L’impératif Présent (Imperative Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb classifier
Introduction to the verb classifier
The English translation of the French verb classifier is “to classify.” The infinitive form of the verb is pronounced “klah-see-fee-yay.”
The origin of the word “classifier” comes from the Latin word “classificare,” which means “to divide into classes.” In everyday French, the verb is used in the L’impératif Présent tense to give commands or instructions. It is often used when giving orders, making requests, or giving advice.
Here are three simple examples of how the classifier is used in the L’impératif Présent tense, with their English translations:
- “Classifiez vos affaires avant de partir !” (Classify your belongings before leaving!)
- “Classifions les documents par catégorie.” (Let’s classify the documents by category.)
- “Classifie-le selon son niveau de priorité.” (Classify it according to its level of priority.)
Table of the L’impératif Présent (Imperative Present) Tense Conjugation of classifier
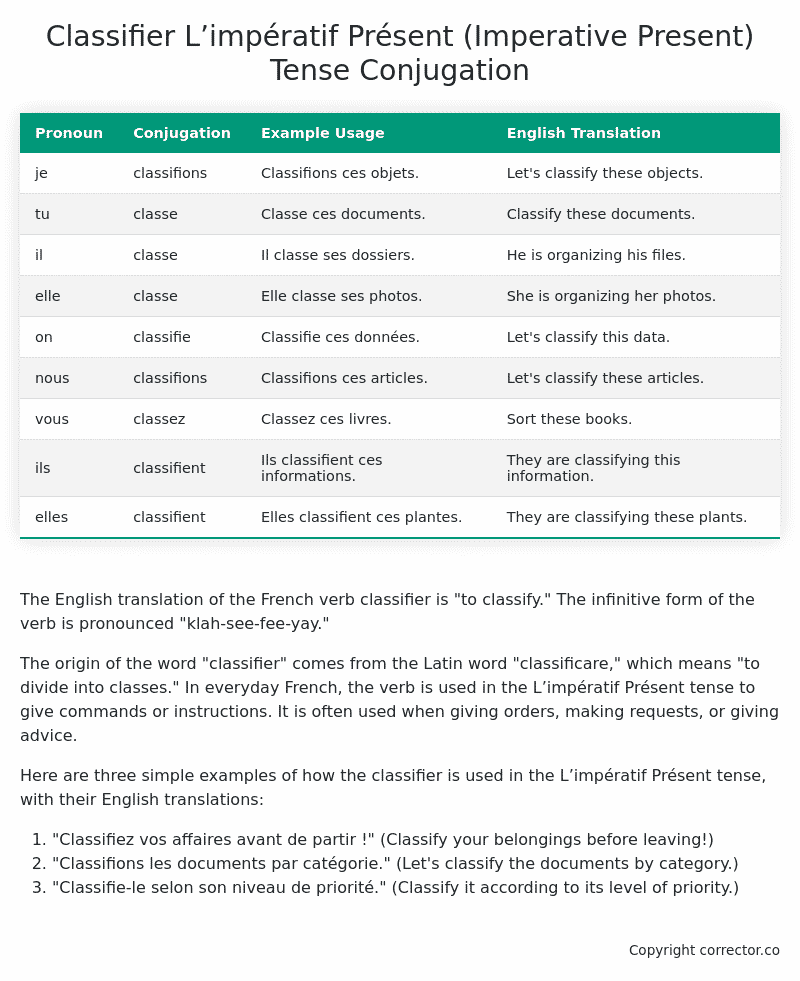
| Pronoun | Conjugation | Example Usage | English Translation |
|---|---|---|---|
| je | classifions | Classifions ces objets. | Let’s classify these objects. |
| tu | classe | Classe ces documents. | Classify these documents. |
| il | classe | Il classe ses dossiers. | He is organizing his files. |
| elle | classe | Elle classe ses photos. | She is organizing her photos. |
| on | classifie | Classifie ces données. | Let’s classify this data. |
| nous | classifions | Classifions ces articles. | Let’s classify these articles. |
| vous | classez | Classez ces livres. | Sort these books. |
| ils | classifient | Ils classifient ces informations. | They are classifying this information. |
| elles | classifient | Elles classifient ces plantes. | They are classifying these plants. |
Other Conjugations for Classifier.
Le Present (Present Tense) Conjugation of the French Verb classifier
Imparfait (Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb classifier
Passé Simple (Simple Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb classifier
Passé Composé (Present Perfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb classifier
Futur Simple (Simple Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb classifier
Futur Proche (Near Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb classifier
Plus-que-parfait (Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb classifier
Passé Antérieur (Past Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb classifier
Futur Antérieur (Future Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb classifier
Subjonctif Présent (Subjunctive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb classifier
Subjonctif Passé (Subjunctive Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb classifier
Subjonctif Imparfait (Subjunctive Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb classifier
Subjonctif Plus-que-parfait (Subjunctive Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb classifier
Conditionnel Présent (Conditional Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb classifier
Conditionnel Passé (Conditional Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb classifier
L’impératif Présent (Imperative Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb classifier (this article)
L’infinitif Présent (Infinitive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb classifier
Struggling with French verbs or the language in general? Why not use our free French Grammar Checker – no registration required!
Get a FREE Download Study Sheet of this Conjugation 🔥
Simply right click the image below, click “save image” and get your free reference for the classifier L’impératif Présent tense conjugation!
Classifier – About the French L’impératif Présent (Imperative Present) Tense
Usage
Giving commands
Making requests
Offering advice
Expressing desires
Conjugation Formation
Interactions with other tenses
Want More?
I hope you enjoyed this article on the verb classifier. Still in a learning mood? Check out another TOTALLY random French verb conjugation!


