Subjonctif Passé (Subjunctive Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb bouffer
Introduction to the verb bouffer
The English translation of the French verb bouffer is “to devour” or “to gobble up.” The infinitive form of bouffer is pronounced as “boo-fay.”
Bouffer comes from the Old French word “boffer” which means “to puff” or “to blow.” It is most often used in informal or colloquial French, especially in the Subjonctif Passé tense, to express a strong or exaggerated action or emotion.
Here are three simple examples of its usage in the Subjonctif Passé tense:
1) J’espère que tu as bouffé ton dîner avant de sortir. (I hope you devoured your dinner before going out.)
2) Il faut que j’aie bouffé un kilo de chocolat hier soir. (I must have gobbled up a kilo of chocolate last night.)
3) Nous attendons que les enfants aient bouffé leur soupe avant de leur donner du dessert. (We’re waiting for the children to have finished their soup before giving them dessert.)
Overall, bouffer is often used in everyday French to describe the act of eating quickly and voraciously or to add emphasis to an action. It is not considered a formal verb and is more commonly used in spoken language rather than in written form.
Table of the Subjonctif Passé (Subjunctive Past) Tense Conjugation of bouffer
| Pronoun | Conjugation | Example Usage | English Translation |
|---|---|---|---|
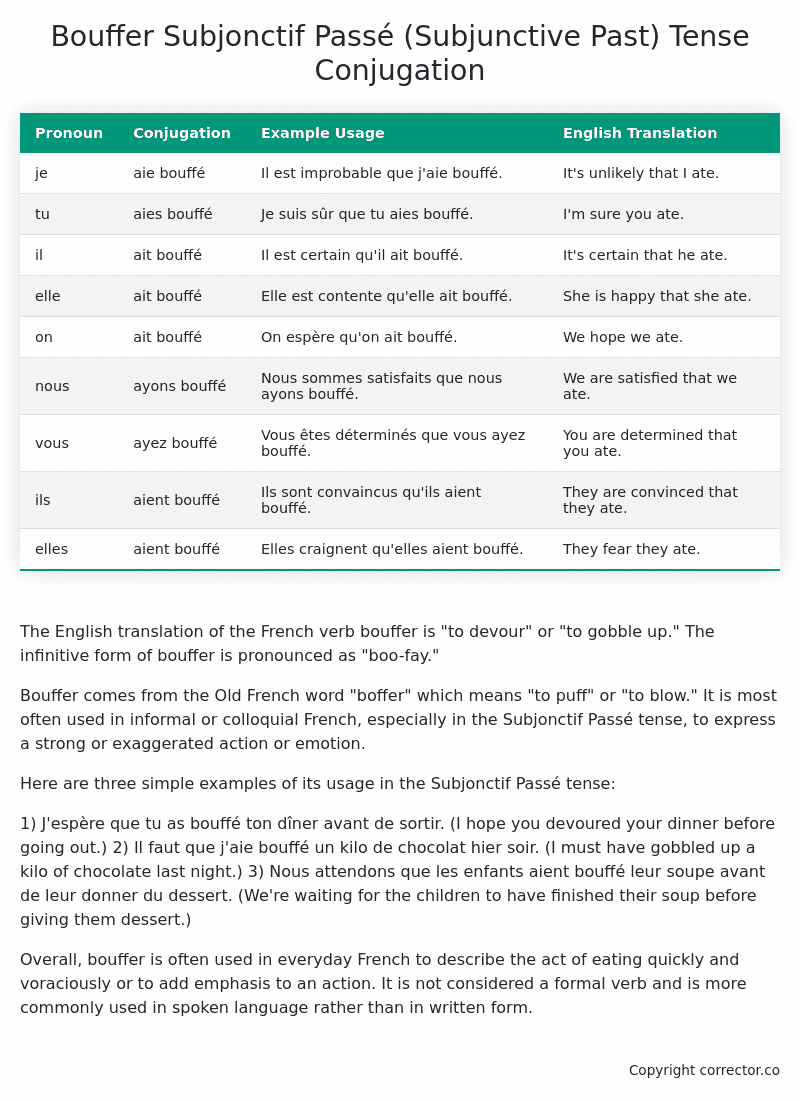
| je | aie bouffé | Il est improbable que j’aie bouffé. | It’s unlikely that I ate. |
| tu | aies bouffé | Je suis sûr que tu aies bouffé. | I’m sure you ate. |
| il | ait bouffé | Il est certain qu’il ait bouffé. | It’s certain that he ate. |
| elle | ait bouffé | Elle est contente qu’elle ait bouffé. | She is happy that she ate. |
| on | ait bouffé | On espère qu’on ait bouffé. | We hope we ate. |
| nous | ayons bouffé | Nous sommes satisfaits que nous ayons bouffé. | We are satisfied that we ate. |
| vous | ayez bouffé | Vous êtes déterminés que vous ayez bouffé. | You are determined that you ate. |
| ils | aient bouffé | Ils sont convaincus qu’ils aient bouffé. | They are convinced that they ate. |
| elles | aient bouffé | Elles craignent qu’elles aient bouffé. | They fear they ate. |
Other Conjugations for Bouffer.
Le Present (Present Tense) Conjugation of the French Verb bouffer
Imparfait (Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb bouffer
Passé Simple (Simple Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb bouffer
Passé Composé (Present Perfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb bouffer
Futur Simple (Simple Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb bouffer
Futur Proche (Near Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb bouffer
Plus-que-parfait (Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb bouffer
Passé Antérieur (Past Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb bouffer
Futur Antérieur (Future Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb bouffer
Subjonctif Présent (Subjunctive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb bouffer
Subjonctif Passé (Subjunctive Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb bouffer (this article)
Subjonctif Imparfait (Subjunctive Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb bouffer
Subjonctif Plus-que-parfait (Subjunctive Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb bouffer
Conditionnel Présent (Conditional Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb bouffer
Conditionnel Passé (Conditional Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb bouffer
L’impératif Présent (Imperative Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb bouffer
L’infinitif Présent (Infinitive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb bouffer
Struggling with French verbs or the language in general? Why not use our free French Grammar Checker – no registration required!
Get a FREE Download Study Sheet of this Conjugation 🔥
Simply right click the image below, click “save image” and get your free reference for the bouffer Subjonctif Passé tense conjugation!
Bouffer – About the French Subjonctif Passé (Subjunctive Past) Tense
Formation of the Subjonctif Passé
Everyday Usage Patterns
Interactions with Other Tenses
Present tense
Future tense
Conditional
Summary
I hope you enjoyed this article on the verb bouffer. Still in a learning mood? Check out another TOTALLY random French verb conjugation!


