Subjonctif Imparfait (Subjunctive Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb contre-attaquer
Introduction to the verb contre-attaquer
The English translation of contre-attaquer is “to counterattack.” The infinitive form is pronounced “kontr-at-ta-ke.”
The origin of the word contre-attaquer comes from the French words “contre” meaning “against” and “attaquer” meaning “to attack.” It is most often used in everyday French in the Subjonctif Imparfait tense, which expresses a hypothetical or uncertain action in the past.
Examples:
-
Je craignais que l’ennemi ne contre-attaquât, mais heureusement, nous avions prévu une stratégie de défense solide. (I was afraid that the enemy would counterattack, but fortunately, we had planned a strong defense strategy.)
-
Il était important que nous contre-attaquassions immédiatement après leur première attaque. (It was important that we counterattacked immediately after their first attack.)
-
Il me semblait qu’ils contre-attaquaient constamment pour prendre le contrôle de la situation. (It seemed to me that they were constantly counterattacking to take control of the situation.)
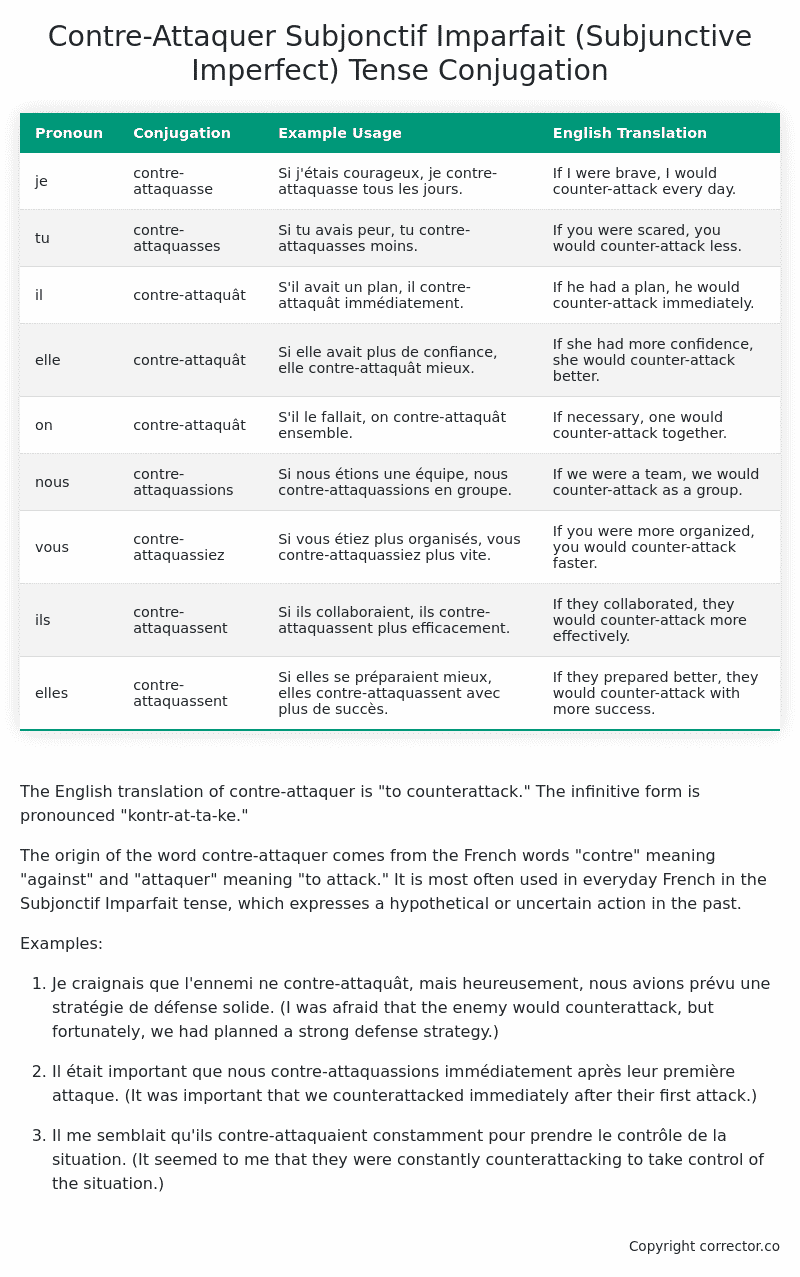
Table of the Subjonctif Imparfait (Subjunctive Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of contre-attaquer
| Pronoun | Conjugation | Example Usage | English Translation |
|---|---|---|---|
| je | contre-attaquasse | Si j’étais courageux, je contre-attaquasse tous les jours. | If I were brave, I would counter-attack every day. |
| tu | contre-attaquasses | Si tu avais peur, tu contre-attaquasses moins. | If you were scared, you would counter-attack less. |
| il | contre-attaquât | S’il avait un plan, il contre-attaquât immédiatement. | If he had a plan, he would counter-attack immediately. |
| elle | contre-attaquât | Si elle avait plus de confiance, elle contre-attaquât mieux. | If she had more confidence, she would counter-attack better. |
| on | contre-attaquât | S’il le fallait, on contre-attaquât ensemble. | If necessary, one would counter-attack together. |
| nous | contre-attaquassions | Si nous étions une équipe, nous contre-attaquassions en groupe. | If we were a team, we would counter-attack as a group. |
| vous | contre-attaquassiez | Si vous étiez plus organisés, vous contre-attaquassiez plus vite. | If you were more organized, you would counter-attack faster. |
| ils | contre-attaquassent | Si ils collaboraient, ils contre-attaquassent plus efficacement. | If they collaborated, they would counter-attack more effectively. |
| elles | contre-attaquassent | Si elles se préparaient mieux, elles contre-attaquassent avec plus de succès. | If they prepared better, they would counter-attack with more success. |
Other Conjugations for Contre-Attaquer.
Le Present (Present Tense) Conjugation of the French Verb contre-attaquer
Imparfait (Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb contre-attaquer
Passé Simple (Simple Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb contre-attaquer
Passé Composé (Present Perfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb contre-attaquer
Futur Simple (Simple Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb contre-attaquer
Futur Proche (Near Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb contre-attaquer
Plus-que-parfait (Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb contre-attaquer
Passé Antérieur (Past Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb contre-attaquer
Futur Antérieur (Future Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb contre-attaquer
Subjonctif Présent (Subjunctive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb contre-attaquer
Subjonctif Passé (Subjunctive Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb contre-attaquer
Subjonctif Imparfait (Subjunctive Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb contre-attaquer (this article)
Conditionnel Présent (Conditional Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb contre-attaquer
Conditionnel Passé (Conditional Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb contre-attaquer
L’impératif Présent (Imperative Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb contre-attaquer
L’infinitif Présent (Infinitive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb contre-attaquer
Struggling with French verbs or the language in general? Why not use our free French Grammar Checker – no registration required!
Get a FREE Download Study Sheet of this Conjugation 🔥
Simply right click the image below, click “save image” and get your free reference for the contre-attaquer Subjonctif Imparfait tense conjugation!
Contre-Attaquer – About the French Subjonctif Imparfait (Subjunctive Imperfect) Tense
Formation
Common Everyday Usage Patterns
Interactions with Other Tenses
Subjonctif Présent
Indicatif Passé Composé
Conditional
Conditional Perfect
Summary
I hope you enjoyed this article on the verb contre-attaquer. Still in a learning mood? Check out another TOTALLY random French verb conjugation!


