serait furieuse si elle capéât son loyer. | She would be furious if she gambled away her rent. |
| on | capéât | Si on capéât en équipe, on aurait plus de chances de gagner. | If one gambled as a team, one would have more chances of winning. |
| nous | capéassions | Si nous capéassions ensemble, nous aurions plus de fun. | If we gambled together, we would have more fun. |
| vous | capéassiez | Si vous capéassiez moins, vous perdriez moins. | If you gambled less, you would lose less. |
| ils | capéassent | S’ils capéassent plus, ils pourraient devenir riches. | If they gambled more, they could become rich. |
| elles | capéassent | Si elles capéassent plus souvent, elles s’endetteraient moins. | If they gambled more often, they would get into less debt. |
Other Conjugations for Capéer.
Le Present (Present Tense) Conjugation of the French Verb capéer
Imparfait (Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb capéer
Passé Simple (Simple Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb capéer
Passé Composé (Present Perfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb capéer
Futur Simple (Simple Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb capéer
Futur Proche (Near Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb capéer
Plus-que-parfait (Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb capéer
Passé Antérieur (Past Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb capéer
Futur Antérieur (Future Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb capéer
Subjonctif Présent (Subjunctive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb capéer
Subjonctif Passé (Subjunctive Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb capéer
Subjonctif Imparfait (Subjunctive Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb capéer (this article)
Subjonctif Plus-que-parfait (Subjunctive Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb capéer
Conditionnel Présent (Conditional Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb capéer
Conditionnel Passé (Conditional Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb capéer
L’impératif Présent (Imperative Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb capéer
L’infinitif Présent (Infinitive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb capéer
Struggling with French verbs or the language in general? Why not use our free French Grammar Checker – no registration required!
Get a FREE Download Study Sheet of this Conjugation 🔥
Simply right click the image below, click “save image” and get your free reference for the capéer Subjonctif Imparfait tense conjugation!
Capéer – About the French Subjonctif Imparfait (Subjunctive Imperfect) Tense
Formation
Common Everyday Usage Patterns
Interactions with Other Tenses
Subjonctif Présent
Indicatif Passé Composé
Conditional
Conditional Perfect
Summary
I hope you enjoyed this article on the verb capéer. Still in a learning mood? Check out another TOTALLY random French verb conjugation!


