L’infinitif Présent (Infinitive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb calmer
Introduction to the verb calmer
The English translation of the French verb calmer is “to calm” or “to soothe.” The infinitive form, calmer, is pronounced “kal-may.”
The word calmer comes from the Latin word “calmare” meaning “to soothe” or “to quiet.” It entered the French language in the 12th century.
In everyday French, calmer is most often used in the L’infinitif Présent tense, which is the equivalent of the infinitive present tense in English.
Three simple examples of calmer used in the L’infinitif Présent tense are:
-
Je veux calmer mes nerfs après une longue journée de travail. (I want to calm my nerves after a long day at work.)
-
Nous devons calmer la situation avant qu’elle ne dégénère. (We need to calm the situation before it escalates.)
-
Tu peux calmer ton chien en lui donnant ses jouets préférés. (You can calm your dog by giving him his favorite toys.)
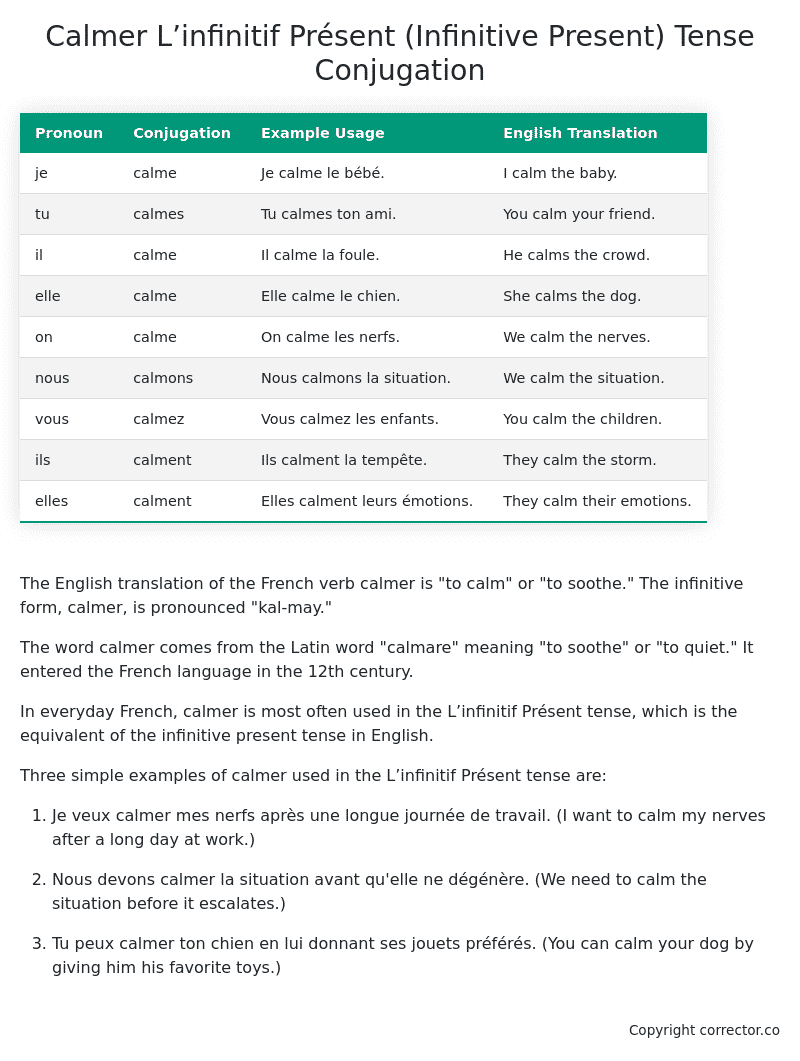
Table of the L’infinitif Présent (Infinitive Present) Tense Conjugation of calmer
| Pronoun | Conjugation | Example Usage | English Translation |
|---|---|---|---|
| je | calme | Je calme le bébé. | I calm the baby. |
| tu | calmes | Tu calmes ton ami. | You calm your friend. |
| il | calme | Il calme la foule. | He calms the crowd. |
| elle | calme | Elle calme le chien. | She calms the dog. |
| on | calme | On calme les nerfs. | We calm the nerves. |
| nous | calmons | Nous calmons la situation. | We calm the situation. |
| vous | calmez | Vous calmez les enfants. | You calm the children. |
| ils | calment | Ils calment la tempête. | They calm the storm. |
| elles | calment | Elles calment leurs émotions. | They calm their emotions. |
Other Conjugations for Calmer.
Le Present (Present Tense) Conjugation of the French Verb calmer
Imparfait (Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb calmer
Passé Simple (Simple Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb calmer
Passé Composé (Present Perfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb calmer
Futur Simple (Simple Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb calmer
Futur Proche (Near Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb calmer
Plus-que-parfait (Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb calmer
Passé Antérieur (Past Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb calmer
Futur Antérieur (Future Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb calmer
Subjonctif Présent (Subjunctive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb calmer
Subjonctif Passé (Subjunctive Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb calmer
Subjonctif Imparfait (Subjunctive Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb calmer
Subjonctif Plus-que-parfait (Subjunctive Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb calmer
Conditionnel Présent (Conditional Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb calmer
Conditionnel Passé (Conditional Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb calmer
L’impératif Présent (Imperative Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb calmer
L’infinitif Présent (Infinitive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb calmer (this article)
Struggling with French verbs or the language in general? Why not use our free French Grammar Checker – no registration required!
Get a FREE Download Study Sheet of this Conjugation 🔥
Simply right click the image below, click “save image” and get your free reference for the calmer L’infinitif Présent tense conjugation!
Calmer – About the French L’infinitif Présent (Infinitive Present) Tense
Forming the Infinitive Present
Common Everyday Usage Patterns
As a Verb’s Dictionary Form
After Modal Verbs
As an Imperative
In Infinitive Clauses
Interactions with Other Tenses
Present Tense
Future Tense
Conditional Tense
Passé Composé
Imperfect Tense
Subjunctive and Conditional Moods
Summary
Want More?
I hope you enjoyed this article on the verb calmer. Still in a learning mood? Check out another TOTALLY random French verb conjugation!


