L’infinitif Présent (Infinitive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb défiscaliser
Introduction to the verb défiscaliser
The English translation of the French verb défiscaliser is “to exempt from taxes” or “to reduce taxes.” It is pronounced as “day-fee-ska-lee-zay” in its infinitive form.
Défiscaliser originated from the combination of the prefix “dé-” which means “undo” or “remove” and the word “fiscal” which refers to taxes. It is a relatively new word in the French language, first appearing in the 1970s during discussions about tax reforms.
In everyday French, défiscaliser is most often used in the L’infinitif Présent tense as a means of describing actions or strategies used to reduce or eliminate taxes. It can also be used in a figurative sense to refer to avoiding or evading a financial burden.
Here are three simple examples of its usage in this tense, with the respective English translations:
- Je cherche un moyen de défiscaliser mes revenus. (I am looking for a way to reduce my taxes on income.)
- Les entreprises peuvent défiscaliser certains investissements. (Companies can exempt certain investments from taxes.)
- Il faut bien défiscaliser si on veut économiser de l’argent. (You have to find ways to reduce taxes if you want to save money.)
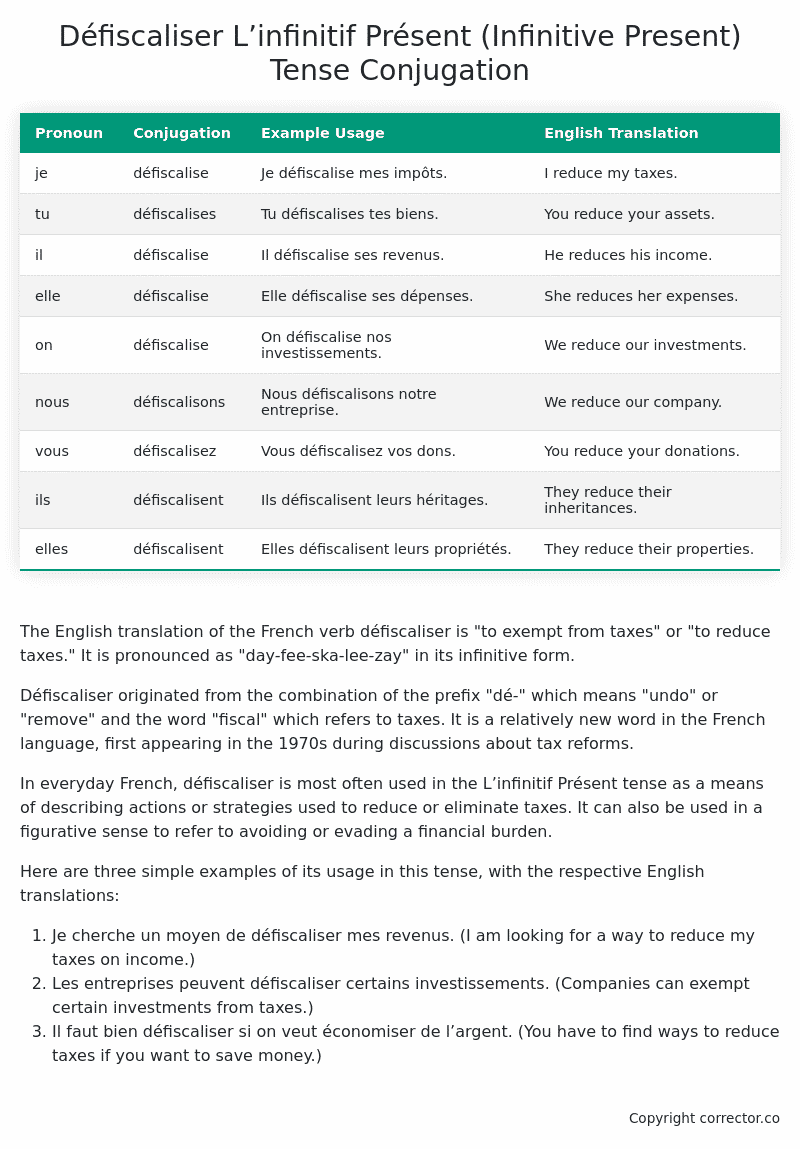
Table of the L’infinitif Présent (Infinitive Present) Tense Conjugation of défiscaliser
| Pronoun | Conjugation | Example Usage | English Translation |
|---|---|---|---|
| je | défiscalise | Je défiscalise mes impôts. | I reduce my taxes. |
| tu | défiscalises | Tu défiscalises tes biens. | You reduce your assets. |
| il | défiscalise | Il défiscalise ses revenus. | He reduces his income. |
| elle | défiscalise | Elle défiscalise ses dépenses. | She reduces her expenses. |
| on | défiscalise | On défiscalise nos investissements. | We reduce our investments. |
| nous | défiscalisons | Nous défiscalisons notre entreprise. | We reduce our company. |
| vous | défiscalisez | Vous défiscalisez vos dons. | You reduce your donations. |
| ils | défiscalisent | Ils défiscalisent leurs héritages. | They reduce their inheritances. |
| elles | défiscalisent | Elles défiscalisent leurs propriétés. | They reduce their properties. |
Other Conjugations for Défiscaliser.
Le Present (Present Tense) Conjugation of the French Verb défiscaliser
Imparfait (Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb défiscaliser
Passé Simple (Simple Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb défiscaliser
Passé Composé (Present Perfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb défiscaliser
Futur Simple (Simple Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb défiscaliser
Futur Proche (Near Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb défiscaliser
Plus-que-parfait (Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb défiscaliser
Passé Antérieur (Past Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb défiscaliser
Futur Antérieur (Future Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb défiscaliser
Subjonctif Présent (Subjunctive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb défiscaliser
Subjonctif Passé (Subjunctive Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb défiscaliser
Subjonctif Imparfait (Subjunctive Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb défiscaliser
Conditionnel Présent (Conditional Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb défiscaliser
Conditionnel Passé (Conditional Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb défiscaliser
L’impératif Présent (Imperative Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb défiscaliser
L’infinitif Présent (Infinitive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb défiscaliser (this article)
Struggling with French verbs or the language in general? Why not use our free French Grammar Checker – no registration required!
Get a FREE Download Study Sheet of this Conjugation 🔥
Simply right click the image below, click “save image” and get your free reference for the défiscaliser L’infinitif Présent tense conjugation!
Défiscaliser – About the French L’infinitif Présent (Infinitive Present) Tense
Forming the Infinitive Present
Common Everyday Usage Patterns
As a Verb’s Dictionary Form
After Modal Verbs
As an Imperative
In Infinitive Clauses
Interactions with Other Tenses
Present Tense
Future Tense
Conditional Tense
Passé Composé
Imperfect Tense
Subjunctive and Conditional Moods
Summary
Want More?
I hope you enjoyed this article on the verb défiscaliser. Still in a learning mood? Check out another TOTALLY random French verb conjugation!


