L’infinitif Présent (Infinitive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb basaner
Introduction to the verb basaner
The English translation of basaner is “to tan” or “to sunbathe.” It is pronounced as “bah-sah-neh.”
The origin of basaner can be traced back to the Latin word “bassus,” meaning low or short. In French, it evolved to “bas,” meaning low or deep, and eventually became “basaner,” which literally means “to make low” or “to deepen.”
In everyday French, basaner is most often used in its reflexive form, se basaner, to mean “to sunbathe.”
- Je vais me basaner sur la plage cet après-midi. (I am going to sunbathe on the beach this afternoon.)
- Tu devrais te basaner un peu, tu es trop pâle. (You should tan a bit, you are too pale.)
- Ils se sont basanés toute la journée et ont attrapé un coup de soleil. (They sunbathed all day and got a sunburn.)
Note: In the present tense, the reflexive pronoun “se” is placed before the verb, so it becomes “se basaner.” However, in other tenses, the reflexive pronoun is placed after the verb: Je me suis basané(e), Tu te basanais, Ils se basaneront, etc. This is a common feature of reflexive verbs in French.
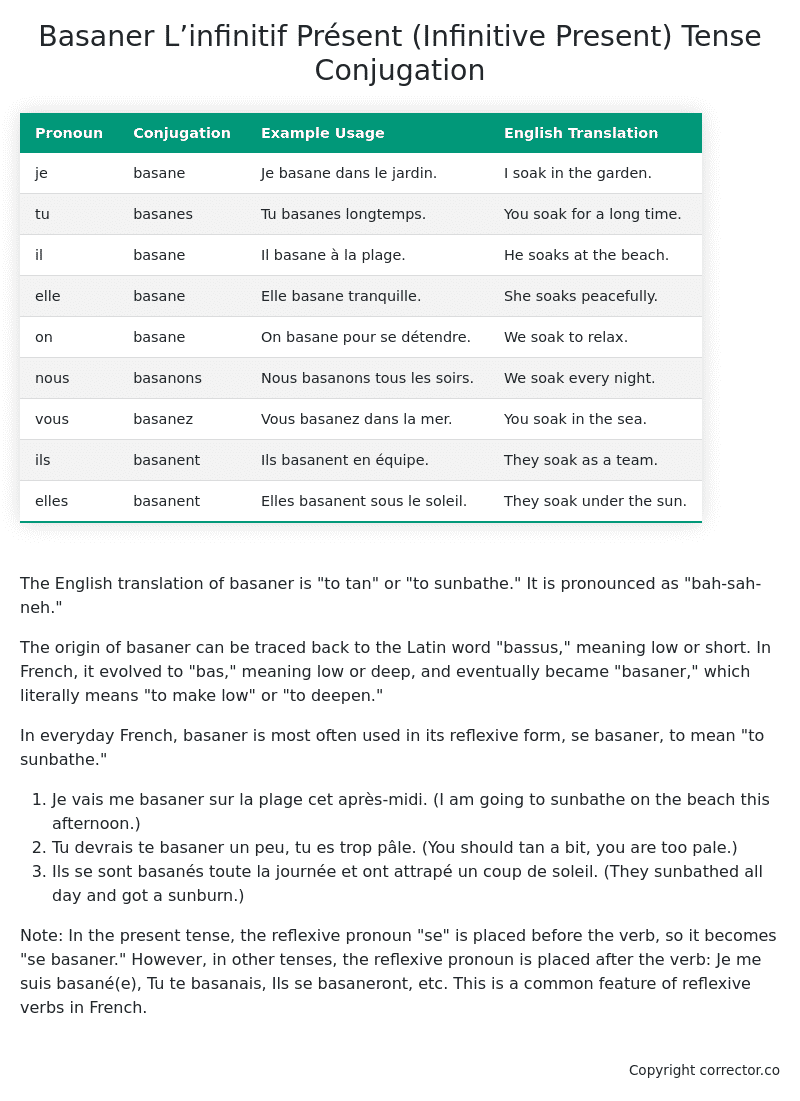
Table of the L’infinitif Présent (Infinitive Present) Tense Conjugation of basaner
| Pronoun | Conjugation | Example Usage | English Translation |
|---|---|---|---|
| je | basane | Je basane dans le jardin. | I soak in the garden. |
| tu | basanes | Tu basanes longtemps. | You soak for a long time. |
| il | basane | Il basane à la plage. | He soaks at the beach. |
| elle | basane | Elle basane tranquille. | She soaks peacefully. |
| on | basane | On basane pour se détendre. | We soak to relax. |
| nous | basanons | Nous basanons tous les soirs. | We soak every night. |
| vous | basanez | Vous basanez dans la mer. | You soak in the sea. |
| ils | basanent | Ils basanent en équipe. | They soak as a team. |
| elles | basanent | Elles basanent sous le soleil. | They soak under the sun. |
Other Conjugations for Basaner.
Le Present (Present Tense) Conjugation of the French Verb basaner
Imparfait (Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb basaner
Passé Simple (Simple Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb basaner
Passé Composé (Present Perfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb basaner
Futur Simple (Simple Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb basaner
Futur Proche (Near Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb basaner
Plus-que-parfait (Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb basaner
Passé Antérieur (Past Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb basaner
Futur Antérieur (Future Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb basaner
Subjonctif Présent (Subjunctive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb basaner
Subjonctif Passé (Subjunctive Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb basaner
Subjonctif Imparfait (Subjunctive Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb basaner
Subjonctif Plus-que-parfait (Subjunctive Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb basaner
Conditionnel Présent (Conditional Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb basaner
Conditionnel Passé (Conditional Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb basaner
L’impératif Présent (Imperative Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb basaner
L’infinitif Présent (Infinitive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb basaner (this article)
Struggling with French verbs or the language in general? Why not use our free French Grammar Checker – no registration required!
Get a FREE Download Study Sheet of this Conjugation 🔥
Simply right click the image below, click “save image” and get your free reference for the basaner L’infinitif Présent tense conjugation!
Basaner – About the French L’infinitif Présent (Infinitive Present) Tense
Forming the Infinitive Present
Common Everyday Usage Patterns
As a Verb’s Dictionary Form
After Modal Verbs
As an Imperative
In Infinitive Clauses
Interactions with Other Tenses
Present Tense
Future Tense
Conditional Tense
Passé Composé
Imperfect Tense
Subjunctive and Conditional Moods
Summary
Want More?
I hope you enjoyed this article on the verb basaner. Still in a learning mood? Check out another TOTALLY random French verb conjugation!


