Subjonctif Imparfait (Subjunctive Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb coûter
Introduction to the verb coûter
The English translation of the French verb coûter is “to cost.” It is pronounced /ku.te/ in its infinitive form.
The language origin of coûter can be traced back to the Latin verb “constare,” meaning “to cost.” It entered the French language in the 12th century and has remained a common verb in everyday usage.
In the Subjonctif Imparfait tense, coûter is used to express a wish, a doubt, or a hypothetical situation in the past. Here are three simple examples of its usage in this tense, along with their English translations:
- Il fallait que cela coûtât cher. – It was necessary for it to be expensive.
- Je souhaitais que ce voyage coûtât moins cher. – I wished that this trip would cost less.
- Si j’avais su, je ne l’aurais pas acheté car cela aurait coûté trop cher. – If I had known, I wouldn’t have bought it because it would have cost too much.
Table of the Subjonctif Imparfait (Subjunctive Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of coûter
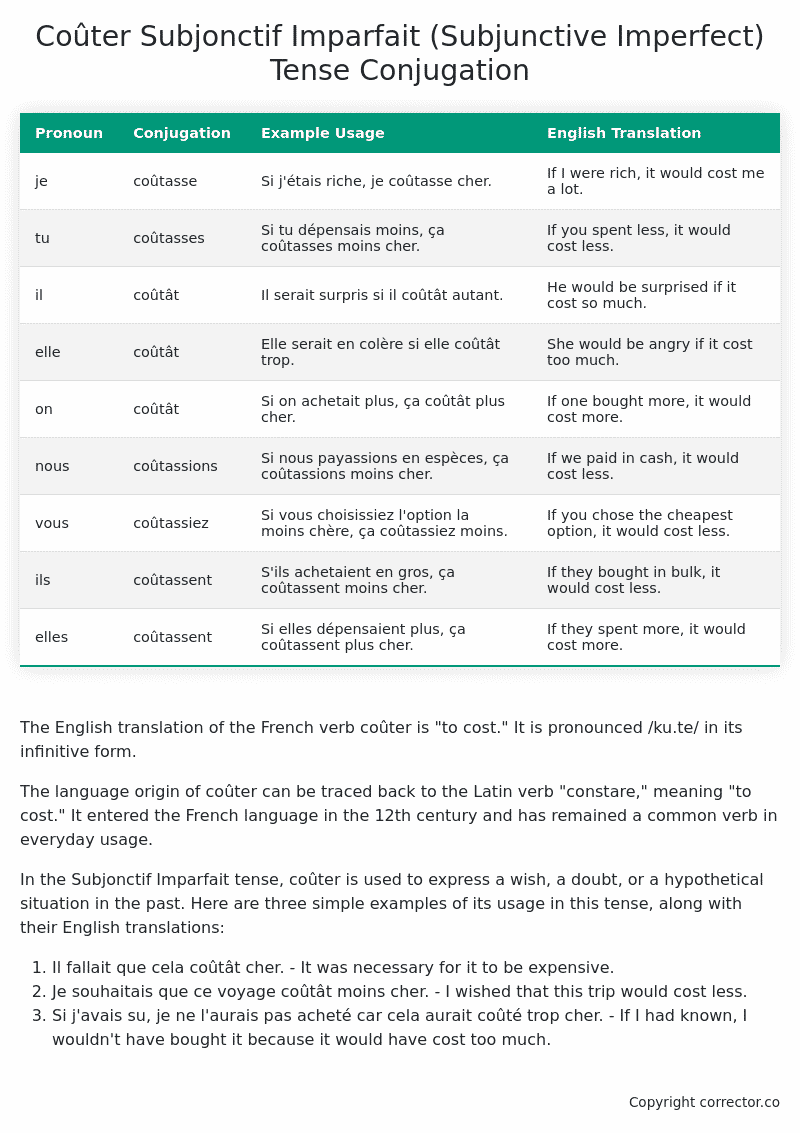
| Pronoun | Conjugation | Example Usage | English Translation |
|---|---|---|---|
| je | coûtasse | Si j’étais riche, je coûtasse cher. | If I were rich, it would cost me a lot. |
| tu | coûtasses | Si tu dépensais moins, ça coûtasses moins cher. | If you spent less, it would cost less. |
| il | coûtât | Il serait surpris si il coûtât autant. | He would be surprised if it cost so much. |
| elle | coûtât | Elle serait en colère si elle coûtât trop. | She would be angry if it cost too much. |
| on | coûtât | Si on achetait plus, ça coûtât plus cher. | If one bought more, it would cost more. |
| nous | coûtassions | Si nous payassions en espèces, ça coûtassions moins cher. | If we paid in cash, it would cost less. |
| vous | coûtassiez | Si vous choisissiez l’option la moins chère, ça coûtassiez moins. | If you chose the cheapest option, it would cost less. |
| ils | coûtassent | S’ils achetaient en gros, ça coûtassent moins cher. | If they bought in bulk, it would cost less. |
| elles | coûtassent | Si elles dépensaient plus, ça coûtassent plus cher. | If they spent more, it would cost more. |
Other Conjugations for Coûter.
Le Present (Present Tense) Conjugation of the French Verb coûter
Imparfait (Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb coûter
Passé Simple (Simple Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb coûter
Passé Composé (Present Perfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb coûter
Futur Simple (Simple Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb coûter
Futur Proche (Near Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb coûter
Plus-que-parfait (Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb coûter
Passé Antérieur (Past Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb coûter
Futur Antérieur (Future Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb coûter
Subjonctif Présent (Subjunctive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb coûter
Subjonctif Passé (Subjunctive Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb coûter
Subjonctif Imparfait (Subjunctive Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb coûter (this article)
Subjonctif Plus-que-parfait (Subjunctive Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb coûter
Conditionnel Présent (Conditional Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb coûter
Conditionnel Passé (Conditional Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb coûter
L’impératif Présent (Imperative Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb coûter
L’infinitif Présent (Infinitive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb coûter
Struggling with French verbs or the language in general? Why not use our free French Grammar Checker – no registration required!
Get a FREE Download Study Sheet of this Conjugation 🔥
Simply right click the image below, click “save image” and get your free reference for the coûter Subjonctif Imparfait tense conjugation!
Coûter – About the French Subjonctif Imparfait (Subjunctive Imperfect) Tense
Formation
Common Everyday Usage Patterns
Interactions with Other Tenses
Subjonctif Présent
Indicatif Passé Composé
Conditional
Conditional Perfect
Summary
I hope you enjoyed this article on the verb coûter. Still in a learning mood? Check out another TOTALLY random French verb conjugation!


