Futur Antérieur (Future Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb bégayer
Introduction to the verb bégayer
The English translation of the French verb bégayer is to stutter or stammer. It is pronounced as “bay-ga-yay” in the infinitive form.
The origin of the word bégayer comes from the Old French word “begeier” which means “to stammer”. It has been used in the French language since the 12th century.
In everyday French, bégayer is most often used in the Futur Antérieur tense, which is used to express actions that will have been completed in the future. Some common words used with this tense include “quand” (when), “dès que” (as soon as), and “lorsque” (when).
Here are three simple examples of bégayer in the Futur Antérieur tense, with their respective English translations:
- Je bégayerai quand je parlerai en public demain. (I will stutter when I speak in public tomorrow.)
- Dès que tu arriveras, tu bégayeras sûrement devant le jury. (As soon as you arrive, you will probably stutter in front of the jury.)
- Lorsque nous aurons fini de réciter, nous bégayerons encore quelques mots. (When we have finished reciting, we will still stutter a few words.)
In all of these examples, the verb bégayer is conjugated in the Futur Antérieur tense (future tense of “avoir” + past participle of “bégayer”) to express an action that will have been completed in the future.
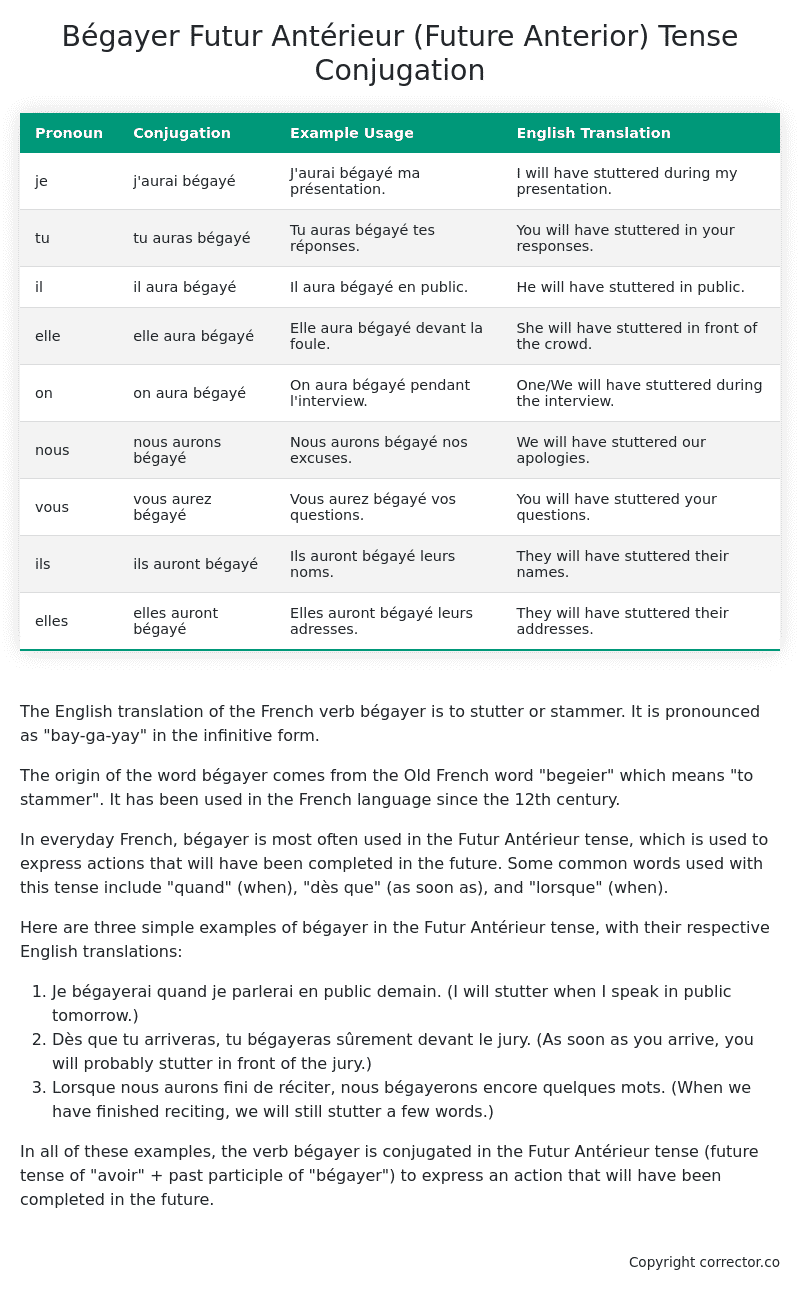
Table of the Futur Antérieur (Future Anterior) Tense Conjugation of bégayer
| Pronoun | Conjugation | Example Usage | English Translation |
|---|---|---|---|
| je | j’aurai bégayé | J’aurai bégayé ma présentation. | I will have stuttered during my presentation. |
| tu | tu auras bégayé | Tu auras bégayé tes réponses. | You will have stuttered in your responses. |
| il | il aura bégayé | Il aura bégayé en public. | He will have stuttered in public. |
| elle | elle aura bégayé | Elle aura bégayé devant la foule. | She will have stuttered in front of the crowd. |
| on | on aura bégayé | On aura bégayé pendant l’interview. | One/We will have stuttered during the interview. |
| nous | nous aurons bégayé | Nous aurons bégayé nos excuses. | We will have stuttered our apologies. |
| vous | vous aurez bégayé | Vous aurez bégayé vos questions. | You will have stuttered your questions. |
| ils | ils auront bégayé | Ils auront bégayé leurs noms. | They will have stuttered their names. |
| elles | elles auront bégayé | Elles auront bégayé leurs adresses. | They will have stuttered their addresses. |
Other Conjugations for Bégayer.
Le Present (Present Tense) Conjugation of the French Verb bégayer
Imparfait (Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb bégayer
Passé Simple (Simple Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb bégayer
Passé Composé (Present Perfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb bégayer
Futur Simple (Simple Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb bégayer
Futur Proche (Near Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb bégayer
Plus-que-parfait (Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb bégayer
Passé Antérieur (Past Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb bégayer
Futur Antérieur (Future Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb bégayer (this article)
Subjonctif Présent (Subjunctive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb bégayer
Subjonctif Passé (Subjunctive Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb bégayer
Subjonctif Imparfait (Subjunctive Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb bégayer
Subjonctif Plus-que-parfait (Subjunctive Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb bégayer
Conditionnel Présent (Conditional Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb bégayer
Conditionnel Passé (Conditional Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb bégayer
L’impératif Présent (Imperative Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb bégayer
L’infinitif Présent (Infinitive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb bégayer
Struggling with French verbs or the language in general? Why not use our free French Grammar Checker – no registration required!
Get a FREE Download Study Sheet of this Conjugation 🔥
Simply right click the image below, click “save image” and get your free reference for the bégayer Futur Antérieur tense conjugation!
Bégayer – About the French Futur Antérieur (Future Anterior) Tense
Construction
Common Everyday Usage Patterns
Interactions with Other Tenses
For example
Summary
I hope you enjoyed this article on the verb bégayer. Still in a learning mood? Check out another TOTALLY random French verb conjugation!


