L’impératif Présent (Imperative Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb garer
Introduction to the verb garer
The English translation of the French verb garer is “to park.” The infinitive form of garer is pronounced as “ga-reh.”
The origin of the word garer can be traced back to the Old French word “guerrer” which meant “to defend” or “to protect.” Over time, it evolved to mean “to guard” and eventually “to park.”
In everyday French, garer is most often used in the imperative present tense when giving instructions or commands to someone. It is a common verb used in daily activities such as parking a car or bike.
Examples:
- Gare ta voiture dans le parking. (Park your car in the parking lot.)
- Il faut que tu te gares sur le côté de la route. (You need to park on the side of the road.)
- Garons nos vélos devant le magasin. (Let’s park our bikes in front of the store.)
English translations:
- Park
- You must park
- Let’s park
Table of the L’impératif Présent (Imperative Present) Tense Conjugation of garer
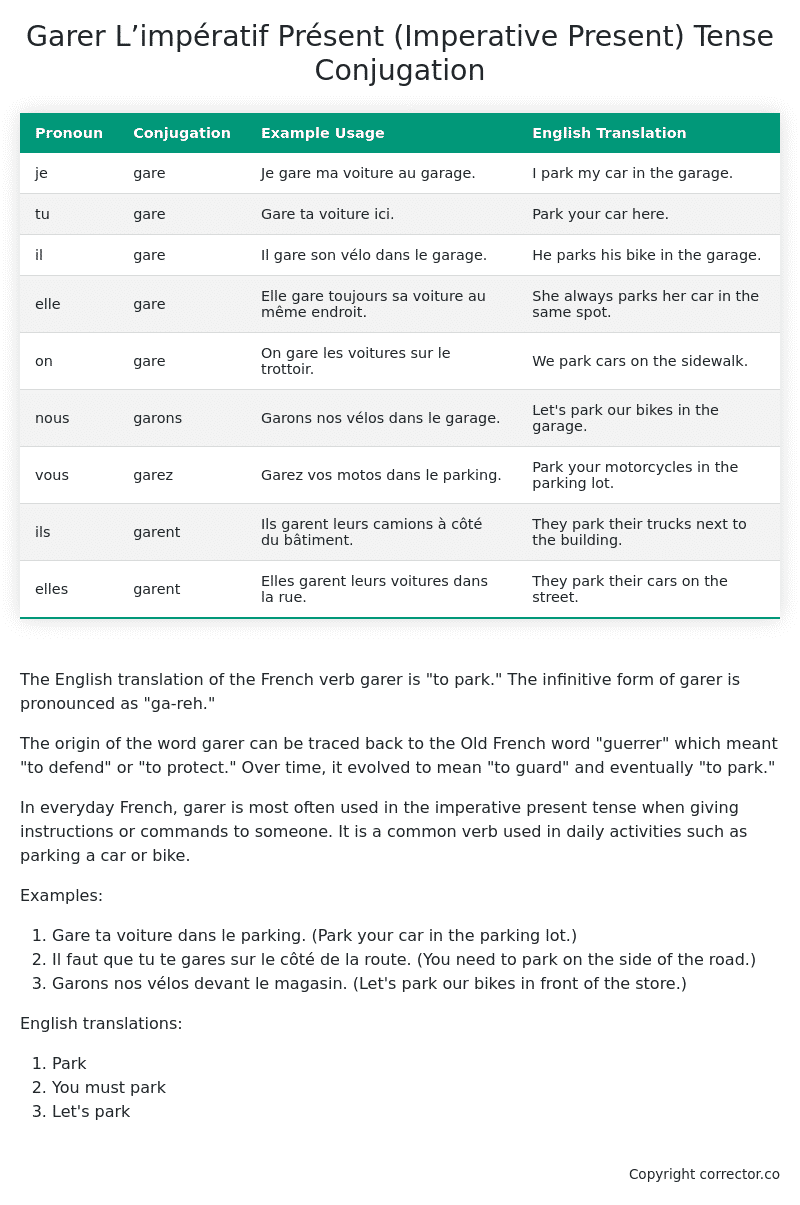
| Pronoun | Conjugation | Example Usage | English Translation |
|---|---|---|---|
| je | gare | Je gare ma voiture au garage. | I park my car in the garage. |
| tu | gare | Gare ta voiture ici. | Park your car here. |
| il | gare | Il gare son vélo dans le garage. | He parks his bike in the garage. |
| elle | gare | Elle gare toujours sa voiture au même endroit. | She always parks her car in the same spot. |
| on | gare | On gare les voitures sur le trottoir. | We park cars on the sidewalk. |
| nous | garons | Garons nos vélos dans le garage. | Let’s park our bikes in the garage. |
| vous | garez | Garez vos motos dans le parking. | Park your motorcycles in the parking lot. |
| ils | garent | Ils garent leurs camions à côté du bâtiment. | They park their trucks next to the building. |
| elles | garent | Elles garent leurs voitures dans la rue. | They park their cars on the street. |
Other Conjugations for Garer.
Le Present (Present Tense) Conjugation of the French Verb garer
Imparfait (Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb garer
Passé Simple (Simple Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb garer
Passé Composé (Present Perfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb garer
Futur Simple (Simple Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb garer
Futur Proche (Near Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb garer
Plus-que-parfait (Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb garer
Passé Antérieur (Past Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb garer
Futur Antérieur (Future Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb garer
Subjonctif Présent (Subjunctive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb garer
Subjonctif Passé (Subjunctive Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb garer
Subjonctif Imparfait (Subjunctive Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb garer
Subjonctif Plus-que-parfait (Subjunctive Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb garer
Conditionnel Présent (Conditional Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb garer
Conditionnel Passé (Conditional Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb garer
L’impératif Présent (Imperative Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb garer (this article)
L’infinitif Présent (Infinitive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb garer
Struggling with French verbs or the language in general? Why not use our free French Grammar Checker – no registration required!
Get a FREE Download Study Sheet of this Conjugation 🔥
Simply right click the image below, click “save image” and get your free reference for the garer L’impératif Présent tense conjugation!
Garer – About the French L’impératif Présent (Imperative Present) Tense
Usage
Giving commands
Making requests
Offering advice
Expressing desires
Conjugation Formation
Interactions with other tenses
Want More?
I hope you enjoyed this article on the verb garer. Still in a learning mood? Check out another TOTALLY random French verb conjugation!


