L’infinitif Présent (Infinitive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb azurer
Introduction to the verb azurer
The English translation of the French verb azurer is “to azure.” It is pronounced “ah-zur-ay.”
The word azurer comes from the Old French word “azur,” meaning “blue,” and is derived from the Persian word “lazhward.” It is most often used in everyday French to describe the action of coloring or painting something blue or azure.
In the L’infinitif Présent tense, azurer is used as follows:
- Je vais azurer le mur de ma chambre en bleu. (I am going to paint my bedroom wall blue.)
- Nous devons azurer les tuiles du toit pour les protéger. (We must paint the roof tiles to protect them.)
- Tu peux azurer ce tissu en utilisant de la teinture. (You can dye this fabric to make it blue.)
Overall, azurer is a versatile verb that can be used in various contexts to describe the action of coloring something blue. Its origin can be traced back to the Persians, showing the influence of other cultures on the French language.
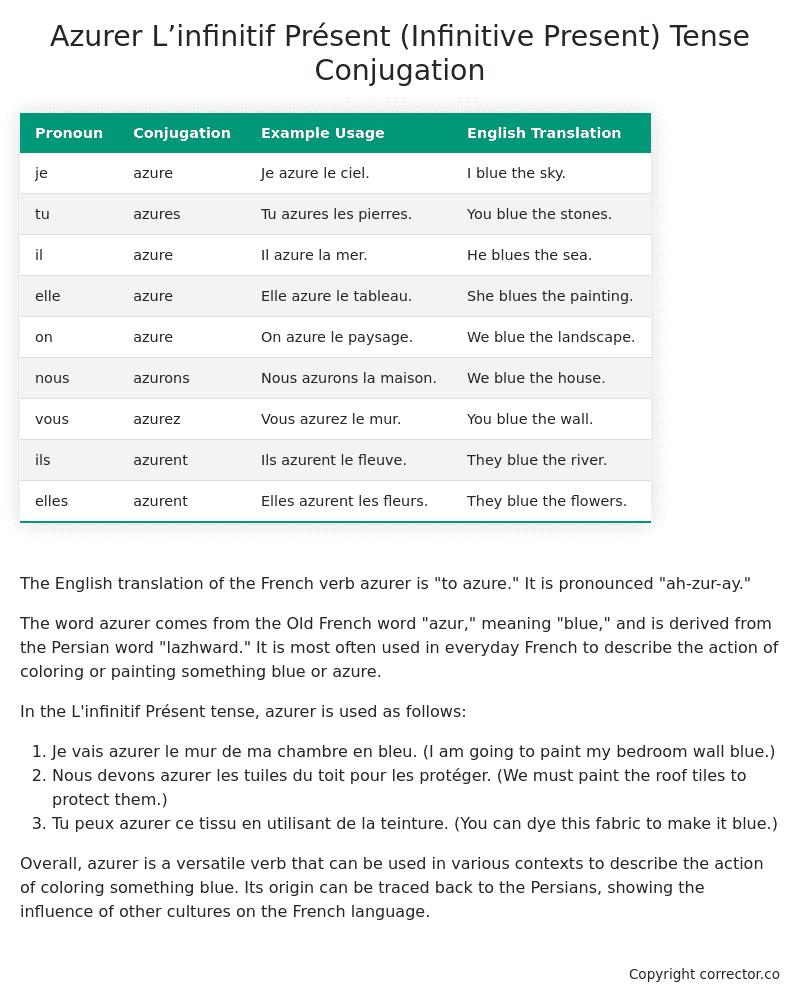
Table of the L’infinitif Présent (Infinitive Present) Tense Conjugation of azurer
| Pronoun | Conjugation | Example Usage | English Translation |
|---|---|---|---|
| je | azure | Je azure le ciel. | I blue the sky. |
| tu | azures | Tu azures les pierres. | You blue the stones. |
| il | azure | Il azure la mer. | He blues the sea. |
| elle | azure | Elle azure le tableau. | She blues the painting. |
| on | azure | On azure le paysage. | We blue the landscape. |
| nous | azurons | Nous azurons la maison. | We blue the house. |
| vous | azurez | Vous azurez le mur. | You blue the wall. |
| ils | azurent | Ils azurent le fleuve. | They blue the river. |
| elles | azurent | Elles azurent les fleurs. | They blue the flowers. |
Other Conjugations for Azurer.
Le Present (Present Tense) Conjugation of the French Verb azurer
Imparfait (Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb azurer
Passé Simple (Simple Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb azurer
Passé Composé (Present Perfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb azurer
Futur Simple (Simple Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb azurer
Futur Proche (Near Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb azurer
Plus-que-parfait (Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb azurer
Passé Antérieur (Past Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb azurer
Futur Antérieur (Future Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb azurer
Subjonctif Présent (Subjunctive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb azurer
Subjonctif Passé (Subjunctive Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb azurer
Subjonctif Imparfait (Subjunctive Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb azurer
Subjonctif Plus-que-parfait (Subjunctive Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb azurer
Conditionnel Présent (Conditional Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb azurer
Conditionnel Passé (Conditional Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb azurer
L’impératif Présent (Imperative Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb azurer
L’infinitif Présent (Infinitive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb azurer (this article)
Struggling with French verbs or the language in general? Why not use our free French Grammar Checker – no registration required!
Get a FREE Download Study Sheet of this Conjugation 🔥
Simply right click the image below, click “save image” and get your free reference for the azurer L’infinitif Présent tense conjugation!
Azurer – About the French L’infinitif Présent (Infinitive Present) Tense
Forming the Infinitive Present
Common Everyday Usage Patterns
As a Verb’s Dictionary Form
After Modal Verbs
As an Imperative
In Infinitive Clauses
Interactions with Other Tenses
Present Tense
Future Tense
Conditional Tense
Passé Composé
Imperfect Tense
Subjunctive and Conditional Moods
Summary
Want More?
I hope you enjoyed this article on the verb azurer. Still in a learning mood? Check out another TOTALLY random French verb conjugation!


