Subjonctif Passé (Subjunctive Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb alléger
Introduction to the verb alléger
The English translation of the French verb alléger is “to lighten” or “to ease”. It is pronounced as “ah-leh-zheh” in its infinitive form.
The word alléger comes from the Latin word “levigare” which means “to smooth” or “to lighten”. In everyday French, it is most often used to describe the action of making something less heavy or burdensome.
In the Subjonctif Passé tense, alléger is used to express a hypothetical or uncertain action in the past. It is formed by using the auxiliary verb “avoir” or “être” in the subjonctif présent tense, followed by the past participle of alléger.
Three simple examples of its usage in this tense are:
-
J’aurais aimé que tu aies allégé tes valises avant de partir en vacances. (I wish you had lightened your suitcases before leaving for vacation.)
-
Il faut que nous soyons allégés de nos dettes pour pouvoir acheter une maison. (We need to be relieved from our debts in order to buy a house.)
-
Elle était triste que nous ayons allégé notre relation. (She was sad that we had lightened our relationship.)
Table of the Subjonctif Passé (Subjunctive Past) Tense Conjugation of alléger
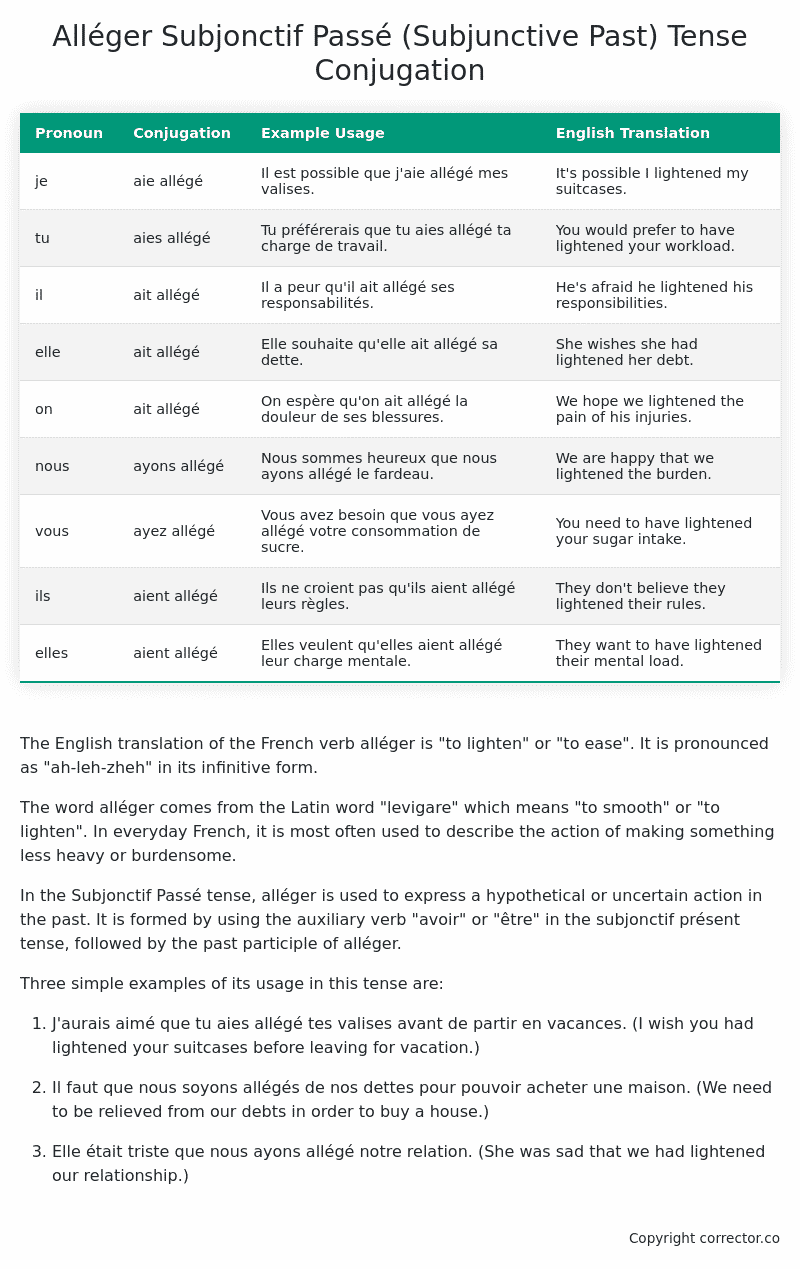
| Pronoun | Conjugation | Example Usage | English Translation |
|---|---|---|---|
| je | aie allégé | Il est possible que j’aie allégé mes valises. | It’s possible I lightened my suitcases. |
| tu | aies allégé | Tu préférerais que tu aies allégé ta charge de travail. | You would prefer to have lightened your workload. |
| il | ait allégé | Il a peur qu’il ait allégé ses responsabilités. | He’s afraid he lightened his responsibilities. |
| elle | ait allégé | Elle souhaite qu’elle ait allégé sa dette. | She wishes she had lightened her debt. |
| on | ait allégé | On espère qu’on ait allégé la douleur de ses blessures. | We hope we lightened the pain of his injuries. |
| nous | ayons allégé | Nous sommes heureux que nous ayons allégé le fardeau. | We are happy that we lightened the burden. |
| vous | ayez allégé | Vous avez besoin que vous ayez allégé votre consommation de sucre. | You need to have lightened your sugar intake. |
| ils | aient allégé | Ils ne croient pas qu’ils aient allégé leurs règles. | They don’t believe they lightened their rules. |
| elles | aient allégé | Elles veulent qu’elles aient allégé leur charge mentale. | They want to have lightened their mental load. |
Other Conjugations for Alléger.
Le Present (Present Tense) Conjugation of the French Verb alléger
Imparfait (Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb alléger
Passé Simple (Simple Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb alléger
Passé Composé (Present Perfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb alléger
Futur Simple (Simple Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb alléger
Futur Proche (Near Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb alléger
Plus-que-parfait (Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb alléger
Passé Antérieur (Past Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb alléger
Futur Antérieur (Future Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb alléger
Subjonctif Présent (Subjunctive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb alléger
Subjonctif Passé (Subjunctive Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb alléger (this article)
Subjonctif Imparfait (Subjunctive Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb alléger
Subjonctif Plus-que-parfait (Subjunctive Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb alléger
Conditionnel Présent (Conditional Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb alléger
Conditionnel Passé (Conditional Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb alléger
L’impératif Présent (Imperative Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb alléger
L’infinitif Présent (Infinitive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb alléger
Struggling with French verbs or the language in general? Why not use our free French Grammar Checker – no registration required!
Get a FREE Download Study Sheet of this Conjugation 🔥
Simply right click the image below, click “save image” and get your free reference for the alléger Subjonctif Passé tense conjugation!
Alléger – About the French Subjonctif Passé (Subjunctive Past) Tense
Formation of the Subjonctif Passé
Everyday Usage Patterns
Interactions with Other Tenses
Present tense
Future tense
Conditional
Summary
I hope you enjoyed this article on the verb alléger. Still in a learning mood? Check out another TOTALLY random French verb conjugation!


