L’impératif Présent (Imperative Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb augurer
Introduction to the verb augurer
The English translation of the French verb augurer is “to predict” or “to foretell.” It is pronounced as “o-gu-ré.”
The word augurer comes from the Latin “augurari,” meaning “to foretell by interpretation of omens.” In everyday French, it is most often used in the L’impératif Présent tense, which is the imperative form used for giving commands or instructions.
Examples:
- Augure ton avenir avec confiance. (Foretell your future with confidence.)
- N’augurons pas le pire, soyons optimistes. (Let’s not predict the worst, let’s be optimistic.)
- Augurez-leur une vie heureuse et prospère. (Foretell them a happy and prosperous life.)
Table of the L’impératif Présent (Imperative Present) Tense Conjugation of augurer
| Pronoun | Conjugation | Example Usage | English Translation |
|---|---|---|---|
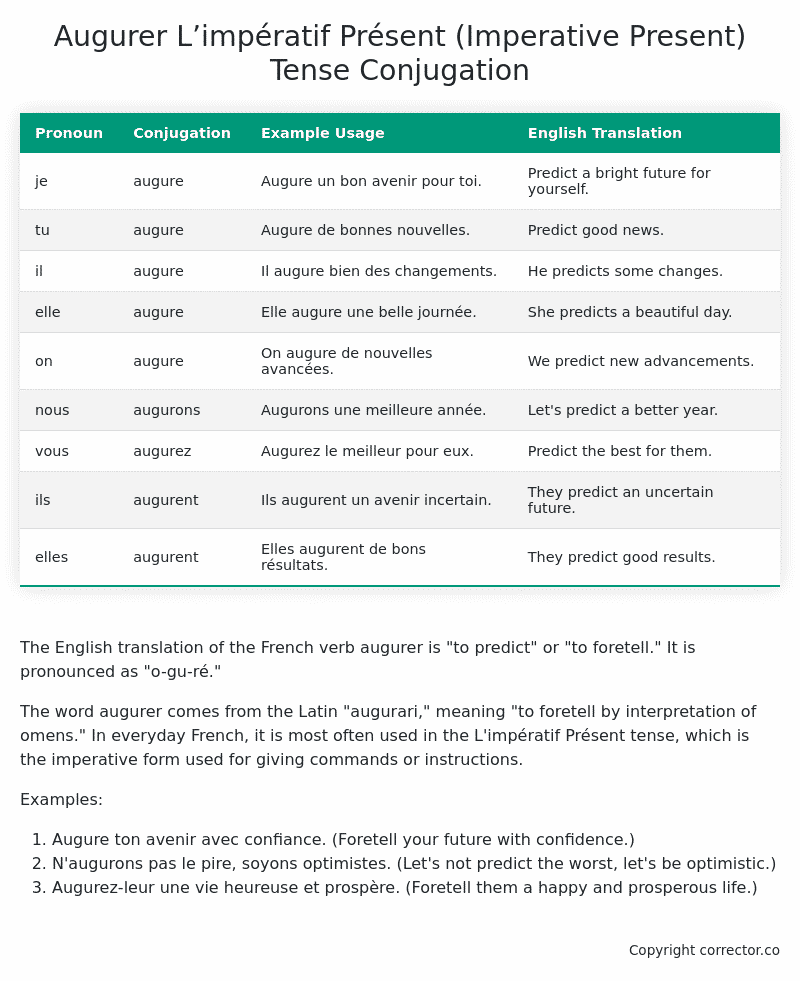
| je | augure | Augure un bon avenir pour toi. | Predict a bright future for yourself. |
| tu | augure | Augure de bonnes nouvelles. | Predict good news. |
| il | augure | Il augure bien des changements. | He predicts some changes. |
| elle | augure | Elle augure une belle journée. | She predicts a beautiful day. |
| on | augure | On augure de nouvelles avancées. | We predict new advancements. |
| nous | augurons | Augurons une meilleure année. | Let’s predict a better year. |
| vous | augurez | Augurez le meilleur pour eux. | Predict the best for them. |
| ils | augurent | Ils augurent un avenir incertain. | They predict an uncertain future. |
| elles | augurent | Elles augurent de bons résultats. | They predict good results. |
Other Conjugations for Augurer.
Le Present (Present Tense) Conjugation of the French Verb augurer
Imparfait (Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb augurer
Passé Simple (Simple Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb augurer
Passé Composé (Present Perfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb augurer
Futur Simple (Simple Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb augurer
Futur Proche (Near Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb augurer
Plus-que-parfait (Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb augurer
Passé Antérieur (Past Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb augurer
Futur Antérieur (Future Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb augurer
Subjonctif Présent (Subjunctive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb augurer
Subjonctif Passé (Subjunctive Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb augurer
Subjonctif Imparfait (Subjunctive Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb augurer
Subjonctif Plus-que-parfait (Subjunctive Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb augurer
Conditionnel Présent (Conditional Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb augurer
Conditionnel Passé (Conditional Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb augurer
L’impératif Présent (Imperative Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb augurer (this article)
L’infinitif Présent (Infinitive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb augurer
Struggling with French verbs or the language in general? Why not use our free French Grammar Checker – no registration required!
Get a FREE Download Study Sheet of this Conjugation 🔥
Simply right click the image below, click “save image” and get your free reference for the augurer L’impératif Présent tense conjugation!
Augurer – About the French L’impératif Présent (Imperative Present) Tense
Usage
Giving commands
Making requests
Offering advice
Expressing desires
Conjugation Formation
Interactions with other tenses
Want More?
I hope you enjoyed this article on the verb augurer. Still in a learning mood? Check out another TOTALLY random French verb conjugation!


