Subjonctif Imparfait (Subjunctive Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb embarder
Introduction to the verb embarder
The English translation of the French verb embarder is “to veer” or “to swerve.” It is pronounced as [ɑ̃baʁde].
The origin of the word embarder can be traced back to the Old French word “enbarrer,” which means “to block” or “to obstruct.” In modern French, it is most often used in its infinitive form and means “to make a sudden change of direction” or “to lose control and swerve.”
In everyday French, the verb embarder is commonly used in the Subjonctif Imparfait tense to express a hypothetical or uncertain action or event in the past. This tense is formed by using the auxiliary verb “avoir” or “être” in the Imparfait tense followed by the past participle of the verb.
Here are three simple examples of embarder in the Subjonctif Imparfait tense with their English translations:
-
Je craignais qu’il n’embardât subitement sur la route mouillée.
(I was afraid he would suddenly veer on the wet road.) -
Il fallait que nous embardassions brusquement pour éviter l’accident.
(We had to suddenly swerve to avoid the accident.) -
Si tu n’avais pas freiné à temps, vous embarderiez tous les deux.
(If you hadn’t braked in time, you both would have veered off.)
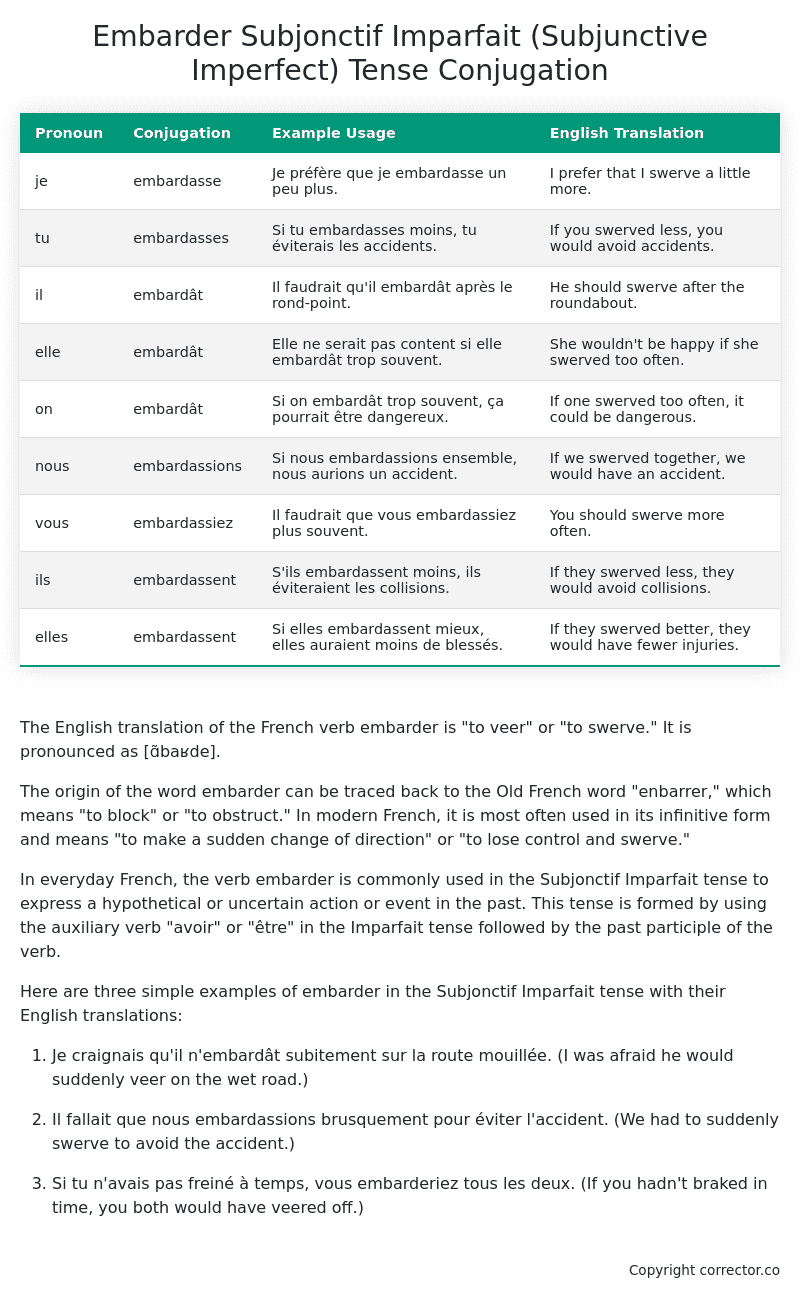
Table of the Subjonctif Imparfait (Subjunctive Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of embarder
| Pronoun | Conjugation | Example Usage | English Translation |
|---|---|---|---|
| je | embardasse | Je préfère que je embardasse un peu plus. | I prefer that I swerve a little more. |
| tu | embardasses | Si tu embardasses moins, tu éviterais les accidents. | If you swerved less, you would avoid accidents. |
| il | embardât | Il faudrait qu’il embardât après le rond-point. | He should swerve after the roundabout. |
| elle | embardât | Elle ne serait pas content si elle embardât trop souvent. | She wouldn’t be happy if she swerved too often. |
| on | embardât | Si on embardât trop souvent, ça pourrait être dangereux. | If one swerved too often, it could be dangerous. |
| nous | embardassions | Si nous embardassions ensemble, nous aurions un accident. | If we swerved together, we would have an accident. |
| vous | embardassiez | Il faudrait que vous embardassiez plus souvent. | You should swerve more often. |
| ils | embardassent | S’ils embardassent moins, ils éviteraient les collisions. | If they swerved less, they would avoid collisions. |
| elles | embardassent | Si elles embardassent mieux, elles auraient moins de blessés. | If they swerved better, they would have fewer injuries. |
Other Conjugations for Embarder.
Le Present (Present Tense) Conjugation of the French Verb embarder
Imparfait (Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb embarder
Passé Simple (Simple Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb embarder
Passé Composé (Present Perfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb embarder
Futur Simple (Simple Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb embarder
Futur Proche (Near Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb embarder
Plus-que-parfait (Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb embarder
Passé Antérieur (Past Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb embarder
Futur Antérieur (Future Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb embarder
Subjonctif Présent (Subjunctive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb embarder
Subjonctif Passé (Subjunctive Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb embarder
Subjonctif Imparfait (Subjunctive Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb embarder (this article)
Subjonctif Plus-que-parfait (Subjunctive Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb embarder
Conditionnel Présent (Conditional Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb embarder
Conditionnel Passé (Conditional Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb embarder
L’impératif Présent (Imperative Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb embarder
L’infinitif Présent (Infinitive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb embarder
Struggling with French verbs or the language in general? Why not use our free French Grammar Checker – no registration required!
Get a FREE Download Study Sheet of this Conjugation 🔥
Simply right click the image below, click “save image” and get your free reference for the embarder Subjonctif Imparfait tense conjugation!
Embarder – About the French Subjonctif Imparfait (Subjunctive Imperfect) Tense
Formation
Common Everyday Usage Patterns
Interactions with Other Tenses
Subjonctif Présent
Indicatif Passé Composé
Conditional
Conditional Perfect
Summary
I hope you enjoyed this article on the verb embarder. Still in a learning mood? Check out another TOTALLY random French verb conjugation!


