Passé Composé (Present Perfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb blasphémer
Introduction to the verb blasphémer
The English translation of the French verb blasphémer is “to blaspheme.” It is pronounced as “blahs-fay-may” in its infinitive form.
The word blasphémer comes from the Latin word blasphemia, which originated from the Greek word blasphēmos, meaning “evil-speaking.” It is most often used in everyday French in the Passé Composé tense, which is the equivalent of the Present Perfect tense in English. This tense is used to describe actions that have been completed in the recent past.
Examples of usage of blasphémer in the Passé Composé tense are:
- J’ai blasphémé contre dieu hier soir. (I blasphemed against god last night.)
- Elle a blasphémé en écoutant le sermon du prêtre. (She blasphemed while listening to the priest’s sermon.)
- Nous avons blasphémé contre le saint patron de notre village. (We blasphemed against the patron saint of our village.)
In these examples, the verb blasphémer is conjugated in the Passé Composé tense with the auxiliary verb avoir (to have) and the past participle blasphémé. Its usage in everyday French can be seen in expressions like “s’abstenir de blasphémer” (to refrain from blasphemy) or “ne pas blasphémer le nom de dieu” (not to take the name of god in vain).
Table of the Passé Composé (Present Perfect) Tense Conjugation of blasphémer
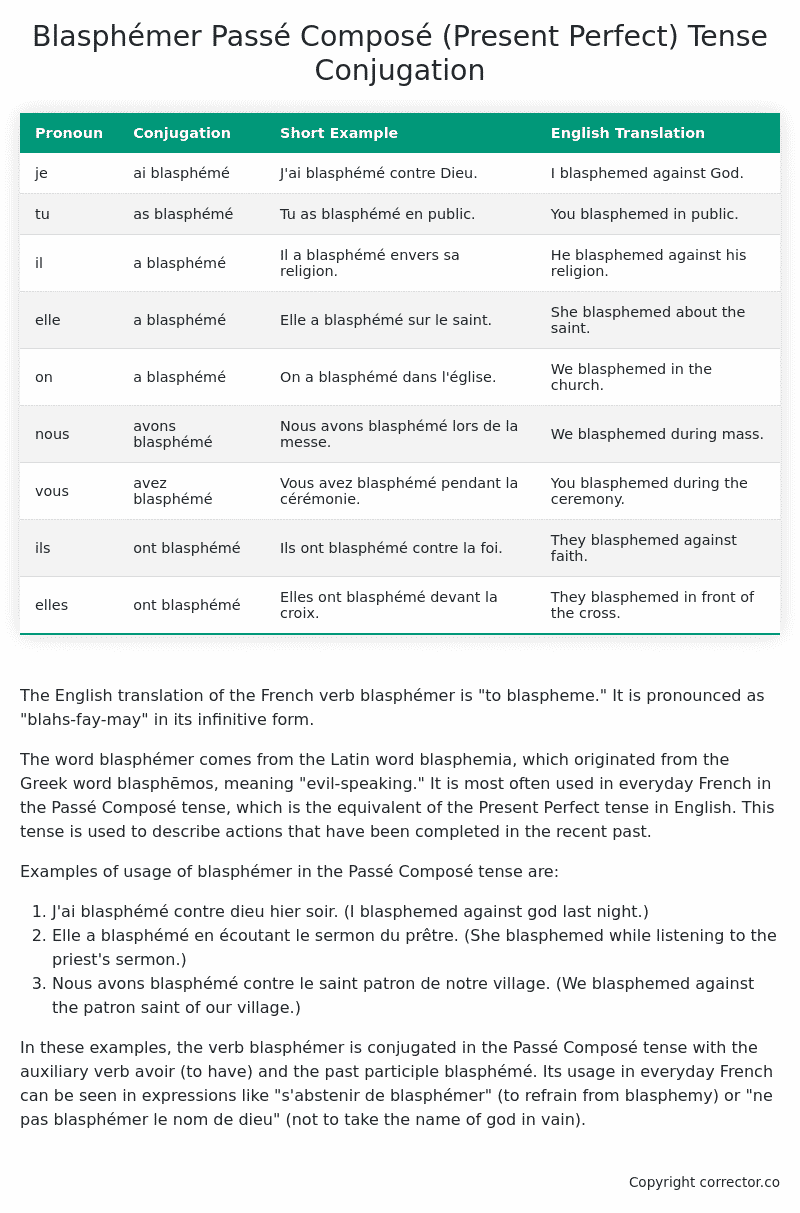
| Pronoun | Conjugation | Short Example | English Translation |
|---|---|---|---|
| je | ai blasphémé | J’ai blasphémé contre Dieu. | I blasphemed against God. |
| tu | as blasphémé | Tu as blasphémé en public. | You blasphemed in public. |
| il | a blasphémé | Il a blasphémé envers sa religion. | He blasphemed against his religion. |
| elle | a blasphémé | Elle a blasphémé sur le saint. | She blasphemed about the saint. |
| on | a blasphémé | On a blasphémé dans l’église. | We blasphemed in the church. |
| nous | avons blasphémé | Nous avons blasphémé lors de la messe. | We blasphemed during mass. |
| vous | avez blasphémé | Vous avez blasphémé pendant la cérémonie. | You blasphemed during the ceremony. |
| ils | ont blasphémé | Ils ont blasphémé contre la foi. | They blasphemed against faith. |
| elles | ont blasphémé | Elles ont blasphémé devant la croix. | They blasphemed in front of the cross. |
Other Conjugations for Blasphémer.
Le Present (Present Tense) Conjugation of the French Verb blasphémer
Imparfait (Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb blasphémer
Passé Simple (Simple Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb blasphémer
Passé Composé (Present Perfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb blasphémer (this article)
Futur Simple (Simple Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb blasphémer
Futur Proche (Near Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb blasphémer
Plus-que-parfait (Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb blasphémer
Passé Antérieur (Past Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb blasphémer
Futur Antérieur (Future Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb blasphémer
Subjonctif Présent (Subjunctive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb blasphémer
Subjonctif Passé (Subjunctive Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb blasphémer
Subjonctif Imparfait (Subjunctive Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb blasphémer
Subjonctif Plus-que-parfait (Subjunctive Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb blasphémer
Conditionnel Présent (Conditional Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb blasphémer
Conditionnel Passé (Conditional Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb blasphémer
L’impératif Présent (Imperative Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb blasphémer
L’infinitif Présent (Infinitive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb blasphémer
Struggling with French verbs or the language in general? Why not use our free French Grammar Checker – no registration required!
Get a FREE Download Study Sheet of this Conjugation 🔥
Simply right click the image below, click “save image” and get your free reference for the blasphémer present perfect tense conjugation!
Blasphémer – About the French Passé Composé (Present Perfect) Tense
Formation of the Passé Composé
Set the auxiliary verb with either
Conjugate the auxiliary verb
Add the past participle
Common everyday usage patterns
Narrating Past Events
Sequential Actions
Describing Completed Actions
Interactions with other tenses
Imperfect Tense
Conditional and Future Tenses
Summary
I hope you enjoyed this article on the verb blasphémer. Still in a learning mood? Check out another TOTALLY random French verb conjugation!


